
Name the female part of the flower. Name its part and draw its diagram?
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: The reproductive component of a plant is flowers. Not only are they active in reproduction but they are also a food source for other living species. They are rich in nectar sources.
Complete answer:
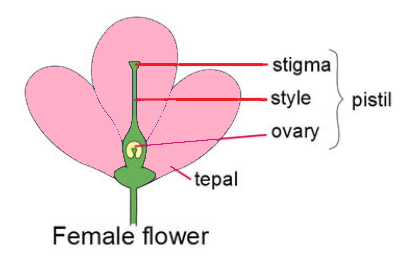
Pistil is the innermost part and a flower's female reproductive organ is usually located in the centre of the flower which consists of three parts including stigma, shape, and ovary. That is known collectively as the pistil.
> Stigma: It is the topmost component or receptive tip of carpels in a floral gynoecium (a sticky knob at the top of the pistil). Sticky surface helps to land and germinate the pollen in. It is attached to the style called the long, tubelike structure. The style leads to the ovary, which includes the ovules called female egg cells.
> Style: The bottom of the pistil contains in between the ovary and the narrowed area. It's the long slender stalk, like a chain, that connects stigma and ovary.
> Ovary: It is the reproductive ductless gland which holds many ovules. It is the base of the female floral component that includes the ovules that become seeds.
Additional information:
A complete flower is the one composed of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils. On the opposite, the one missing one or more of these structures is an incomplete flora. The flower includes sections of both male and female, approximately similar to animal male and female sexes. The flower 's male parts are called stamens and consist of the top anther, and the stalk or filament that supports the anther. In the anther is formed the male contribution or pollen and the ovary is where the seeds develop. Many of the fruits we eat are the thick ovary walls which surround the seeds.
Note: The presence of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil sections differentiates the whole or incomplete flower. A flower contains reproductive parts-stamen and pistil, apart from these parts. A flower may only have female parts, male parts or both.
Complete answer:

Pistil is the innermost part and a flower's female reproductive organ is usually located in the centre of the flower which consists of three parts including stigma, shape, and ovary. That is known collectively as the pistil.
> Stigma: It is the topmost component or receptive tip of carpels in a floral gynoecium (a sticky knob at the top of the pistil). Sticky surface helps to land and germinate the pollen in. It is attached to the style called the long, tubelike structure. The style leads to the ovary, which includes the ovules called female egg cells.
> Style: The bottom of the pistil contains in between the ovary and the narrowed area. It's the long slender stalk, like a chain, that connects stigma and ovary.
> Ovary: It is the reproductive ductless gland which holds many ovules. It is the base of the female floral component that includes the ovules that become seeds.
Additional information:
A complete flower is the one composed of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils. On the opposite, the one missing one or more of these structures is an incomplete flora. The flower includes sections of both male and female, approximately similar to animal male and female sexes. The flower 's male parts are called stamens and consist of the top anther, and the stalk or filament that supports the anther. In the anther is formed the male contribution or pollen and the ovary is where the seeds develop. Many of the fruits we eat are the thick ovary walls which surround the seeds.
Note: The presence of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil sections differentiates the whole or incomplete flower. A flower contains reproductive parts-stamen and pistil, apart from these parts. A flower may only have female parts, male parts or both.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




