
Monohybrid test cross is
A.1:1:1:1
B.1:1
C.9:3:4
D.9:3:3:1
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: A monohybrid is supposed to have two different alleles of the same locus (gene). A test cross is employed to find out if an organism is truly hybrid. For this purpose, a recessive homozygous organism is crossed to the organism under investigation.
Complete answer:
1.Diploid organisms have homologous chromosomes in their genomes. This means two different copies of the same gene each inherited from one parent. Thus, if the total number of chromosomes be represented by n, the complete genome is 2n.
2.Diploid organisms are mostly formed from gametes of parents each of which is haploid (has only one set of all chromosomes).
3.Heterozygous organisms have two different variations (alleles) of the same part of the two different chromosomes (Locus, plural loci; containing genes. For our purpose, each locus is responsible for one character).
4.Homozygous organisms have the same alleles in two homologous chromosomes.
5.Let us consider tall and short plants. Consider tallness to be dominant and represented by ‘T’.
6.Let the shortness be a homozygous recessive character represented by ‘t’. Thus, a homozygous organism will be represented by ‘tt’ genotype for the recessive one and ‘TT’ for the dominant one.
7.A monohybrid will have the genetic composition (genotype) ‘Tt’ and it will be a tall organism (phenotype).
8.Writing crosses using a Punnett square is helpful to understand the ratio of expected offspring
9.Green and blue represent the gametes and white cells the offspring. Blue is the potential monohybrid being tested and green is the homozygous recessive organism used as tester.
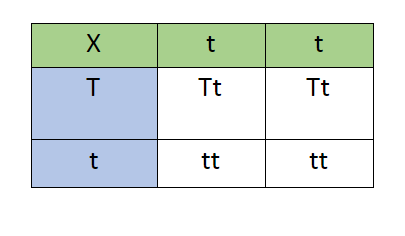
Calculating the genotypic ratio:
50% Tt and 50%tt; 50 percent tall organisms and 50 % short organisms
Hence, Tt: tt is 1:1.
Hence the correct answer is OPTION(B)
Note: Since monohybrid means hybrid in a single locus there are two constituents of the ratio while performing a test cross.
Having more than two components means that hybrid under testing is not monohybrid. For test cross only the homozygous recessive parent must be chosen.
Complete answer:
1.Diploid organisms have homologous chromosomes in their genomes. This means two different copies of the same gene each inherited from one parent. Thus, if the total number of chromosomes be represented by n, the complete genome is 2n.
2.Diploid organisms are mostly formed from gametes of parents each of which is haploid (has only one set of all chromosomes).
3.Heterozygous organisms have two different variations (alleles) of the same part of the two different chromosomes (Locus, plural loci; containing genes. For our purpose, each locus is responsible for one character).
4.Homozygous organisms have the same alleles in two homologous chromosomes.
5.Let us consider tall and short plants. Consider tallness to be dominant and represented by ‘T’.
6.Let the shortness be a homozygous recessive character represented by ‘t’. Thus, a homozygous organism will be represented by ‘tt’ genotype for the recessive one and ‘TT’ for the dominant one.
7.A monohybrid will have the genetic composition (genotype) ‘Tt’ and it will be a tall organism (phenotype).
8.Writing crosses using a Punnett square is helpful to understand the ratio of expected offspring
9.Green and blue represent the gametes and white cells the offspring. Blue is the potential monohybrid being tested and green is the homozygous recessive organism used as tester.

Calculating the genotypic ratio:
50% Tt and 50%tt; 50 percent tall organisms and 50 % short organisms
Hence, Tt: tt is 1:1.
Hence the correct answer is OPTION(B)
Note: Since monohybrid means hybrid in a single locus there are two constituents of the ratio while performing a test cross.
Having more than two components means that hybrid under testing is not monohybrid. For test cross only the homozygous recessive parent must be chosen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




