
Name the tissue where cells are living, thin-walled, isodiametric with intercellular spaces
(a) Prosenchyma
(b) Aerenchyma
(C) Parenchyma
(d) Collenchyma
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: The tissues are of two types based on their dividing capabilities. The ones which cannot divide are further of three types based on the type of material deposited in their cell wall. The tissue which is living and thin-walled can be found in the softer parts of leaves, the pulp of fruits, etc.
Complete answer:
Meristematic tissues can divide to form new cells. They are not restricted to perform any particular set of functions. On the other hand, permanent cells are the mature cells that have lost the ability to divide as they have attained their destined shape, size, and function. They can be parenchymatous, collenchymatous, or sclerenchymatous.
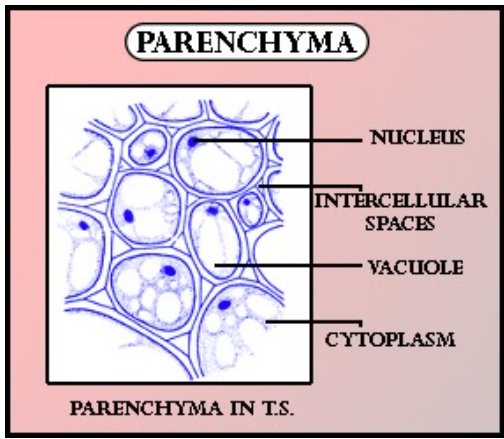
Parenchyma is made up of simple, thin-walled, closely packed isodiametric cells, with little intercellular spaces between them. They are living cells and are the most abundant in plants. Their cell wall contains cellulose with uniform thickening around its periphery. They are located in the cortex of stems and roots, the pulp of fruits, and mesophyll of leaves.
Additional Information:
- Collenchyma is a simple permanent tissue with irregular thickenings of pecto cellulose in specific areas of their walls. They can be only observed in the aerial parts of the plant like petioles, leaves, and stems of dicots. Collenchyma provides mechanical strength coupled with flexibility.
- Parenchyma may be modified to chlorenchyma, aerenchyma, and prosenchyma.
- Aerenchyma is abundant in aquatic plants where the need for floatation is fulfilled by the storage of gases in the air cavities of aerenchyma. Chlorenchyma, as the name suggests, contains chloroplast and thus takes part in the manufacture of food.
-Prosenchyma is a special type of parenchyma found exclusively in vascular tissues for short-distance transport of solutes.
So, the correct answer is ‘Parenchyma.’
Note: -Sclerenchymatous tissue is a type of simple permanent tissues with highly thickened walls and extremely narrow cavities. Little or negligible protoplasm may be present. They are supportive in function. They are of two types - sclereids and fibers.
-Sclereids are found in the grits of guava and pear and in the fruit walls of nuts.
-Sclerenchymatous fibers are elongated and narrow whose ends are interlocked with each other. E.g Jute fibers.
Complete answer:
Meristematic tissues can divide to form new cells. They are not restricted to perform any particular set of functions. On the other hand, permanent cells are the mature cells that have lost the ability to divide as they have attained their destined shape, size, and function. They can be parenchymatous, collenchymatous, or sclerenchymatous.
Parenchyma is made up of simple, thin-walled, closely packed isodiametric cells, with little intercellular spaces between them. They are living cells and are the most abundant in plants. Their cell wall contains cellulose with uniform thickening around its periphery. They are located in the cortex of stems and roots, the pulp of fruits, and mesophyll of leaves.
Additional Information:
- Collenchyma is a simple permanent tissue with irregular thickenings of pecto cellulose in specific areas of their walls. They can be only observed in the aerial parts of the plant like petioles, leaves, and stems of dicots. Collenchyma provides mechanical strength coupled with flexibility.
- Parenchyma may be modified to chlorenchyma, aerenchyma, and prosenchyma.
- Aerenchyma is abundant in aquatic plants where the need for floatation is fulfilled by the storage of gases in the air cavities of aerenchyma. Chlorenchyma, as the name suggests, contains chloroplast and thus takes part in the manufacture of food.
-Prosenchyma is a special type of parenchyma found exclusively in vascular tissues for short-distance transport of solutes.
So, the correct answer is ‘Parenchyma.’
Note: -Sclerenchymatous tissue is a type of simple permanent tissues with highly thickened walls and extremely narrow cavities. Little or negligible protoplasm may be present. They are supportive in function. They are of two types - sclereids and fibers.
-Sclereids are found in the grits of guava and pear and in the fruit walls of nuts.
-Sclerenchymatous fibers are elongated and narrow whose ends are interlocked with each other. E.g Jute fibers.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




