
What is MODEM? Draw its block diagram and explain its working.
Answer
528k+ views
Hint :The term Modem Definition is an acronym for modulator-demodulator. The primary modem function is to convert digital data into an analog form which is suitable for transmission on common carrier circuits (example telephone lines). Modulation is the D/A conversion in which the digital data is placed on the transmission line by modulation of a tone or carrier. Demodulation is the reverse process.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Modem is an abbreviation for Modulator – Demodulator. Modems are used for data transfer from one computer network to another computer network through telephone lines. The computer network works in digital mode, while analog technology is used for carrying messages across phone lines.
The device which performs modulation is called a modulator and the device which recovers the information signal from the modulated carrier is called a demodulator. In data transmission, we usually come across devices which perform both modulation as well as demodulation functions and these devices are called modems. When data is to be transmitted over long distances, modems are needed. In a modem, the input signal modulates a carrier which is transmitted to the distant end. At the distant end, another modem demodulators the received carrier to obtain the digital signal. Thus, a pair of modems is always required. The term ‘modem’ is derived from the words, Modulator and Demodulator.
Modulator converts information from digital mode to analog mode at the transmitting end and demodulator converts the same from analog to digital at receiving end. The process of converting analog signals of one computer network into digital signals of another computer network so they can be processed by a receiving computer is referred to as digitizing.
A modem contains a modulator as well as a demodulator. Nearly all the modems are designed for utilizing the analog voice band service provided by the telecommunication network. Thus, the modulated carrier produced by a modem fits into the 300-400 Hz bandwidth of the speech channel. The figure shows a typical data connection set up using modems. The digital terminal devices exchange digital signals and are known as Data Terminal Equipment (DTE). Two modems are always needed, one at each end. At the transmitting end, the modem converts the digital signal from the DTE into an analog signal by modulating a carrier. At the receiving end, the modem demodulates the carrier and hands over the demodulated digital signal to the DTE.
A dedicated leased circuit or a switched telephone circuit can be used as transmission medium between the two modems. In the latter case, moderns are connected to the local telephone exchanges. Whenever data transmission is needed, connection between the modems is established through the telephone exchanges. Modems are also needed within a building to connect terminals which are located at distances, more than 15 metres from the host.
Block diagram of Modem is as below:
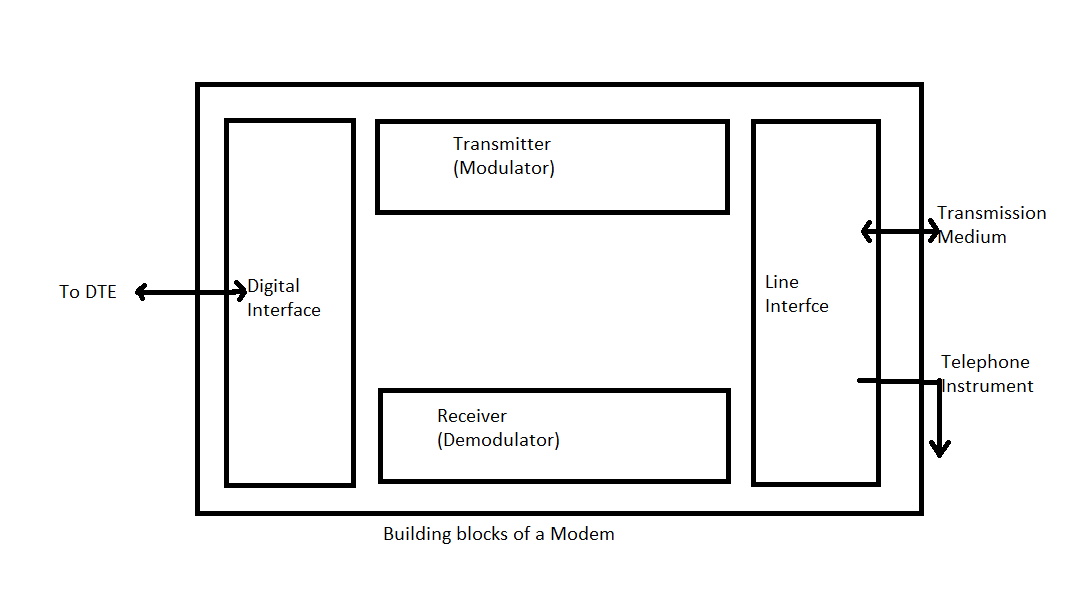
A block diagram of a modem is shown in the above figure, which comprises a transmitter, a receiver and two interfaces. The digital signal to be sent is given to the transmitter. The modulated carrier that is received from the distant end is given to the receiver. TI1e digital interface connects the modem to the DTE which produces and receives the digital signals. In order to transmit it and receive the modulated signals, the line interface connects the modem to the transmission channel. Modems connected to telephone exchanges have additional provision for connecting a telephone instrument, which enables establishment of the telephone connection.
Note :
The transmission medium between the two modems can be a dedicated circuit or a switched telephone circuit. If a switched telephone circuit is used, then the modems are connected to the local telephone exchanges. Whenever data transmission is required connection between the modems is established through telephone exchanges.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Modem is an abbreviation for Modulator – Demodulator. Modems are used for data transfer from one computer network to another computer network through telephone lines. The computer network works in digital mode, while analog technology is used for carrying messages across phone lines.
The device which performs modulation is called a modulator and the device which recovers the information signal from the modulated carrier is called a demodulator. In data transmission, we usually come across devices which perform both modulation as well as demodulation functions and these devices are called modems. When data is to be transmitted over long distances, modems are needed. In a modem, the input signal modulates a carrier which is transmitted to the distant end. At the distant end, another modem demodulators the received carrier to obtain the digital signal. Thus, a pair of modems is always required. The term ‘modem’ is derived from the words, Modulator and Demodulator.
Modulator converts information from digital mode to analog mode at the transmitting end and demodulator converts the same from analog to digital at receiving end. The process of converting analog signals of one computer network into digital signals of another computer network so they can be processed by a receiving computer is referred to as digitizing.
A modem contains a modulator as well as a demodulator. Nearly all the modems are designed for utilizing the analog voice band service provided by the telecommunication network. Thus, the modulated carrier produced by a modem fits into the 300-400 Hz bandwidth of the speech channel. The figure shows a typical data connection set up using modems. The digital terminal devices exchange digital signals and are known as Data Terminal Equipment (DTE). Two modems are always needed, one at each end. At the transmitting end, the modem converts the digital signal from the DTE into an analog signal by modulating a carrier. At the receiving end, the modem demodulates the carrier and hands over the demodulated digital signal to the DTE.
A dedicated leased circuit or a switched telephone circuit can be used as transmission medium between the two modems. In the latter case, moderns are connected to the local telephone exchanges. Whenever data transmission is needed, connection between the modems is established through the telephone exchanges. Modems are also needed within a building to connect terminals which are located at distances, more than 15 metres from the host.
Block diagram of Modem is as below:

A block diagram of a modem is shown in the above figure, which comprises a transmitter, a receiver and two interfaces. The digital signal to be sent is given to the transmitter. The modulated carrier that is received from the distant end is given to the receiver. TI1e digital interface connects the modem to the DTE which produces and receives the digital signals. In order to transmit it and receive the modulated signals, the line interface connects the modem to the transmission channel. Modems connected to telephone exchanges have additional provision for connecting a telephone instrument, which enables establishment of the telephone connection.
Note :
The transmission medium between the two modems can be a dedicated circuit or a switched telephone circuit. If a switched telephone circuit is used, then the modems are connected to the local telephone exchanges. Whenever data transmission is required connection between the modems is established through telephone exchanges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




