
Name the optical instruments which use lenses. Describe it in brief.
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Lenses are used to either magnify the image of a small object or to reduce the size of a large/huge object. Hence instruments used for such purposes have lenses as an important part. Microscopes and telescopes use lenses for their functioning.
Complete answer:
Light microscope and telescope are two of the few examples that use lenses. Firstly, let us understand what a light microscope is.
Light Microscope: It is a device which is used to see the minute details of the objects which we can’t see using our naked eyes. This instrument uses a convex lens and it produces virtual and magnified images of objects. They are usually made by either one or more objective lenses or eyepiece lenses. The first lens magnifies the image of the object and the refracted rays from this lens are incident on the next lens, wherein the image is again magnified and thus, the process continues according to the number of lenses. The reverse process can also happen wherein reduced images of objects are obtained. This can be clearly seen from the following ray diagram.
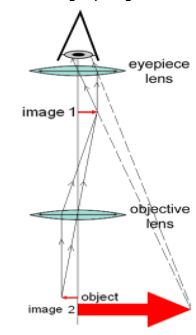
Now, let us move on to the next instrument, which uses lenses for its functioning.
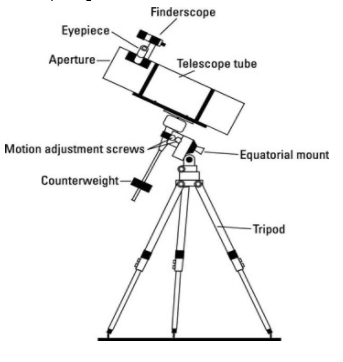
Telescope: It is a device which is used to see the objects which are far away from us, by obtaining a sharp image of these objects. In other words, it produces a magnified and detailed image of an object far away. It uses a convex lens (same as microscope), which helps to magnify the object. The common telescopes which are generally used are known as refracting and reflecting telescopes, which work by refraction and reflection, respectively. This process can also be understood by taking into consideration the object’s emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. A rough and simplified diagram of the telescope is given below for reference.
Note:
Students often get confused between a convex mirror and a convex lens. However, we must consider their refracting and reflecting properties, to differentiate them. A convex mirror diverges the incident rays incident on its surface, whereas a convex lens converges the incident rays incident on its surface.
Complete answer:
Light microscope and telescope are two of the few examples that use lenses. Firstly, let us understand what a light microscope is.
Light Microscope: It is a device which is used to see the minute details of the objects which we can’t see using our naked eyes. This instrument uses a convex lens and it produces virtual and magnified images of objects. They are usually made by either one or more objective lenses or eyepiece lenses. The first lens magnifies the image of the object and the refracted rays from this lens are incident on the next lens, wherein the image is again magnified and thus, the process continues according to the number of lenses. The reverse process can also happen wherein reduced images of objects are obtained. This can be clearly seen from the following ray diagram.

Now, let us move on to the next instrument, which uses lenses for its functioning.
Telescope: It is a device which is used to see the objects which are far away from us, by obtaining a sharp image of these objects. In other words, it produces a magnified and detailed image of an object far away. It uses a convex lens (same as microscope), which helps to magnify the object. The common telescopes which are generally used are known as refracting and reflecting telescopes, which work by refraction and reflection, respectively. This process can also be understood by taking into consideration the object’s emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. A rough and simplified diagram of the telescope is given below for reference.

Note:
Students often get confused between a convex mirror and a convex lens. However, we must consider their refracting and reflecting properties, to differentiate them. A convex mirror diverges the incident rays incident on its surface, whereas a convex lens converges the incident rays incident on its surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




