
Name the enzyme that catalyzes the transcription of hnRNA.
Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint: Enzymes are nothing but proteins. As we know, the proverb- all enzymes are proteins but all proteins are not enzymes. So, enzymes are definitely proteins. Enzymes are a catalyst which enhances any reaction or speeds up the process so that the activity can occur at a faster rate. Almost all reactions require enzymes like- transcription, translation, regulation and metabolism, ATP or glucose synthesis. Every major biological process requires a catalyst as a helper to amplify the reaction.
Complete answer:
We learnt about enzymes and how important they are for the metabolic reactions. Let us discuss transcription then, transcription is the major genetic process to build the genetic information which is RNA and also DNA. It is the process of transcription of DNA to RNA particularly messenger RNA. It uses the DNA as a template strand or parent strand and then the RNA is synthesized. This is a complex process. As RNA delivers all the information from DNA and DNA is the building machines of the body which contains genes for the functions, characters etc.
There are three important steps in transcription- Initiation, elongation and termination. The goal of transcription of RNA from a DNA sequence is RNA carries the information which is needed to build a polypeptide. That is protein or protein sub-unit. And as we know, proteins or polypeptide units are the building blocks of the body. The mechanism which codes for the protein formation from RNA is known as translation.
Various enzymes and other cofactors are used in the three process such enzymes are- RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II, co-factors etc. the enzyme RNA polymerase II is responsible for the transcription of eukaryotic hnRNA.
Note:
The enzymes as we discussed RNA polymerase II transcribes hnRNA. hnRNA stands for – heterogenous nuclear RNA. The process it undergoes before processed into mRNA is- capping. The hnRNA needs to undergo changes for converting into functional RNA. It contains both exons and introns. The exons are coding segments whereas the introns are non- functional sequences.
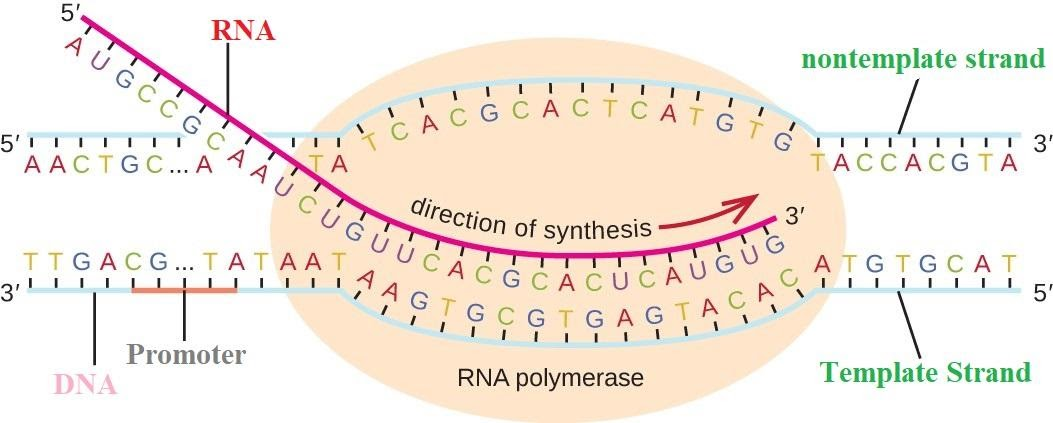
Complete answer:
We learnt about enzymes and how important they are for the metabolic reactions. Let us discuss transcription then, transcription is the major genetic process to build the genetic information which is RNA and also DNA. It is the process of transcription of DNA to RNA particularly messenger RNA. It uses the DNA as a template strand or parent strand and then the RNA is synthesized. This is a complex process. As RNA delivers all the information from DNA and DNA is the building machines of the body which contains genes for the functions, characters etc.
There are three important steps in transcription- Initiation, elongation and termination. The goal of transcription of RNA from a DNA sequence is RNA carries the information which is needed to build a polypeptide. That is protein or protein sub-unit. And as we know, proteins or polypeptide units are the building blocks of the body. The mechanism which codes for the protein formation from RNA is known as translation.
Various enzymes and other cofactors are used in the three process such enzymes are- RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II, co-factors etc. the enzyme RNA polymerase II is responsible for the transcription of eukaryotic hnRNA.
Note:
The enzymes as we discussed RNA polymerase II transcribes hnRNA. hnRNA stands for – heterogenous nuclear RNA. The process it undergoes before processed into mRNA is- capping. The hnRNA needs to undergo changes for converting into functional RNA. It contains both exons and introns. The exons are coding segments whereas the introns are non- functional sequences.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




