
How do you name alkenes using systematic names?
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon provides information about the possible structural types it may represent
The alkenes are hydrocarbons which have carbon-carbon double bond functional groups and are unsaturated hydrocarbons with the molecular formula is \[\text{Cn}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{nCn}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{n,}\] which is also the same molecular formula as cycloalkenes.
Alkenes are named as we do alkanes, but with the ending ene and giving the double bond the highest numbering priority.
Complete step by step answer:
The common family of hydrocarbons found in crude oil is the alkenes. In this family there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond. This double bond makes a big difference to the chemistry of the compounds of the family.
When naming alkanes:
Find the longest continuous chain of carbon that contains carbons of the double bond.
Give the lowest possible number to $\text{C}=\text{C}$ or priority is given to carbon double bonds.
Add substituent and their positions to the name of the alkene as prefixes.
Identify stereoisomers.
For example
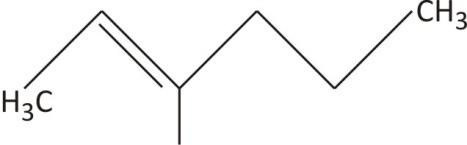
This a six carbon chain hexane with double bond between ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}-{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}$. The base name becomes hex-2-ene.
The methyl group at $\text{C}-5$ changes the name to $5-$methylhex$-2-$ ene.
The full name for the compound is $5-$methylhex$-2-$ ene.
Note: The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon provides information about the possible structural types it may represent. For example, consider compounds having the formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}\]. The formula of the five-carbon alkane pentane is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}\] so the difference in hydrogen content is 4. This difference suggests such compounds may have a triple bond, two double bonds, a ring plus a double bond, or two rings. Hence a nomenclature system should be adopted. Alkenes can act as substitute groups. Alkanes with Unbranched carbon chains are simply named by the number of carbon in the chain
The alkenes are hydrocarbons which have carbon-carbon double bond functional groups and are unsaturated hydrocarbons with the molecular formula is \[\text{Cn}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{nCn}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{n,}\] which is also the same molecular formula as cycloalkenes.
Alkenes are named as we do alkanes, but with the ending ene and giving the double bond the highest numbering priority.
Complete step by step answer:
The common family of hydrocarbons found in crude oil is the alkenes. In this family there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond. This double bond makes a big difference to the chemistry of the compounds of the family.
When naming alkanes:
Find the longest continuous chain of carbon that contains carbons of the double bond.
Give the lowest possible number to $\text{C}=\text{C}$ or priority is given to carbon double bonds.
Add substituent and their positions to the name of the alkene as prefixes.
Identify stereoisomers.
For example

This a six carbon chain hexane with double bond between ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}-{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}$. The base name becomes hex-2-ene.
The methyl group at $\text{C}-5$ changes the name to $5-$methylhex$-2-$ ene.
The full name for the compound is $5-$methylhex$-2-$ ene.
Note: The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon provides information about the possible structural types it may represent. For example, consider compounds having the formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}\]. The formula of the five-carbon alkane pentane is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}\] so the difference in hydrogen content is 4. This difference suggests such compounds may have a triple bond, two double bonds, a ring plus a double bond, or two rings. Hence a nomenclature system should be adopted. Alkenes can act as substitute groups. Alkanes with Unbranched carbon chains are simply named by the number of carbon in the chain
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




