
Name the specific cell which carries out budding in Hydra.
Give one example of an organism other than hydra which performs budding to reproduce,
Differentiate between them the way they carry out budding.
Show budding in Hydra diagrammatically.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Budding is an asexual way in which new organisms are produced. A new organism is formed from a small portion of the body of the parent in this method. The newly developed organism, since this is asexual reproduction, is a replica of the parent and is genetically identical.
Complete answer:
In the process of budding, organisms like hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction. In hydra, due to repeated cell division at one specific location, a bud develops as an outgrowth.
Two organisms that reproduce by budding are Hydra and Yeast. Their budding is explained below.
Hydra is reproduced through asexual and sexual techniques. Asexual reproduction occurs either by budding or through fission. Budding in Hydra seems to be the standard method of reproduction and occurs at all times of the year. In the middle of the body, a bud is usually formed by rapid interstitial cell multiplication. These are soon transformed into other necessary types of cells, thus generating a bulging of the wall of the body into which the coelenteron extends. At its free end, the bud elongates and develops a circle of tentacles in the midst of which a mouth is perforated. By constricting its base, a fully shaped bud breaks away from the parent.
Generally, budding occurs in yeast during the abundant supply of nutrition. A small bud emerges as an outgrowth of the parent body in this process of reproduction. Later, two parts of the nucleus of the parent yeast are separated and one of the nuclei shifts into the bud. The newly created bud divides into a new cell and finally grows individually.
The diagram of budding in hydra is shown below:
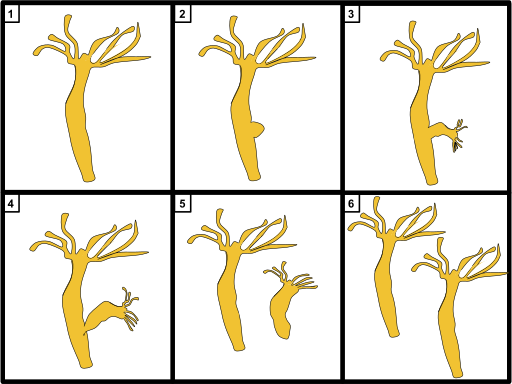
Note:- Hydra is one of the most basic metazoans. It is of the microscopic size which, attached to stones or water weeds, lives in clean freshwater ponds. It is usually attached or with any solid object to submerged vegetation. When it is undisturbed, without any obvious reason, its body remains stretched with tentacles spread out and shows expansion and contraction. It has a carnivorous habit and feeds on tiny insects, larvae of insects and small crustaceans.
Complete answer:
In the process of budding, organisms like hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction. In hydra, due to repeated cell division at one specific location, a bud develops as an outgrowth.
Two organisms that reproduce by budding are Hydra and Yeast. Their budding is explained below.
Hydra is reproduced through asexual and sexual techniques. Asexual reproduction occurs either by budding or through fission. Budding in Hydra seems to be the standard method of reproduction and occurs at all times of the year. In the middle of the body, a bud is usually formed by rapid interstitial cell multiplication. These are soon transformed into other necessary types of cells, thus generating a bulging of the wall of the body into which the coelenteron extends. At its free end, the bud elongates and develops a circle of tentacles in the midst of which a mouth is perforated. By constricting its base, a fully shaped bud breaks away from the parent.
Generally, budding occurs in yeast during the abundant supply of nutrition. A small bud emerges as an outgrowth of the parent body in this process of reproduction. Later, two parts of the nucleus of the parent yeast are separated and one of the nuclei shifts into the bud. The newly created bud divides into a new cell and finally grows individually.
The diagram of budding in hydra is shown below:

Note:- Hydra is one of the most basic metazoans. It is of the microscopic size which, attached to stones or water weeds, lives in clean freshwater ponds. It is usually attached or with any solid object to submerged vegetation. When it is undisturbed, without any obvious reason, its body remains stretched with tentacles spread out and shows expansion and contraction. It has a carnivorous habit and feeds on tiny insects, larvae of insects and small crustaceans.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




