
Name and explain the techniques used in the separation and isolation of DNA fragments to be used in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: The technique is based on the principle that when a charged molecule is put in an electric field, it shifts according to its charge towards the positive or negative side.
Complete answer:
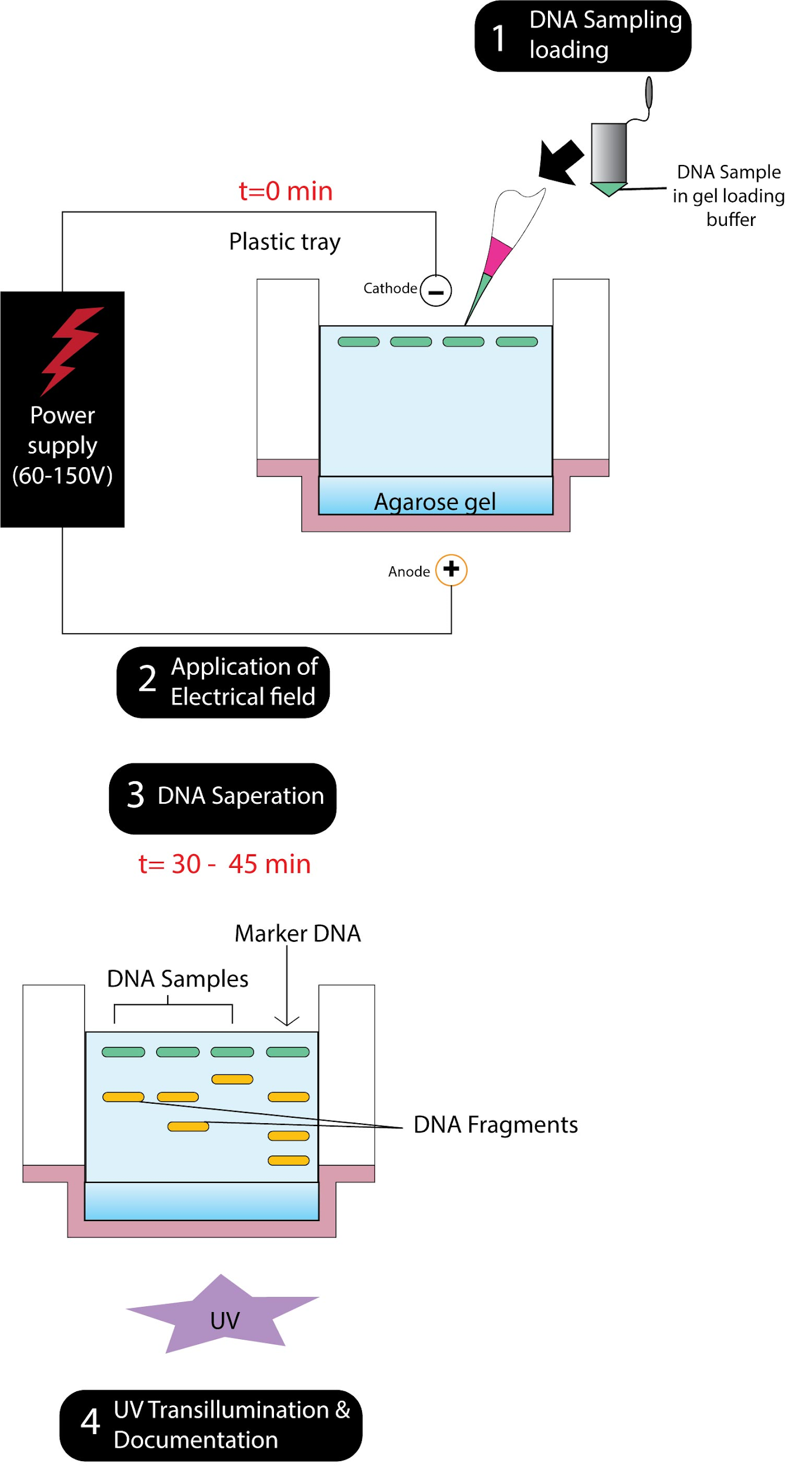
DNA fragment isolation can be done using electrophoresis of agarose or polyacrylamide gel. When genomic DNA is digested with a restriction enzyme extracted from any tissue of a plant or animal species, it is broken into segments. Until a molecular probe is used to detect segments which have sequences identical to those in the probe (for molecular probes, see later in this section), segments of various sizes may be separated by gel electrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis requires movement under a well-formed on one edge of the gel of fragments or molecules. The gel can be a cylinder or a slab, about 10 cm long and 0.5 cm thick (usually a slab for cloning expt.), roughly. The fragment rate of motion is inversely associated with the size of fragments or molecules, so that heavier fragments stay closer to the loading site while the lighter fragments travel away. Fragments of various sizes will appear on the gel as bands and can be examined for further study or isolated. Agarose gels are used more often, but polyacrylamide gels are used for the separation of fragments that vary by a few base pairs. More commonly used for DNA sequencing experiments- polyacrylamide gels.
Additional Information:
A common laboratory technique used to classify, measure, and purify fragments of nucleic acid is electrophoresis. Samples are placed into agarose or acrylamide gel wells and exposed to an electric field, allowing the nucleic acids that have been negatively charged to migrate toward the positive electrode.
A molecular size marker also referred to as a protein ladder, DNA ladder, or RNA ladder is a series of standards that are used during electrophoresis to determine the approximate size of a molecule running on a gel, using the theory that through a gel matrix, molecular weight is inversely proportional to the rate of migration. Therefore, markers effectively have a logarithmic scale on which to measure the size of the other fragments when used in gel electrophoresis.
Note: To differentiate between samples of genetic material, DNA fingerprinting uses gel electrophoresis. Enzymes that chop them at certain characteristic points are treated with human DNA molecules, reducing the DNA to a series of bits of more manageable sizes. The DNA fragments are loaded into a gel and put in an electrical field, which sorts the DNA fragments into different bands electrophoretically. To make them visible to imaging techniques, these bands may be colored with a radioactive dye.
Complete answer:
DNA fragment isolation can be done using electrophoresis of agarose or polyacrylamide gel. When genomic DNA is digested with a restriction enzyme extracted from any tissue of a plant or animal species, it is broken into segments. Until a molecular probe is used to detect segments which have sequences identical to those in the probe (for molecular probes, see later in this section), segments of various sizes may be separated by gel electrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis requires movement under a well-formed on one edge of the gel of fragments or molecules. The gel can be a cylinder or a slab, about 10 cm long and 0.5 cm thick (usually a slab for cloning expt.), roughly. The fragment rate of motion is inversely associated with the size of fragments or molecules, so that heavier fragments stay closer to the loading site while the lighter fragments travel away. Fragments of various sizes will appear on the gel as bands and can be examined for further study or isolated. Agarose gels are used more often, but polyacrylamide gels are used for the separation of fragments that vary by a few base pairs. More commonly used for DNA sequencing experiments- polyacrylamide gels.
Additional Information:
A common laboratory technique used to classify, measure, and purify fragments of nucleic acid is electrophoresis. Samples are placed into agarose or acrylamide gel wells and exposed to an electric field, allowing the nucleic acids that have been negatively charged to migrate toward the positive electrode.
A molecular size marker also referred to as a protein ladder, DNA ladder, or RNA ladder is a series of standards that are used during electrophoresis to determine the approximate size of a molecule running on a gel, using the theory that through a gel matrix, molecular weight is inversely proportional to the rate of migration. Therefore, markers effectively have a logarithmic scale on which to measure the size of the other fragments when used in gel electrophoresis.
Note: To differentiate between samples of genetic material, DNA fingerprinting uses gel electrophoresis. Enzymes that chop them at certain characteristic points are treated with human DNA molecules, reducing the DNA to a series of bits of more manageable sizes. The DNA fragments are loaded into a gel and put in an electrical field, which sorts the DNA fragments into different bands electrophoretically. To make them visible to imaging techniques, these bands may be colored with a radioactive dye.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




