
How many monochlorination products are possible for?
A.$2 - methylpropane$
B.$2 - methyl$ butane
Answer
547.2k+ views
Hint:The compound given above are branched hydrocarbons especially saturated \[\left( { - ane} \right)\] is written at the end. Here firstly draw the structure of hydrocarbon and make the monochlorination product. It means that you have to do chlorination only one time so after that the product we would get will be major.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the question we have asked for a monochlorination product of two hydrocarbons which are $2 - methylpropane$ and $2 - methyl$ butane. So, let’s start by drawing these two compounds. The chlorination can happen by using some reagents like sulfuryl chloride, hydrochloric acid with sulphur dioxide etc.
If we use $HCl + S{O_2}$ then we get the chlorination product at that side where it will be major. The chlorination happens after the formation of carbocation in some cases first. We have to make the carbocation first and then check the stability of the carbocation. If more stable carbocation can be formed by a rearrangement process then we have to make the stable one.
A.
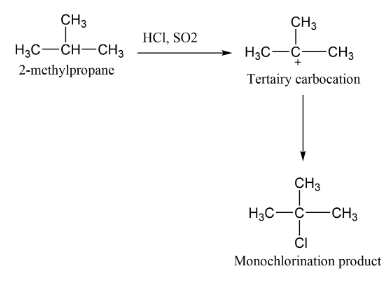
The carbocation formed here is tertiary carbocation so therefore the attack of chlorine will form the major product $2 - chloro,2 - methylpropane$ .
Next we have $2 - methyl$ butane in which the product will be form in place of same reagent that is $HCl + S{O_2}$ as shown in the figure.
B.
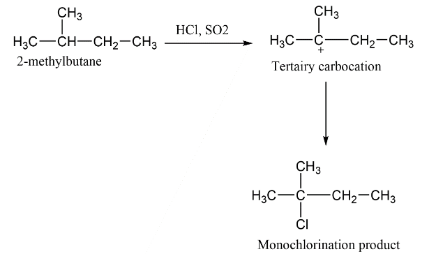
Here in case of $2 - methyl$ butane the carbocation formed is stable one which is tertiary carbocation and which on attack by chlorine by the reagents forms $2 - chloro,2 - methyl$ butane.
Note: The process is a monochlorination process hence we get chlorine atoms at the most stable site, if further chlorination is applied the next more stable carbocation will form and we get the next stable dechlorinated product. This choice of making carbocation first and then substituting chlorine at that place is an easy method because by this chances of mistakes are less.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the question we have asked for a monochlorination product of two hydrocarbons which are $2 - methylpropane$ and $2 - methyl$ butane. So, let’s start by drawing these two compounds. The chlorination can happen by using some reagents like sulfuryl chloride, hydrochloric acid with sulphur dioxide etc.
If we use $HCl + S{O_2}$ then we get the chlorination product at that side where it will be major. The chlorination happens after the formation of carbocation in some cases first. We have to make the carbocation first and then check the stability of the carbocation. If more stable carbocation can be formed by a rearrangement process then we have to make the stable one.
A.

The carbocation formed here is tertiary carbocation so therefore the attack of chlorine will form the major product $2 - chloro,2 - methylpropane$ .
Next we have $2 - methyl$ butane in which the product will be form in place of same reagent that is $HCl + S{O_2}$ as shown in the figure.
B.

Here in case of $2 - methyl$ butane the carbocation formed is stable one which is tertiary carbocation and which on attack by chlorine by the reagents forms $2 - chloro,2 - methyl$ butane.
Note: The process is a monochlorination process hence we get chlorine atoms at the most stable site, if further chlorination is applied the next more stable carbocation will form and we get the next stable dechlorinated product. This choice of making carbocation first and then substituting chlorine at that place is an easy method because by this chances of mistakes are less.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




