
Nitration of benzene is:
(A) Nucleophilic substitution
(B) Nucleophilic addition
(C) Electrophilic substitution
(D) Free radical substitution
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: In this reaction benzene is reacted with concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid. Conc. sulphuric acid being strong donates a proton to nitric acid to form an ion which attaches to the benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all let us see what is meant by nitration of benzene.
A reaction where benzene (${C_6}{H_6}$) will react with concentrated nitric acid ($conc.HN{O_3}$) at 323-333K in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid ($conc.{H_2}S{O_4}$) resulting in the formation of nitrobenzene is known as nitration of benzene.
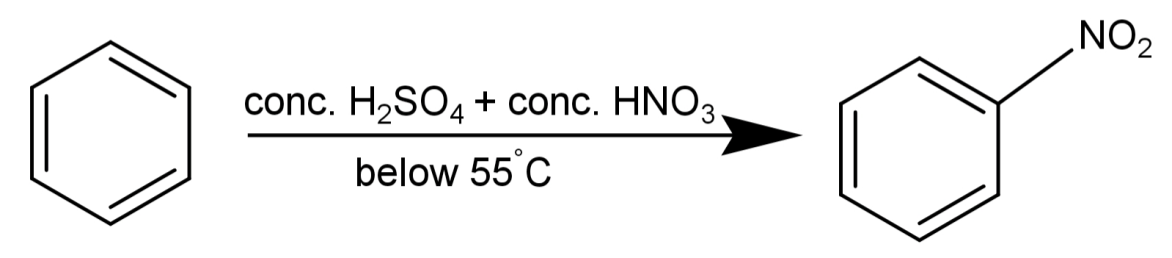
-We will now talk about the mechanism of this reaction:
Step-1) The two strong acids: $conc.{H_2}S{O_4}$ and $conc.HN{O_3}$ react with each other to form a very strong electrophile called the nitronium ion. Nitric acid accepts a proton from sulphuric acid because sulphuric acid is a stronger acid.
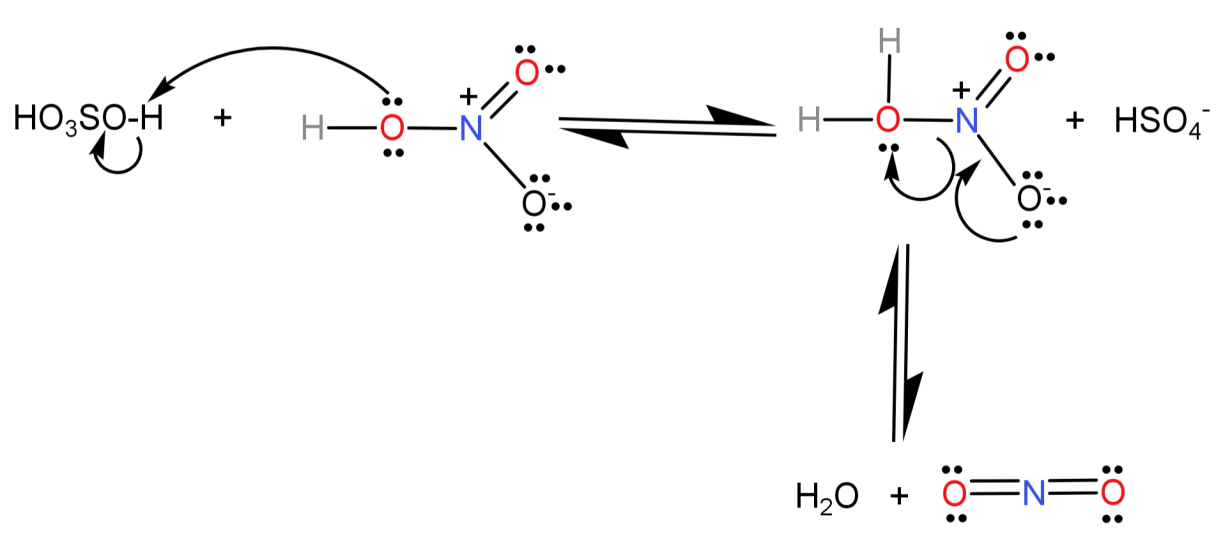
Step-2) Now benzene will react with this positively charged nitronium ion (electrophile) and leads to the formation of an arenium ion (by breaking one of the N=O bonds).
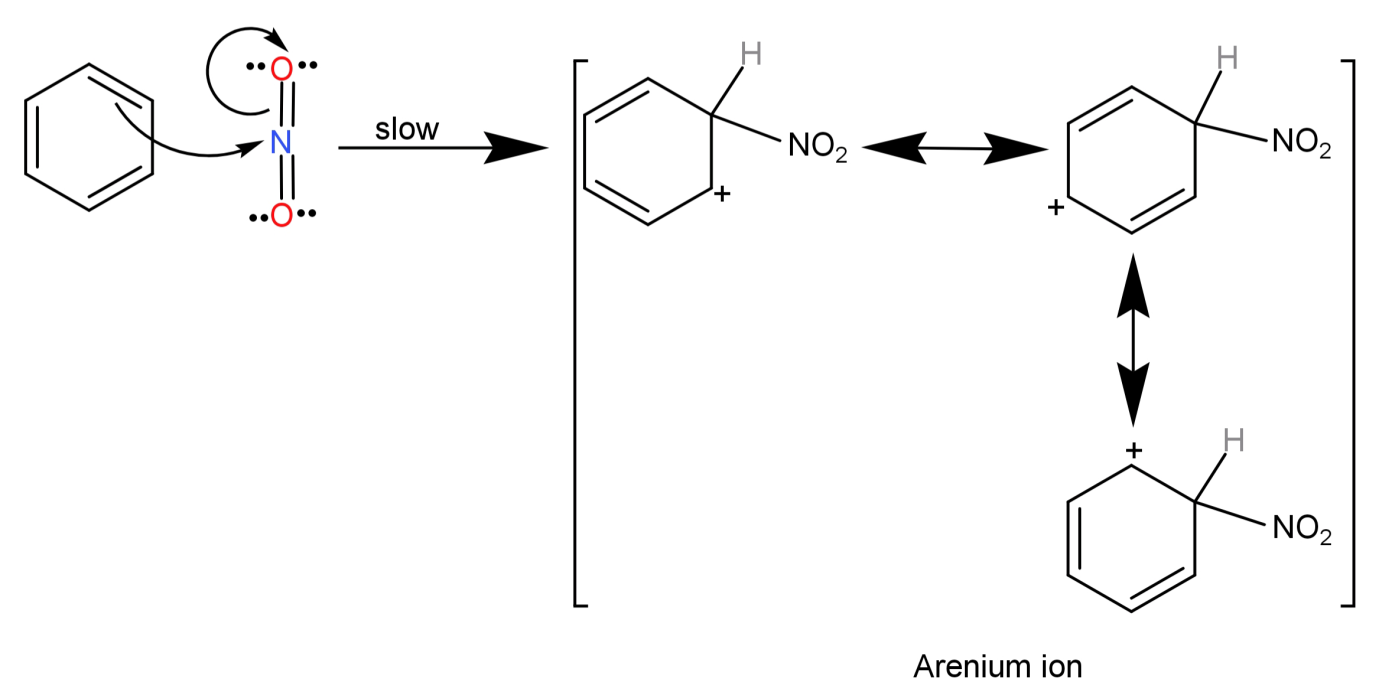
Step-3) Finally the arenium ion loses a proton to a lewis base (to regain its aromaticity) and leads to the formation of our final product nitrobenzene (${C_6}{H_5}N{O_2}$).
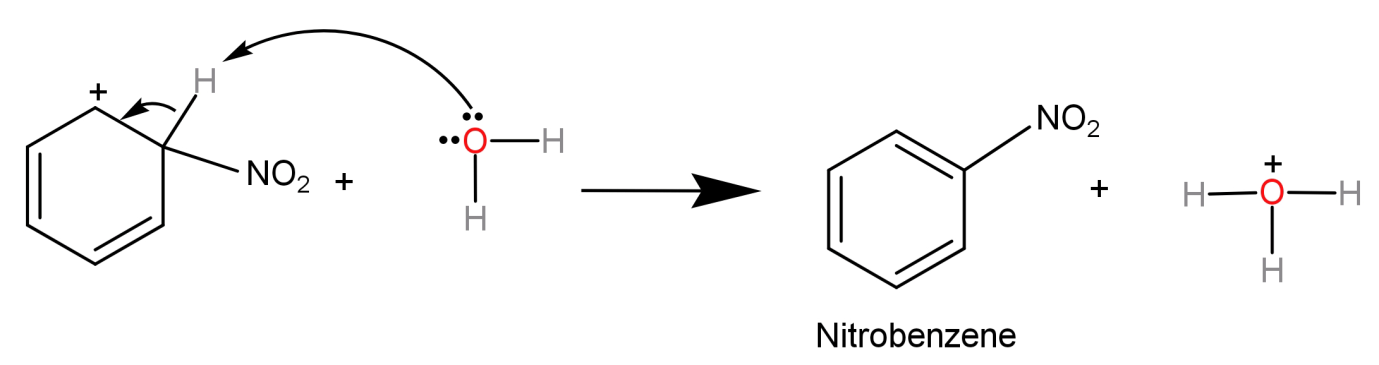
Here we can see that we have replaced a hydrogen atom from the benzene ring with a strong electrophile (nitronium ion, $NO_2^ + $), and hence we can call nitration of benzene as an electrophilic substitution reaction.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: An electrophile is an ion which is itself positively charged and gets attracted to electron rich atoms or molecules, while a nucleophile is an ion which itself is negatively charged and gets attracted to electron deficient atoms or compounds. So, in an electrophilic substitution reaction an electrophile replaces another electrophile.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all let us see what is meant by nitration of benzene.
A reaction where benzene (${C_6}{H_6}$) will react with concentrated nitric acid ($conc.HN{O_3}$) at 323-333K in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid ($conc.{H_2}S{O_4}$) resulting in the formation of nitrobenzene is known as nitration of benzene.
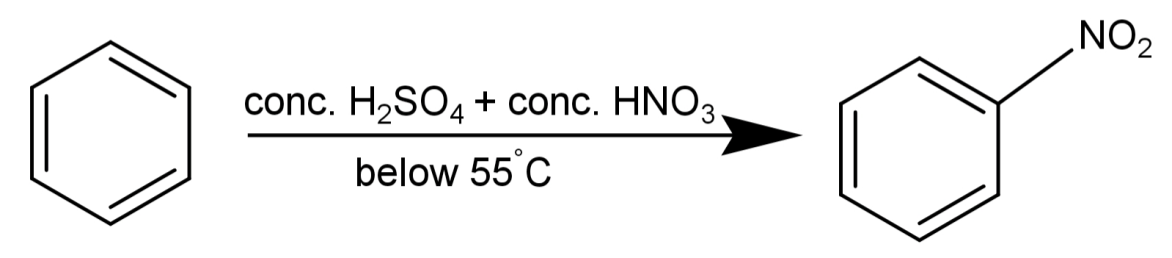
-We will now talk about the mechanism of this reaction:
Step-1) The two strong acids: $conc.{H_2}S{O_4}$ and $conc.HN{O_3}$ react with each other to form a very strong electrophile called the nitronium ion. Nitric acid accepts a proton from sulphuric acid because sulphuric acid is a stronger acid.

Step-2) Now benzene will react with this positively charged nitronium ion (electrophile) and leads to the formation of an arenium ion (by breaking one of the N=O bonds).

Step-3) Finally the arenium ion loses a proton to a lewis base (to regain its aromaticity) and leads to the formation of our final product nitrobenzene (${C_6}{H_5}N{O_2}$).

Here we can see that we have replaced a hydrogen atom from the benzene ring with a strong electrophile (nitronium ion, $NO_2^ + $), and hence we can call nitration of benzene as an electrophilic substitution reaction.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: An electrophile is an ion which is itself positively charged and gets attracted to electron rich atoms or molecules, while a nucleophile is an ion which itself is negatively charged and gets attracted to electron deficient atoms or compounds. So, in an electrophilic substitution reaction an electrophile replaces another electrophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




