
Name two cell organelles that are double membrane bound. What are the characteristics of these two organelles? State their functions and draw labelled diagrams of both.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: The cell organelles are involved in performing different functions. Mitochondria are a double membrane organelle that produces energy for the cell. Chloroplasts are double membrane organelles found in plant cells that help in photosynthesis.
Complete answer:
The cell is the basic building block of life. There are certain components within a cell called cell organelles that perform specific functions such as making new material in the cell, removing the waste material from the cell, etc. Because of these organelles, the cell is able to live and perform all its functions.
Each mitochondrion is a dual membrane-bound structure. The outer membrane is very porous and the inner membrane is highly folded. These folds have a large surface area for ATP-generating chemical reactions.
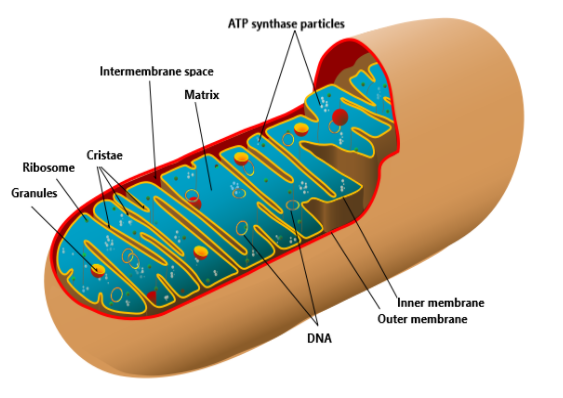
Fig: Mitochondria
Mitochondria provides the energy required for various chemical processes crucial to life in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) molecules. The body uses energy contained in ATP for the creation of new chemical compounds and for mechanical purposes.
Plastids are found in the plant cells. They are distinguished by the presence of pigments. On the basis of the pigment type, plastids can be classified as chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts. Chloroplasts are bound by a double membrane. They can be circular, ovoid or discoid. The space confined by the internal membrane of the chloroplast is called stroma. A variety of structured flattened membrane sacs called thylakoids are found in the stroma. Thylakoids are placed in stacks called grana or intergranal thylakoids.Chloroplasts include chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments responsible for absorbing the light energy needed for photosynthesis.
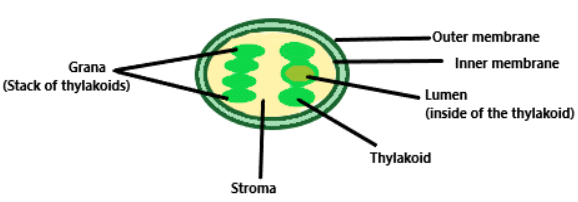
Fig: Chloroplast
Note:Each cell acquires its structure and ability to operate by arranging its membrane and organelles in a particular way. Thus, the cell has a specific structural organisation. This helps cells undertake tasks such as respiration, nutrition, waste disposal, or the production of new proteins.
Complete answer:
The cell is the basic building block of life. There are certain components within a cell called cell organelles that perform specific functions such as making new material in the cell, removing the waste material from the cell, etc. Because of these organelles, the cell is able to live and perform all its functions.
Each mitochondrion is a dual membrane-bound structure. The outer membrane is very porous and the inner membrane is highly folded. These folds have a large surface area for ATP-generating chemical reactions.

Fig: Mitochondria
Mitochondria provides the energy required for various chemical processes crucial to life in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) molecules. The body uses energy contained in ATP for the creation of new chemical compounds and for mechanical purposes.
Plastids are found in the plant cells. They are distinguished by the presence of pigments. On the basis of the pigment type, plastids can be classified as chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts. Chloroplasts are bound by a double membrane. They can be circular, ovoid or discoid. The space confined by the internal membrane of the chloroplast is called stroma. A variety of structured flattened membrane sacs called thylakoids are found in the stroma. Thylakoids are placed in stacks called grana or intergranal thylakoids.Chloroplasts include chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments responsible for absorbing the light energy needed for photosynthesis.

Fig: Chloroplast
Note:Each cell acquires its structure and ability to operate by arranging its membrane and organelles in a particular way. Thus, the cell has a specific structural organisation. This helps cells undertake tasks such as respiration, nutrition, waste disposal, or the production of new proteins.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




