
Natural rubber is a polymer of:
(a) Neoprene
(b) Chloroprene
(c) Isoprene
(d) Styrene
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: The compound is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with five carbon atoms. It has two double bonds and a methyl group attached as a substituent to the main carbon chain.
Complete answer:
Natural rubber is derived from the bark of rubber trees. This tree is abundantly found in countries like India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Malaysia and also in the continent of South America.
Chemically, natural rubber is the polymer of isoprene. The IUPAC name of this compound is$\text{2-methyl-1,3-butadiene}$. It is also called$\text{cis-1,4-polyisoprene}$. The structure of this monomer unit is as follows:
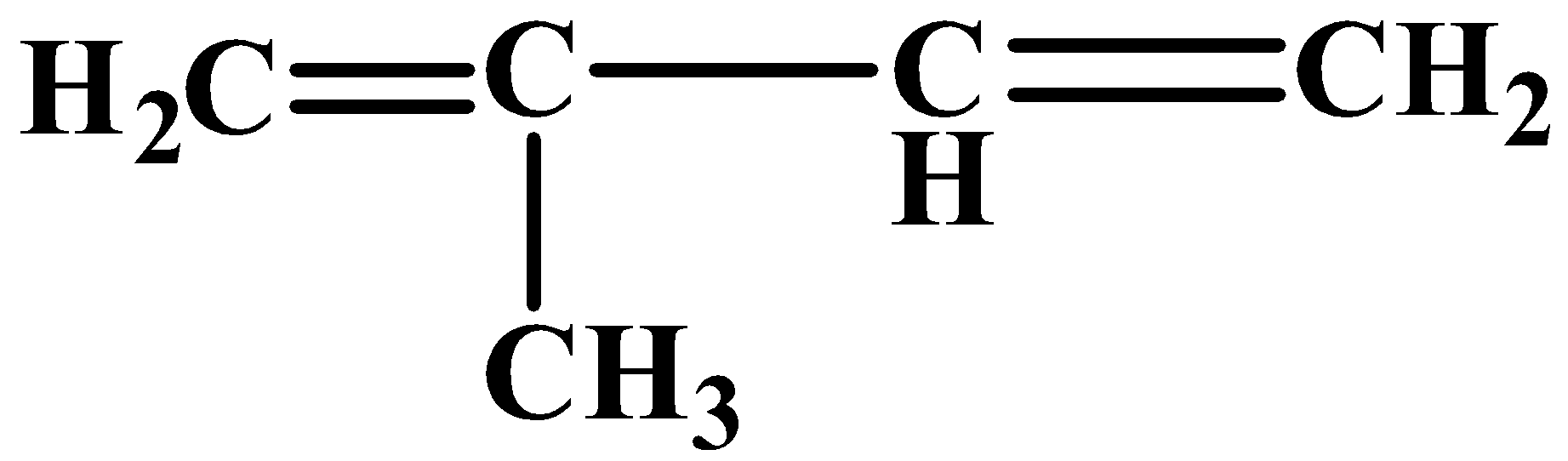
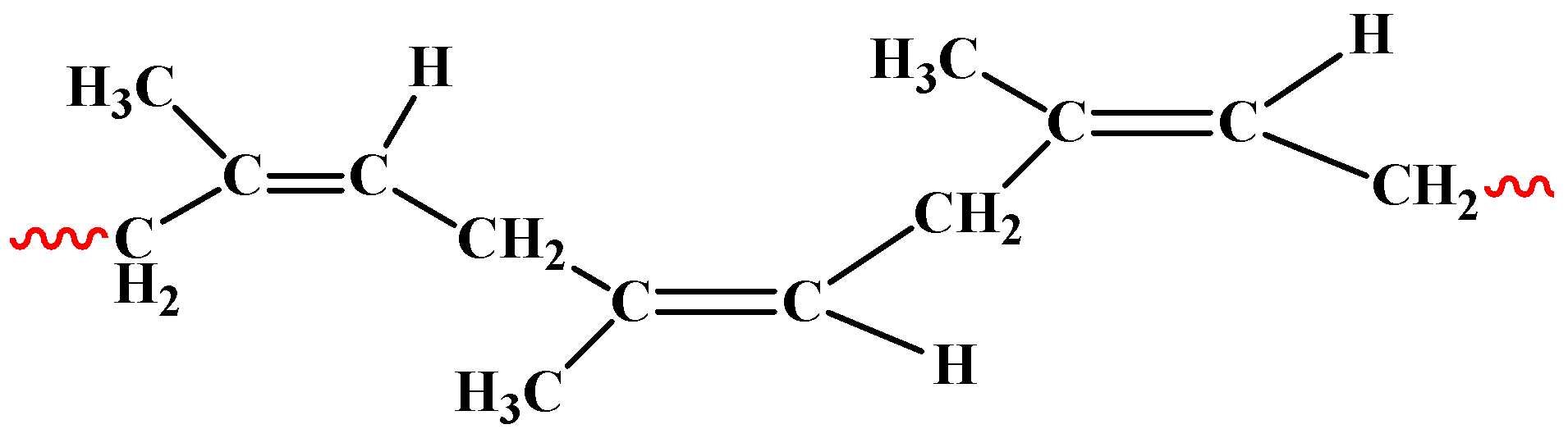
The polymer-which is natural rubber- structure is as follows:
Additional information:
- The natural rubber loses its shape at elevated temperatures and is also brittle at lower temperatures.
- It is not hard enough to use as we desire.
- It has extreme elastic properties and therefore is not good on its own
Owing to the above factors, the natural rubber is taken through a process called vulcanisation. In this process, sulphur is added to it in regulated amounts. The sulphur breaks the double bonds present in the polymeric chains and in this way stiffens the rubber. The chemical structure of vulcanised rubber is as follows:
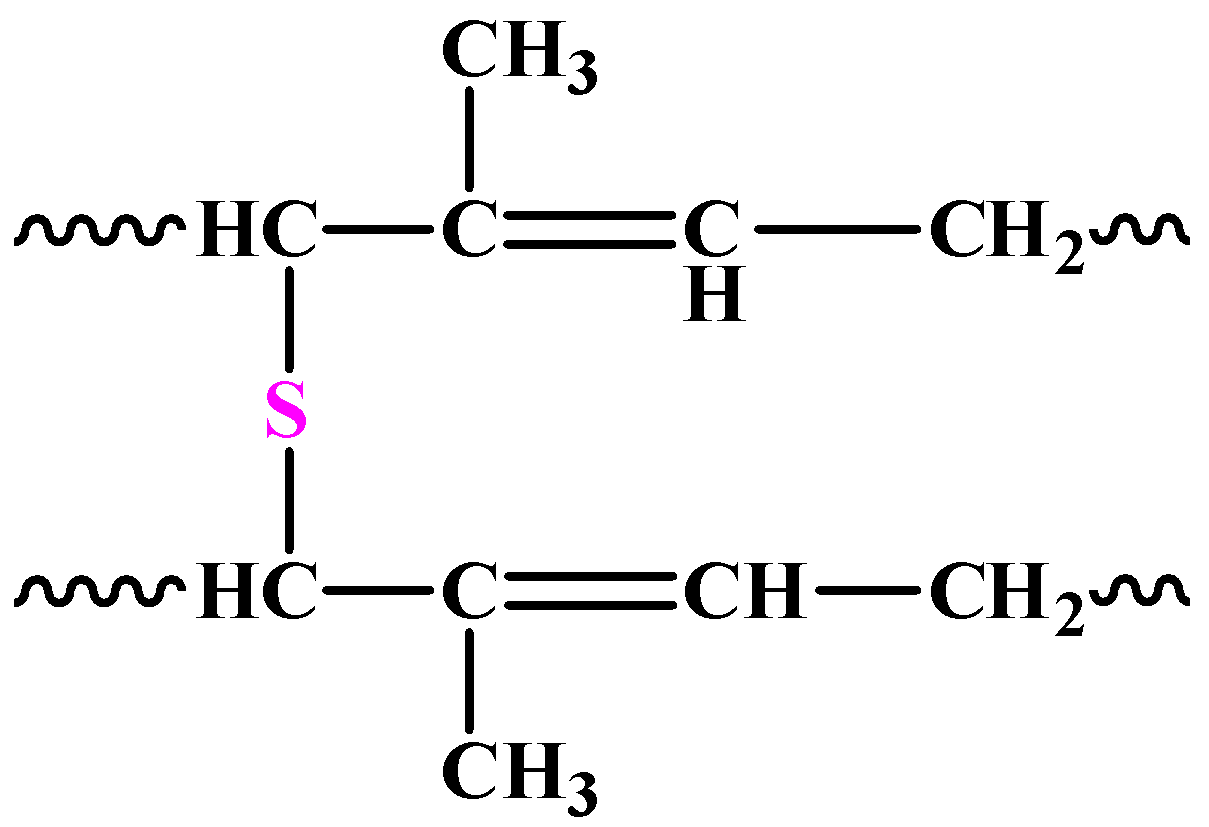
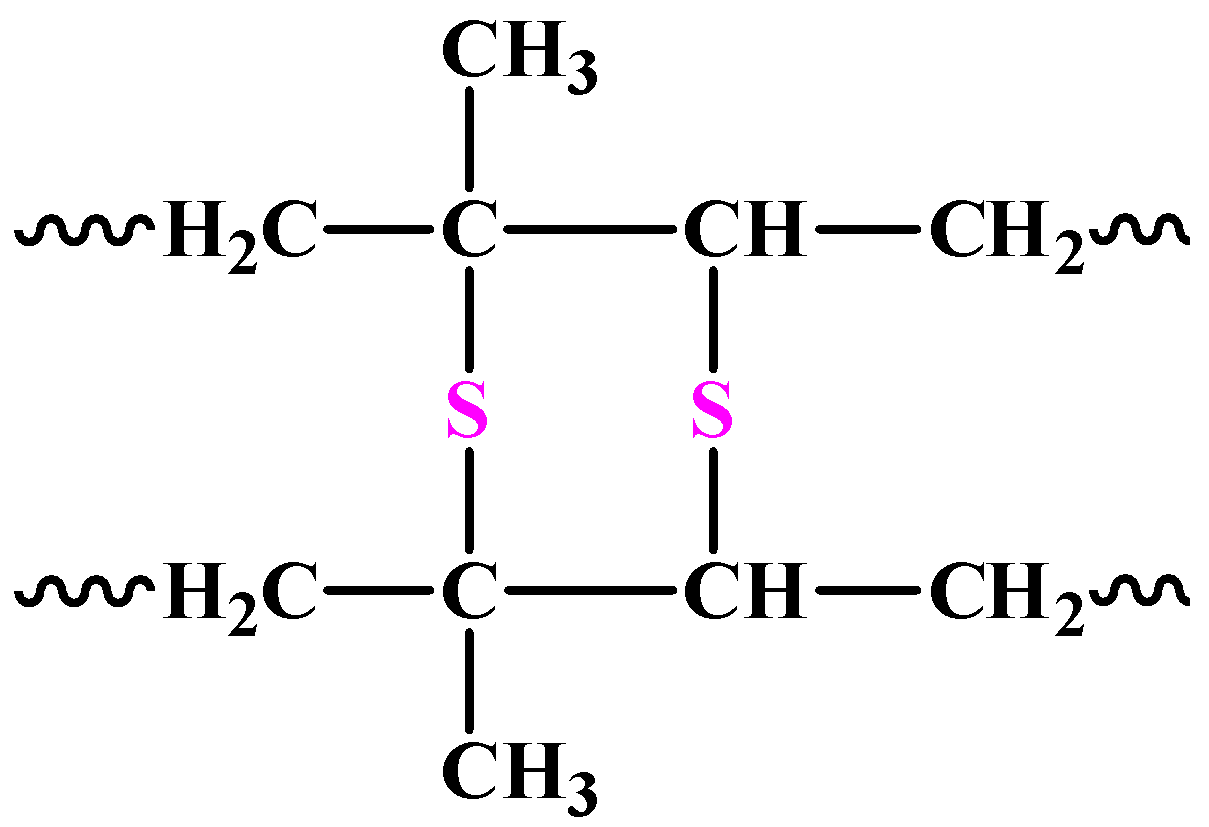
The two structures above are the most probable ones because of the many forms the sulphur atoms could take in the polymer.
Note: Although it is said that rubber is a natural polymer of isoprene units, it is not exactly true. The natural rubber contains many other chemical compounds and impurities that we do not require and therefore these are removed in the purification process. Humans also add other things so as to improvise the properties of rubber and use in a way which is desired by us.
Complete answer:
Natural rubber is derived from the bark of rubber trees. This tree is abundantly found in countries like India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Malaysia and also in the continent of South America.
Chemically, natural rubber is the polymer of isoprene. The IUPAC name of this compound is$\text{2-methyl-1,3-butadiene}$. It is also called$\text{cis-1,4-polyisoprene}$. The structure of this monomer unit is as follows:
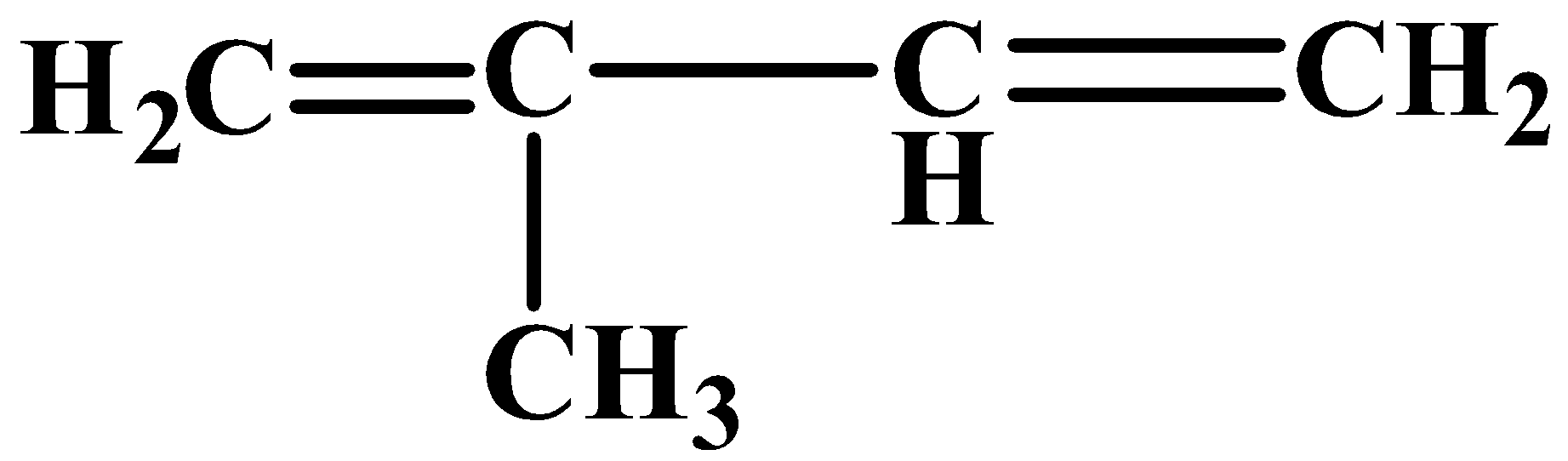
The polymer-which is natural rubber- structure is as follows:

Additional information:
- The natural rubber loses its shape at elevated temperatures and is also brittle at lower temperatures.
- It is not hard enough to use as we desire.
- It has extreme elastic properties and therefore is not good on its own
Owing to the above factors, the natural rubber is taken through a process called vulcanisation. In this process, sulphur is added to it in regulated amounts. The sulphur breaks the double bonds present in the polymeric chains and in this way stiffens the rubber. The chemical structure of vulcanised rubber is as follows:
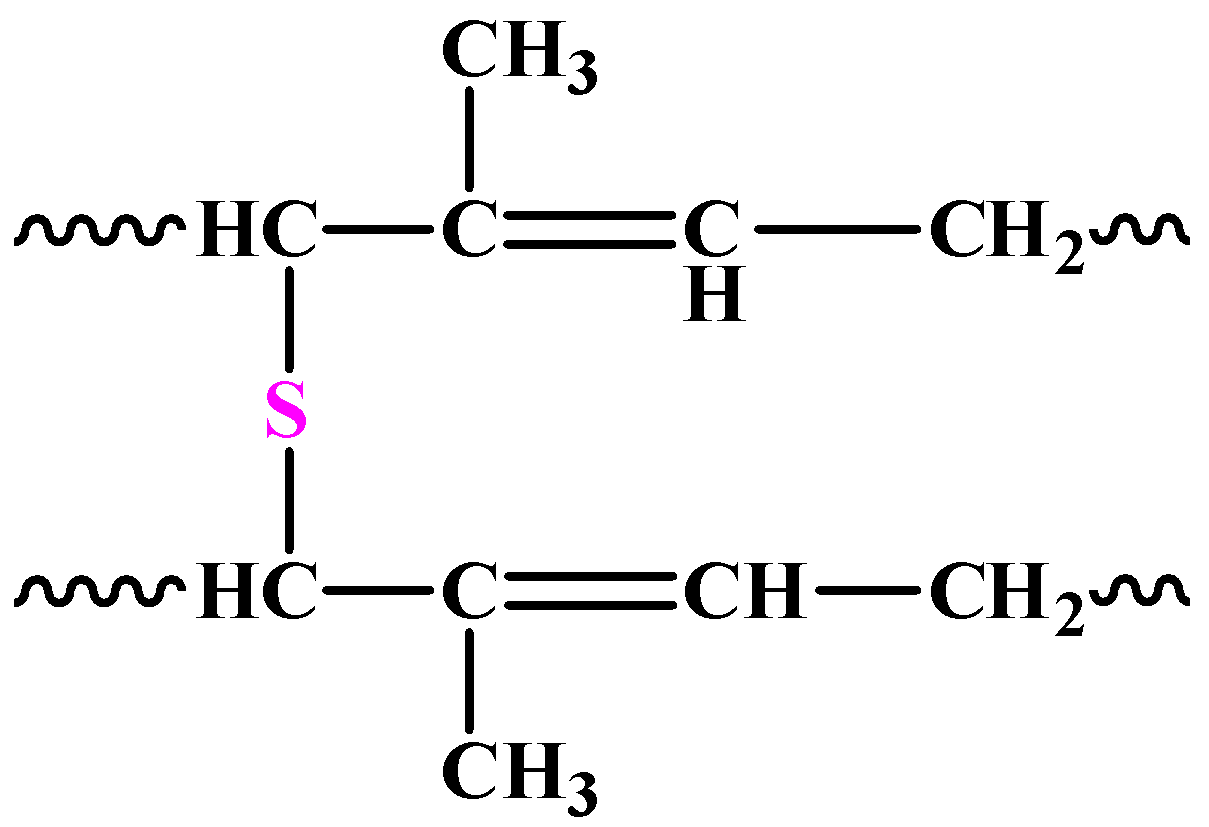

The two structures above are the most probable ones because of the many forms the sulphur atoms could take in the polymer.
Note: Although it is said that rubber is a natural polymer of isoprene units, it is not exactly true. The natural rubber contains many other chemical compounds and impurities that we do not require and therefore these are removed in the purification process. Humans also add other things so as to improvise the properties of rubber and use in a way which is desired by us.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




