
Name the first restriction endonuclease.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: The first restriction endonuclease was isolated from a Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria which can cause pneumonia or bloodstream infections. The restriction endonuclease is an enzyme commonly known as molecular scissors. It is an important tool in recombinant DNA technology.
Complete answer:
W.Arber was the first scientist who postulated about ‘restriction enzymes.’ He noticed the fragmentation of bacteriophage’s DNA into smaller pieces when bacteriophage injects its DNA into the bacteria. In 1970, Hamilton-Smith and his coworkers first isolated a restriction enzyme from the bacterium Haemophilus Influenzae and named it HindII which recognizes a six pair dsDNA sequence.
Additional Information:
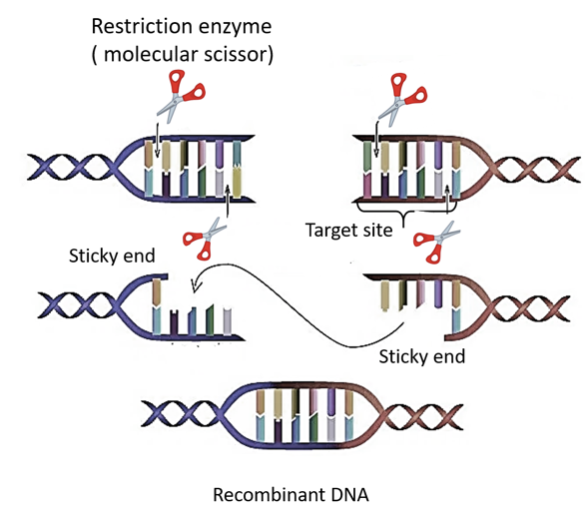
- A restriction endonuclease is an enzyme isolated from bacteria that can cut dsDNA into fragments. It does so by recognizing specific nucleotide sequences as ‘recognition’ or ‘restriction site’. The term ‘restriction’ comes from the observation that these enzymes hamper or obstruct the entry of foreign DNA in the bacteria.
- The naming of restriction endonuclease involves the abbreviations of the bacterial species from which the enzyme is isolated. E.g., ‘Eco’ for E. coli and ‘Hin’ for H. influenzae. Roman numerals are also used to indicate the sequence of discovery if more than one restriction enzyme has been isolated from the same bacterial strain.
- EcoRII is isolated from gram- negative Escherichia coli. It recognizes a six pair dsDNA sequence 5’- CCWGG- 3’ where W = either Adenine (A) or Thymine (T). It produces sticky ends.
Note: The action of restriction enzymes is either blunt or staggered cuts. Blunt ends occur when both ends of cut DNA have a base pair. While in staggered cuts, both the ends of DNA do not possess a base pair, rather single nucleotides are present. These are known as sticky ends. After the staggering cuts, the resulting restriction DNA fragments possess 5’ overhangs or 3’ overhangs.
Complete answer:
W.Arber was the first scientist who postulated about ‘restriction enzymes.’ He noticed the fragmentation of bacteriophage’s DNA into smaller pieces when bacteriophage injects its DNA into the bacteria. In 1970, Hamilton-Smith and his coworkers first isolated a restriction enzyme from the bacterium Haemophilus Influenzae and named it HindII which recognizes a six pair dsDNA sequence.
Additional Information:
- A restriction endonuclease is an enzyme isolated from bacteria that can cut dsDNA into fragments. It does so by recognizing specific nucleotide sequences as ‘recognition’ or ‘restriction site’. The term ‘restriction’ comes from the observation that these enzymes hamper or obstruct the entry of foreign DNA in the bacteria.

- The naming of restriction endonuclease involves the abbreviations of the bacterial species from which the enzyme is isolated. E.g., ‘Eco’ for E. coli and ‘Hin’ for H. influenzae. Roman numerals are also used to indicate the sequence of discovery if more than one restriction enzyme has been isolated from the same bacterial strain.
- EcoRII is isolated from gram- negative Escherichia coli. It recognizes a six pair dsDNA sequence 5’- CCWGG- 3’ where W = either Adenine (A) or Thymine (T). It produces sticky ends.
Note: The action of restriction enzymes is either blunt or staggered cuts. Blunt ends occur when both ends of cut DNA have a base pair. While in staggered cuts, both the ends of DNA do not possess a base pair, rather single nucleotides are present. These are known as sticky ends. After the staggering cuts, the resulting restriction DNA fragments possess 5’ overhangs or 3’ overhangs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




