
Mixture of $Ph - CHO$ and $HCHO$is treated with $NaOH$ then Cannizzaro reaction involves :
(A) Oxidation of $HCHO$
(B) Reduction of $HCHO$
(C) Oxidation of $Ph - CHO$
(D) Reduction of $Ph - CHO$
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Some examples of Cannizzaro reaction are formaldehyde, benzaldehyde, etc. There are two types of Cannizzaro reactions, self Cannizzaro and cross Cannizzaro. Self Cannizzaro reaction is the reaction involving condensation of the same aldehyde molecule. And the cross Cannizzaro reaction is the one involving two different aldehydes.
Complete step by step answer:
When two molecules of aldehydes not containing $\alpha $hydrogen are reacted with 50 $\% $ alkalies undergo oxidation-reduction disproportionate to give corresponding alcohols and salts of carboxylic acid. This reaction is called Cannizzaro's reaction.
The reaction between benzaldehyde and formaldehyde is an example of cross Cannizzaro reaction and is given as
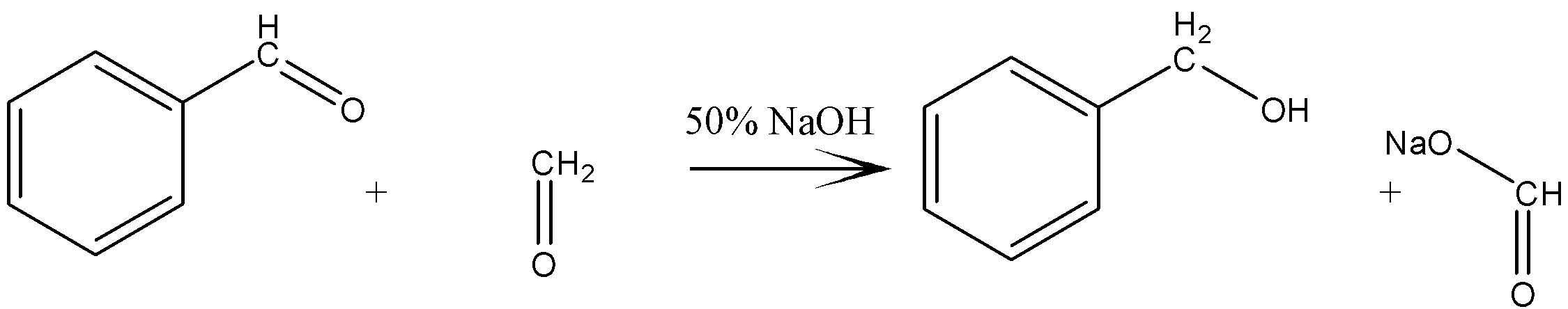
Here, benzaldehyde gets reduced to benzyl alcohol by gaining two hydrogen atoms and formaldehyde is oxidized to sodium formate by gaining two oxygen atoms. So, this is an example of a redox reaction.
In a redox reaction, one of the reactants is oxidized and the other is reduced simultaneously. Oxidation is defined as the gain of oxygen atoms or loss of hydrogen atoms with an increase in oxidation number.
The reduction is defined as the loss of oxygen atoms or gain of hydrogen atoms with a decrease in oxidation number.
So, $Ph - CHO$is undergoing reduction, and $HCHO$ is undergoing oxidation.
So, the correct answer is option A,D.
Note: In cross Cannizzaro, the smaller aldehyde undergoes oxidation and the bigger aldehyde, reduction.
And also, for carrying out the Cannizzaro reaction, the condition of 50 $\% $ NaOH and absence of $\alpha $ hydrogen is necessary. $\alpha $ Hydrogen is defined as the hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom i.e. the carbon atom next to the functional group.
Complete step by step answer:
When two molecules of aldehydes not containing $\alpha $hydrogen are reacted with 50 $\% $ alkalies undergo oxidation-reduction disproportionate to give corresponding alcohols and salts of carboxylic acid. This reaction is called Cannizzaro's reaction.
The reaction between benzaldehyde and formaldehyde is an example of cross Cannizzaro reaction and is given as

Here, benzaldehyde gets reduced to benzyl alcohol by gaining two hydrogen atoms and formaldehyde is oxidized to sodium formate by gaining two oxygen atoms. So, this is an example of a redox reaction.
In a redox reaction, one of the reactants is oxidized and the other is reduced simultaneously. Oxidation is defined as the gain of oxygen atoms or loss of hydrogen atoms with an increase in oxidation number.
The reduction is defined as the loss of oxygen atoms or gain of hydrogen atoms with a decrease in oxidation number.
So, $Ph - CHO$is undergoing reduction, and $HCHO$ is undergoing oxidation.
So, the correct answer is option A,D.
Note: In cross Cannizzaro, the smaller aldehyde undergoes oxidation and the bigger aldehyde, reduction.
And also, for carrying out the Cannizzaro reaction, the condition of 50 $\% $ NaOH and absence of $\alpha $ hydrogen is necessary. $\alpha $ Hydrogen is defined as the hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom i.e. the carbon atom next to the functional group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




