
Nitration of benzoic acid gives:
A. Ortho and para nitrobenzoic acid
B. Meta nitrobenzoic acid
C. Nitrobenzene
D. None.
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint- In order to solve the given problem, first we will see what is benzoic acid and further we will see the process of nitration for the benzene and also the products formed after the nitration. On the basis of this process, we will select the correct option amongst the given ones.
Complete answer:
Benzoic acid is an aromatic acid that is susceptible to the normal electrophilic benzene ring replacement reactions such as nitration.
The nitration of benzoic acid thus results in the formation of a compound called 3-Nitrobenzoic acid.
That is because the group "-COOH" present in benzoic acid is electron-withdrawal, thus it is meta-directing.
Because of this the electrophilic substitution reaction happens in the benzoic acid meta position.
The chemical equation involved in the reaction is:
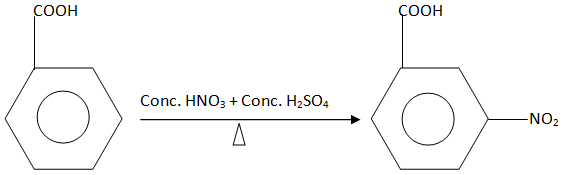
Hence, nitration of benzoic acid gives meta nitrobenzoic acid.
So, the correct option is B.
Additional information-
Aromatic ring substituents affect the extent of this aromatic electrophilic substitution. The deactivation of groups such as certain nitro groups has an effect of electron-removal. These groups deactivate the reaction (slow) and steer the electrophilic nitronium ion to attack the meta aromatic position. The meta-directing substituents are deactivated by sulfonyl, cyano groups, keto, esters, and carboxylates. Nitration can be stimulated by activating groups such as amino, hydroxy and methyl groups, resulting in para and ortho isomers as well as amides and ethers.
Note- Nitration is a general class of chemical processes in which a nitro group is introduced into an organic compound. The term is often wrongly applied to the specific cycle of nitrate esters formation between alcohols and nitric acid (as happens in nitroglycerine synthesis). Benzene is a synthetic chemical and is commonly used. Benzene is present in crude oil and is a major part of petrol. It's used to make plastics, resins, synthetic fibers, rubber lubricants, dyes, detergents, drugs and pesticides.
Complete answer:
Benzoic acid is an aromatic acid that is susceptible to the normal electrophilic benzene ring replacement reactions such as nitration.
The nitration of benzoic acid thus results in the formation of a compound called 3-Nitrobenzoic acid.
That is because the group "-COOH" present in benzoic acid is electron-withdrawal, thus it is meta-directing.
Because of this the electrophilic substitution reaction happens in the benzoic acid meta position.
The chemical equation involved in the reaction is:

Hence, nitration of benzoic acid gives meta nitrobenzoic acid.
So, the correct option is B.
Additional information-
Aromatic ring substituents affect the extent of this aromatic electrophilic substitution. The deactivation of groups such as certain nitro groups has an effect of electron-removal. These groups deactivate the reaction (slow) and steer the electrophilic nitronium ion to attack the meta aromatic position. The meta-directing substituents are deactivated by sulfonyl, cyano groups, keto, esters, and carboxylates. Nitration can be stimulated by activating groups such as amino, hydroxy and methyl groups, resulting in para and ortho isomers as well as amides and ethers.
Note- Nitration is a general class of chemical processes in which a nitro group is introduced into an organic compound. The term is often wrongly applied to the specific cycle of nitrate esters formation between alcohols and nitric acid (as happens in nitroglycerine synthesis). Benzene is a synthetic chemical and is commonly used. Benzene is present in crude oil and is a major part of petrol. It's used to make plastics, resins, synthetic fibers, rubber lubricants, dyes, detergents, drugs and pesticides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




