
What is the molecular geometry of a nitrogen molecule \[{N_2}\]?
Answer
520.5k+ views
Hint:The shape and geometry of the molecule can be determined with the help of hybridization of the molecule or by applying VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion) theory. The shape of the molecule is highly affected if lone pairs of electrons are present on any atom in a molecule.
Complete answer:
For determining the geometry of the nitrogen molecule, first we need to sketch its Lewis structure.
Lewis structure: It is the simplified diagram of a molecule representing the number of valence electrons present in an atom. The number of non-bonded valence electrons i.e., lone pairs of electrons are represented by dots on the atom.
The electronic configuration of nitrogen atom \[ = 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}\]
According to the electronic configuration, the number of valence electrons present in a nitrogen atom \[5\], in which \[3\]electrons are unpaired whereas \[2\]electrons are paired.
Therefore, the Lewis structure of \[{N_2}\]molecule is as follows:
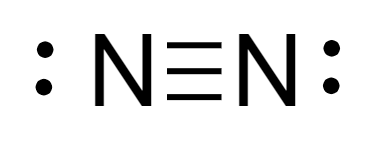
Steric number: It is the summation number of atoms bonded to the central atom via single bond and the number of lone pairs of electrons present on the atom.
For nitrogen molecule, steric number of nitrogen atom \[ = 2\]
Therefore, the hybridization of molecule \[ = sp\]
The bond angle between atoms \[{180^o}\]
So, the molecular geometry of the molecule is linear.
As there is appreciable distance between the lone pair of electrons on each atom. Therefore, the shape of the nitrogen molecule will be the same as its molecular geometry.
Note:
According to the VSEPR theory, the electron pairs are placed in such a way that there is maximum distance between them so as to minimise the repulsions. The forces of repulsion decrease in the order \[l.p - l.p > l.p - b.p > b.p - b.p\].
Complete answer:
For determining the geometry of the nitrogen molecule, first we need to sketch its Lewis structure.
Lewis structure: It is the simplified diagram of a molecule representing the number of valence electrons present in an atom. The number of non-bonded valence electrons i.e., lone pairs of electrons are represented by dots on the atom.
The electronic configuration of nitrogen atom \[ = 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}\]
According to the electronic configuration, the number of valence electrons present in a nitrogen atom \[5\], in which \[3\]electrons are unpaired whereas \[2\]electrons are paired.
Therefore, the Lewis structure of \[{N_2}\]molecule is as follows:

Steric number: It is the summation number of atoms bonded to the central atom via single bond and the number of lone pairs of electrons present on the atom.
For nitrogen molecule, steric number of nitrogen atom \[ = 2\]
Therefore, the hybridization of molecule \[ = sp\]
The bond angle between atoms \[{180^o}\]
So, the molecular geometry of the molecule is linear.
As there is appreciable distance between the lone pair of electrons on each atom. Therefore, the shape of the nitrogen molecule will be the same as its molecular geometry.
Note:
According to the VSEPR theory, the electron pairs are placed in such a way that there is maximum distance between them so as to minimise the repulsions. The forces of repulsion decrease in the order \[l.p - l.p > l.p - b.p > b.p - b.p\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




