
Nephridiopores presents over the body of earthworm belong to
A. Integumentary nephridia
B. Septal nephridia
C. Pharyngeal nephridia
D. Protonephridia
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: For the disposal of metabolic waste of the body, excretory organs are helpful. Earthworms belong to the phylum Annelida and they are known for their metameric segmentation of the body. The metameric segmentation body is divided into segments both internally and externally and these segments are called metamers.
Complete answer:
The excretory organs in the earthworm are segmentally arranged coiled tubules. These coiled tubules are called nephridia. These regulate the volume and composition of body fluids. Integumentary nephridia are attached to the lining of segment 3 to the last that open on the body surface. Nephridiopores of the earthworm belong to integumentary nephridia.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Additional information:
Nephridia are very much similar to the vertebrate kidney which expels the metabolic waste from the body. Earthworms have slightly more advanced excretory structures. Excluding the first two and last section of the body, each section contains nephridia.
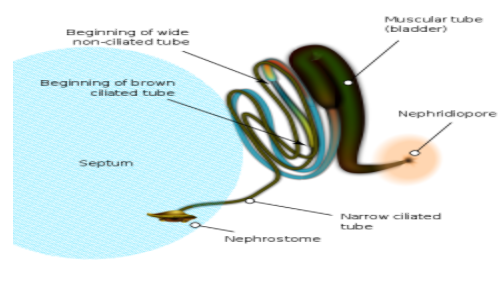
In earthworms nephridia are found in clusters around parts of the body of the earthworm. Each works as waste ducts but each has a distinctive function as well. Nephridium consists of an opening called nephrostome and there is a further opening called nephridiopore.
Body fluids are pumped by the nephrostomes in a complex tubular framework and then critical substances are absorbed and waste materials are returned to the lumen and then the subsequent body fluids are carried through nephridiopores.
Note: There are three types of nephridia present in earthworms, based on the location, septal nephridia, Pharyngeal nephridia, and integumentary nephridia. Septal nephridia attached to the septa, while pharyngeal nephridia attached to the gut and integumentary nephridia attached to the inner lining of the body wall.
Complete answer:
The excretory organs in the earthworm are segmentally arranged coiled tubules. These coiled tubules are called nephridia. These regulate the volume and composition of body fluids. Integumentary nephridia are attached to the lining of segment 3 to the last that open on the body surface. Nephridiopores of the earthworm belong to integumentary nephridia.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Additional information:
Nephridia are very much similar to the vertebrate kidney which expels the metabolic waste from the body. Earthworms have slightly more advanced excretory structures. Excluding the first two and last section of the body, each section contains nephridia.

In earthworms nephridia are found in clusters around parts of the body of the earthworm. Each works as waste ducts but each has a distinctive function as well. Nephridium consists of an opening called nephrostome and there is a further opening called nephridiopore.
Body fluids are pumped by the nephrostomes in a complex tubular framework and then critical substances are absorbed and waste materials are returned to the lumen and then the subsequent body fluids are carried through nephridiopores.
Note: There are three types of nephridia present in earthworms, based on the location, septal nephridia, Pharyngeal nephridia, and integumentary nephridia. Septal nephridia attached to the septa, while pharyngeal nephridia attached to the gut and integumentary nephridia attached to the inner lining of the body wall.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




