
Name one halogen of period.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Halogen are the group 17 elements next to the noble gases. The period is the horizontal rows in the periodic table and the group is the vertical columns. Thus, the group 17 is formed by elements from period 2 to period 6 consecutively.
Complete step by step answer:
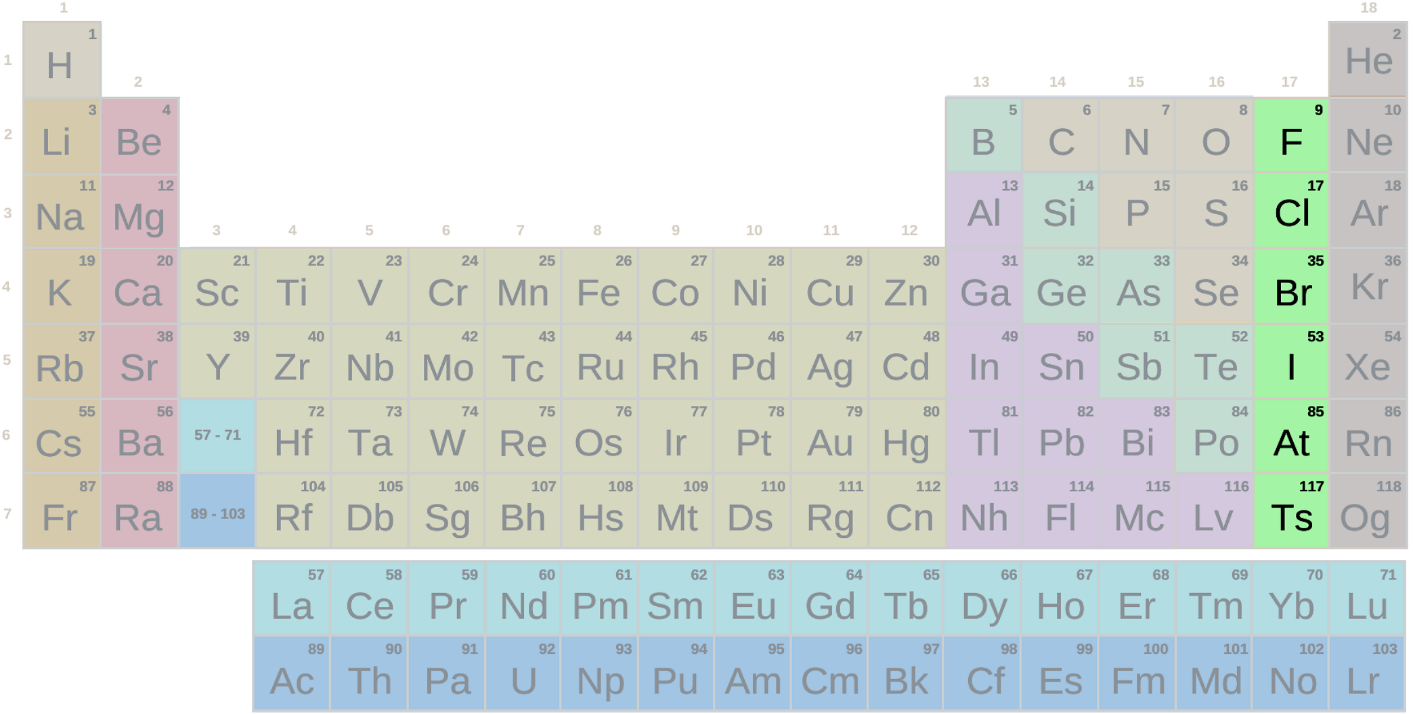
The halogen group is the Group 17 (7A family) elements consisting of:
- Fluorine from period 2,
- Chlorine from period 3,
- Bromine from period 4,
- Iodine from period 5,
- Astatine from period 6.
The halogen group elements are non-metals having the electronic configuration of outermost shell as \[n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{5}}\],that is seven valence electrons which makes them highly reactive as they tend to fulfil the stable configuration of eight electrons in its outermost shell.
As we move down the group, from period 2 to 6, the size of the atom increases with the addition of electron shells which causes more electron repulsion and thus covers more space.
With the increase in the size, the Van der Waal dispersion force increases due to the ease of movement of electrons to form temporary dipoles. These dipoles form interactions between neighbouring molecules. Thus, the halogens exist as diatoms \[{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\text{,}\,\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]and so on.
The increased intermolecular force makes it difficult to break them, thus requiring more energy and increasing its boiling and melting point down the group.
Also, fluorine is the most electronegative element in the group due to its small size. It has a greater tendency to attract the bonding pair of electrons. Whereas, down the group this pairing electron gets further away from the nucleus, thus, less strongly attracted and they act as poor oxidising agents down the group.
Note: All the halogen form hydrides on combining with hydrogen, which is acidic. They also combine with metals forming salt.
Complete step by step answer:
The halogen group is the Group 17 (7A family) elements consisting of:
- Fluorine from period 2,
- Chlorine from period 3,
- Bromine from period 4,
- Iodine from period 5,
- Astatine from period 6.

The halogen group elements are non-metals having the electronic configuration of outermost shell as \[n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{5}}\],that is seven valence electrons which makes them highly reactive as they tend to fulfil the stable configuration of eight electrons in its outermost shell.
As we move down the group, from period 2 to 6, the size of the atom increases with the addition of electron shells which causes more electron repulsion and thus covers more space.
With the increase in the size, the Van der Waal dispersion force increases due to the ease of movement of electrons to form temporary dipoles. These dipoles form interactions between neighbouring molecules. Thus, the halogens exist as diatoms \[{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\text{,}\,\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]and so on.
The increased intermolecular force makes it difficult to break them, thus requiring more energy and increasing its boiling and melting point down the group.
Also, fluorine is the most electronegative element in the group due to its small size. It has a greater tendency to attract the bonding pair of electrons. Whereas, down the group this pairing electron gets further away from the nucleus, thus, less strongly attracted and they act as poor oxidising agents down the group.
Note: All the halogen form hydrides on combining with hydrogen, which is acidic. They also combine with metals forming salt.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




