
What is the most common type of disaccharide?
A.\[{C_{10}}{H_{18}}{O_{19}}\]
B.\[{C_{10}}{H_{20}}{O_{10}}\]
C.\[{C_{11}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}\]
D.\[{C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}\]
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint : Monosaccharide is a carbohydrate composed of simple elements carbon \[C\], hydrogen \[(H)\], and Oxygen\[(O)\]. Two monosaccharide molecules forms a bond that results in a disaccharide molecule. Some common example of the disaccharides are – sucrose, maltose, and lactose.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To solve this question first we need to understand carbohydrates and composition of the disaccharides.
Carbohydrates are the naturally occurring compounds. These have four main categories – Monosaccharide, disaccharide, oligosaccharide and polysaccharide.
Carbohydrates are simple sugars and the disaccharides are known as “double sugars “because they are composed of two monosaccharide units joined by ether bonds. They have \[\alpha ,\beta \] - glycosidic linkage. And the hemi acetyl hydroxyl group resulted from the oxygen always participates in bond formation.
And the general formula for the disaccharides are\[{C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}\].
Some common disaccharides are
\[sucrose = glu\cos e + fructose\]
\[Maltose = glu\cos e + glu\cos e\]
\[Lactose = glu\cos e + galactose\]
Let’s look at the structure of the maltose to understand its composition.
Maltose consists of two molecules of glucose joined by \[\alpha - 1,4 - \]glycoside linkage. During the bond formation water molecule is released.
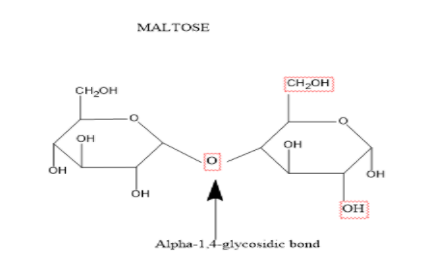
In case of maltose only one hameactyl hydroxyl group participates in bond formation and the second one retains the properties of a reducing sugar.
Whereas, in case of sucrose, it is made of glucose and fructose, so both the hemi acetyl group is involved in bond formation thus the sucrose does not have reducing property.
Lactose is also a reducing sugar.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note :
It is to keep in mind that the non – reducing nature of some disaccharides such as sucrose and trehalose is advantageous also as they confer these double sugars stability. And the stability is the major criteria for the storage of the sugar, this is the reason why sucrose is also known as “table sugar”.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To solve this question first we need to understand carbohydrates and composition of the disaccharides.
Carbohydrates are the naturally occurring compounds. These have four main categories – Monosaccharide, disaccharide, oligosaccharide and polysaccharide.
Carbohydrates are simple sugars and the disaccharides are known as “double sugars “because they are composed of two monosaccharide units joined by ether bonds. They have \[\alpha ,\beta \] - glycosidic linkage. And the hemi acetyl hydroxyl group resulted from the oxygen always participates in bond formation.
And the general formula for the disaccharides are\[{C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}\].
Some common disaccharides are
\[sucrose = glu\cos e + fructose\]
\[Maltose = glu\cos e + glu\cos e\]
\[Lactose = glu\cos e + galactose\]
Let’s look at the structure of the maltose to understand its composition.
Maltose consists of two molecules of glucose joined by \[\alpha - 1,4 - \]glycoside linkage. During the bond formation water molecule is released.

In case of maltose only one hameactyl hydroxyl group participates in bond formation and the second one retains the properties of a reducing sugar.
Whereas, in case of sucrose, it is made of glucose and fructose, so both the hemi acetyl group is involved in bond formation thus the sucrose does not have reducing property.
Lactose is also a reducing sugar.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note :
It is to keep in mind that the non – reducing nature of some disaccharides such as sucrose and trehalose is advantageous also as they confer these double sugars stability. And the stability is the major criteria for the storage of the sugar, this is the reason why sucrose is also known as “table sugar”.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




