
Name the type of solid in ${S_8}$ molecule.
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint:
Solids are classified in two types that are crystalline and amorphous. The crystalline solids have regular organization of atoms arranged in long range order, whereas the amorphous solids lack this long-range order. Infect, there are many amorphous solids which are capable of flowing.
Complete step by step answer:
The crystalline solids are of four types which are known as ionic solids, molecular solids, network or covalent solid and metallic solids.
The ionic solids contain alternating positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. The ionic crystals or solids have high melting points and are hard and brittle. The ionic solids are held together by ionic bonds. They also cannot conduct electricity.
The covalent solids contain atoms at the lattice points of the crystal, with each atom being covalently bonded to its nearest neighbor atoms. These types of solids are three dimensional. These solids are also hard and brittle with extremely high melting and boiling points because they contain many strong covalent bonds. They do not conduct the electricity as there are no free charges that can move.
The metallic crystals have metal cations which are surrounded by movable valence electrons. These electrons are also known as delocalized electrons which do not belong to any one atom but are capable of moving through the entire lattice. Due to this, metallic solids are good conductors of electricity. Generally, these solids have a wide range of melting points.
The molecular solids consist of molecules at the lattice points of the crystals and they are held together by relatively weak intermolecular forces. These weak intermolecular forces. These weak intermolecular forces may be dispersion forces, dipole $ - $ dipole forces and hydrogen bonds. These forces are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds. As a result, the molecular solids are having much lower melting and boiling points. The molecular solids are also poor conductors of electricity due to lack of free electrons.
Now the ${S_8}$ a molecule, known as Octasulphur, has a crown like structure which is shown below.
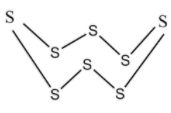
Octasulfur
In the ${S_8}$ molecules, the Sulphur atoms are attached to each other by weak London forces between the molecules. Also, it does not conduct electricity because of the lack of free electrons.
So, ${S_8}$ molecules are the molecular solids.
Note: Octasulfur is an irregular molecule. It is a yellow $ - $ odourless and tasteless solid. ${S_8}$ is the most common allotrope of Sulphur. ${S_8}$ is a homomonocyclic compound.
-It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature.
Solids are classified in two types that are crystalline and amorphous. The crystalline solids have regular organization of atoms arranged in long range order, whereas the amorphous solids lack this long-range order. Infect, there are many amorphous solids which are capable of flowing.
Complete step by step answer:
The crystalline solids are of four types which are known as ionic solids, molecular solids, network or covalent solid and metallic solids.
The ionic solids contain alternating positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. The ionic crystals or solids have high melting points and are hard and brittle. The ionic solids are held together by ionic bonds. They also cannot conduct electricity.
The covalent solids contain atoms at the lattice points of the crystal, with each atom being covalently bonded to its nearest neighbor atoms. These types of solids are three dimensional. These solids are also hard and brittle with extremely high melting and boiling points because they contain many strong covalent bonds. They do not conduct the electricity as there are no free charges that can move.
The metallic crystals have metal cations which are surrounded by movable valence electrons. These electrons are also known as delocalized electrons which do not belong to any one atom but are capable of moving through the entire lattice. Due to this, metallic solids are good conductors of electricity. Generally, these solids have a wide range of melting points.
The molecular solids consist of molecules at the lattice points of the crystals and they are held together by relatively weak intermolecular forces. These weak intermolecular forces. These weak intermolecular forces may be dispersion forces, dipole $ - $ dipole forces and hydrogen bonds. These forces are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds. As a result, the molecular solids are having much lower melting and boiling points. The molecular solids are also poor conductors of electricity due to lack of free electrons.
Now the ${S_8}$ a molecule, known as Octasulphur, has a crown like structure which is shown below.

Octasulfur
In the ${S_8}$ molecules, the Sulphur atoms are attached to each other by weak London forces between the molecules. Also, it does not conduct electricity because of the lack of free electrons.
So, ${S_8}$ molecules are the molecular solids.
Note: Octasulfur is an irregular molecule. It is a yellow $ - $ odourless and tasteless solid. ${S_8}$ is the most common allotrope of Sulphur. ${S_8}$ is a homomonocyclic compound.
-It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




