
Morphology of flowering plants.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: The flowering plants are multicellular organisms. They grow by cell division and their morphology and their morphological features and traits are genetically determined. Morphology plays an important role in the classification of angiosperm. Morphology deals with the study of forms and features of different plant organs like roots, shoot, leaf, flower, seeds, fruits, etc.
Complete answer:
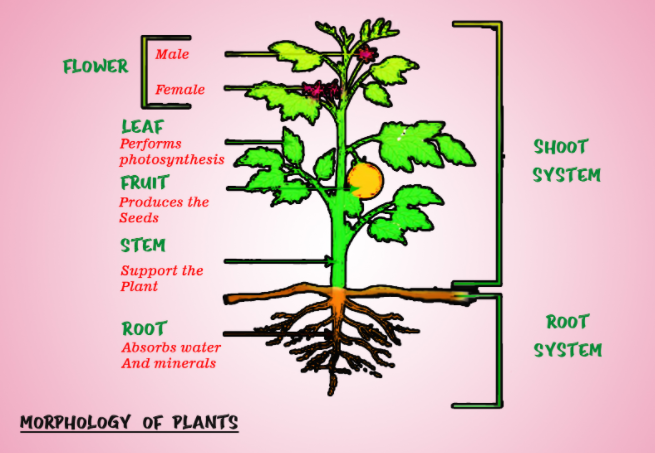
-The Roots:
Roots are cylindrical, underground, and non-green parts of the plant. It is generally the descending portion of the plant axis i.e.; it grows downwards into the soil. It lacks nodes, leaves, buds but gives rise to endogenous lateral branches. Root moves in the direction of gravity (geotropism) and against the direction of light (phototropism). Plants have well-developed root systems, these are of three types:
(1)Taproot system
(2)Fibrous root system
(3)Adventitious root system
Functions of the root are: Absorption of water and mineral from the soil, Provide anchorage to the plant parts, Storage of reserve food material, Synthesis of plant growth regulators.
-The Stem:
The ascending part of the plant axis which bears branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits is called the stem. It generally grows above the ground and hence is considered as the aerial part of the plant. The plumule of the embryo, present in the germinating gives rise to the stem.
Functions of the stem are Bears and support leaves, fruits, flowers, etc., It conducts water and minerals salts from roots to leaves and fruits, acts as a storage of reserve food materials.
-The Leaves:
A leaf is a lateral generally flattened structure borne on the stem. It develops at the node and bears a bud in its exile. Leaves are the most important vegetative organ for photosynthesis.
-The Flower:
A flower is a reproductive unit in the angiosperm. It is a modified shoot, meant for sexual reproduction. It consists of four whorls namely Calyx, Corolla, Androecium, Gynoecium. The swollen part of the pedicle or the stock is called the thalamus.
-The Fruit:
The flowering plant or the angiosperms are characterized by the presence of fruit. After fertilization, the ripened or the mature ovary is called the fruit. Parts of the fruit are Fruit wall and seed.
Note: There are various modifications of roots, stems, leaves.
Fruit formed without fertilization is called parthenocarpic fruits. Example: Banana.
Complete answer:

-The Roots:
Roots are cylindrical, underground, and non-green parts of the plant. It is generally the descending portion of the plant axis i.e.; it grows downwards into the soil. It lacks nodes, leaves, buds but gives rise to endogenous lateral branches. Root moves in the direction of gravity (geotropism) and against the direction of light (phototropism). Plants have well-developed root systems, these are of three types:
(1)Taproot system
(2)Fibrous root system
(3)Adventitious root system
Functions of the root are: Absorption of water and mineral from the soil, Provide anchorage to the plant parts, Storage of reserve food material, Synthesis of plant growth regulators.
-The Stem:
The ascending part of the plant axis which bears branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits is called the stem. It generally grows above the ground and hence is considered as the aerial part of the plant. The plumule of the embryo, present in the germinating gives rise to the stem.
Functions of the stem are Bears and support leaves, fruits, flowers, etc., It conducts water and minerals salts from roots to leaves and fruits, acts as a storage of reserve food materials.
-The Leaves:
A leaf is a lateral generally flattened structure borne on the stem. It develops at the node and bears a bud in its exile. Leaves are the most important vegetative organ for photosynthesis.
-The Flower:
A flower is a reproductive unit in the angiosperm. It is a modified shoot, meant for sexual reproduction. It consists of four whorls namely Calyx, Corolla, Androecium, Gynoecium. The swollen part of the pedicle or the stock is called the thalamus.
-The Fruit:
The flowering plant or the angiosperms are characterized by the presence of fruit. After fertilization, the ripened or the mature ovary is called the fruit. Parts of the fruit are Fruit wall and seed.
Note: There are various modifications of roots, stems, leaves.
Fruit formed without fertilization is called parthenocarpic fruits. Example: Banana.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




