
Name any four characters of the pea plant based on which Mendel studied inheritance.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The characters Mendel picked for his research were related to the flowers, stem, seeds, and seed coats of the pea plants. These characters showed variations in different pea plants.
Complete answer:
To research inheritance, Mendel used pea plants. In pea plants, he found seven distinct characters. They exhibit dominant and recessive characters. They are:
-Round or wrinkled pea shape
-The green or yellow color of the plant
-Constricted or inflated pod shape
-Green or yellow pod color
-Purple or white color flower
-Tall or dwarf plant size
-Axial or terminal position of flowers
Additional Information:
To do so, he first developed pea lines with two distinct feature types, such as tall versus short height. For generations, he grew those lines until they were pure breeding (still producing offspring similar to the parent), then bred them to each other, and observed how the traits were inherited. Besides documenting how the plants looked in each generation, Mendel counted the exact number of plants that showed each trait.
Naturally, pea plants self-fertilize, meaning pollen seeks ova within the same flora. The floral petals remain tightly sealed until pollination is completed to avoid further plant pollination. The outcome is strongly inbred pea plants, or "true-breeding." These are always plants that produce offspring that look like the parent. Mendel prevented the occurrence of unusual traits in offspring by dealing with true-breeding pea plants, which might occur if the plants were not true-breeding. The garden pea also grows to maturity within one season, which means that several generations can be measured within a relatively short period. Lastly, large amounts of garden peas could be grown at the same time, allowing Mendel to conclude that his findings didn't just come about by chance.
Note: A lifelong learner, author, scientist, and man of faith was Johann Gregor Mendel (1822–1884). Mendel's pioneering work was achieved by researching inheritance using the garden pea, Pisum sativum. Mendel also found that the characteristics were inherited independently: one characteristic, such as plant height, did not affect the inheritance of other characteristics, such as flower color or seed shape.
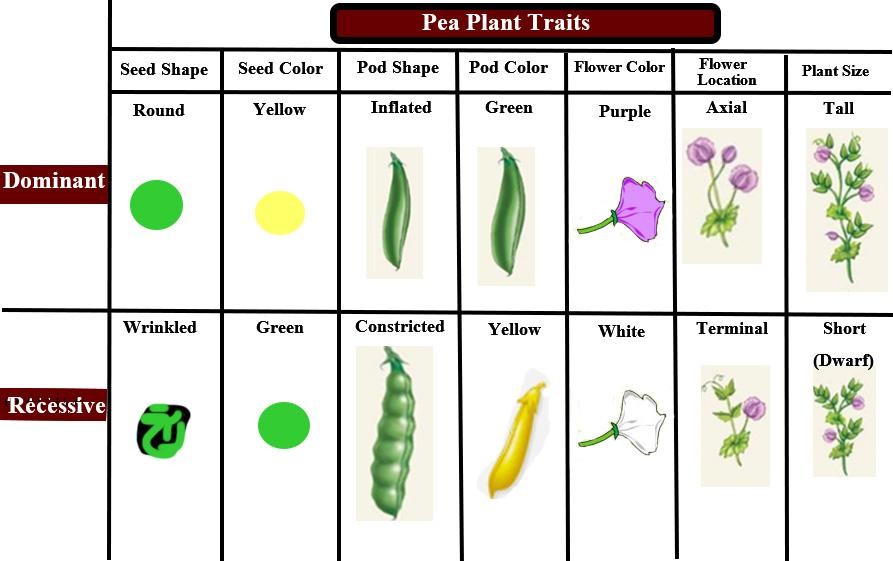
Complete answer:
To research inheritance, Mendel used pea plants. In pea plants, he found seven distinct characters. They exhibit dominant and recessive characters. They are:
-Round or wrinkled pea shape
-The green or yellow color of the plant
-Constricted or inflated pod shape
-Green or yellow pod color
-Purple or white color flower
-Tall or dwarf plant size
-Axial or terminal position of flowers
Additional Information:
To do so, he first developed pea lines with two distinct feature types, such as tall versus short height. For generations, he grew those lines until they were pure breeding (still producing offspring similar to the parent), then bred them to each other, and observed how the traits were inherited. Besides documenting how the plants looked in each generation, Mendel counted the exact number of plants that showed each trait.
Naturally, pea plants self-fertilize, meaning pollen seeks ova within the same flora. The floral petals remain tightly sealed until pollination is completed to avoid further plant pollination. The outcome is strongly inbred pea plants, or "true-breeding." These are always plants that produce offspring that look like the parent. Mendel prevented the occurrence of unusual traits in offspring by dealing with true-breeding pea plants, which might occur if the plants were not true-breeding. The garden pea also grows to maturity within one season, which means that several generations can be measured within a relatively short period. Lastly, large amounts of garden peas could be grown at the same time, allowing Mendel to conclude that his findings didn't just come about by chance.
Note: A lifelong learner, author, scientist, and man of faith was Johann Gregor Mendel (1822–1884). Mendel's pioneering work was achieved by researching inheritance using the garden pea, Pisum sativum. Mendel also found that the characteristics were inherited independently: one characteristic, such as plant height, did not affect the inheritance of other characteristics, such as flower color or seed shape.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




