
Nitration of nitrobenzene at ${125^0}C$ with mixed acids gives:
A.meta-dinitrobenzene
B.ortho-dinitrobenzene
C.para-dinitrobenzene
D.$1,3,5 - $trinitrobenzene
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:In organic chemistry, nitration is the introduction of nitro groups into an organic compound.The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid (as occurs in the synthesis of nitroglycerin).
Complete step by step answer: Nitrobenzene is an organic compound. Its chemical formula is ${C_6}{H_5}N{O_2}$. A hydrogen in benzene is replaced by a nitro group to form nitrobenzene.
Nitration of compounds is a very important chemical reaction in organic chemistry. Nitration is usually carried out using a mixture of concentrated nitric acid ($HN{O_3}$) and concentrated sulphuric acid (${H_2}S{O_4}$). But nitration can be carried out using a mixture of nitric acid or nitrogen oxide with inorganic compounds like ${H_2}S{O_4}$,$B{F_3}$ or organic compounds like acetic anhydride also.
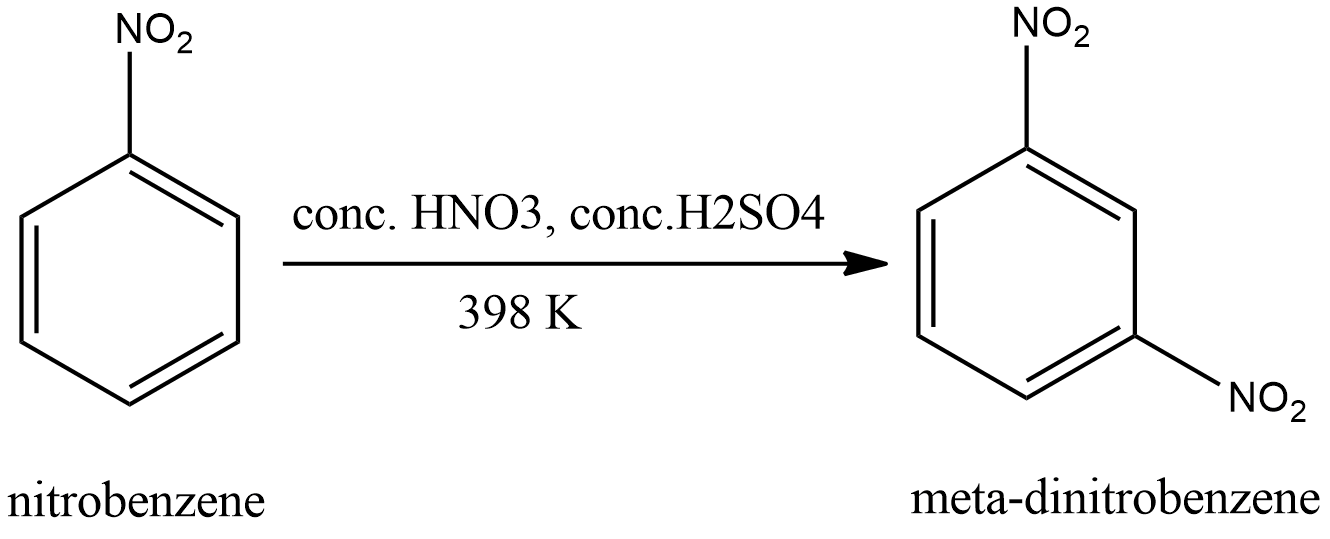
The product of nitration depends on the reactants. Nitrobenzene already contains a nitro-group. Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group. Therefore, it is a meta directing group. Hence the attachment of a new nitro group occurs in the meta position. Hence the product will be meta-dinitrobenzene. The reaction is shown in the figure.
Hence the correct option is A.
Note:
Nitration is an electrophilic substitution reaction. The electrophile is nitronium ion ($N{O^ + }_2$). Nitration of nitrobenzene is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction. Nitration is an exothermic reaction.
Nitration of nitrobenzene is more difficult than that of benzene. The reason behind is the electron withdrawing character of the nitro group. It attracts the electron density on the benzene ring towards it. Then the benzene ring becomes electron deficient. This makes the benzene ring less vulnerable to electrophilic attack.
Nitration of benzene containing electron donating groups give ortho- and para- products.
Complete step by step answer: Nitrobenzene is an organic compound. Its chemical formula is ${C_6}{H_5}N{O_2}$. A hydrogen in benzene is replaced by a nitro group to form nitrobenzene.
Nitration of compounds is a very important chemical reaction in organic chemistry. Nitration is usually carried out using a mixture of concentrated nitric acid ($HN{O_3}$) and concentrated sulphuric acid (${H_2}S{O_4}$). But nitration can be carried out using a mixture of nitric acid or nitrogen oxide with inorganic compounds like ${H_2}S{O_4}$,$B{F_3}$ or organic compounds like acetic anhydride also.
The product of nitration depends on the reactants. Nitrobenzene already contains a nitro-group. Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group. Therefore, it is a meta directing group. Hence the attachment of a new nitro group occurs in the meta position. Hence the product will be meta-dinitrobenzene. The reaction is shown in the figure.

Hence the correct option is A.
Note:
Nitration is an electrophilic substitution reaction. The electrophile is nitronium ion ($N{O^ + }_2$). Nitration of nitrobenzene is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction. Nitration is an exothermic reaction.
Nitration of nitrobenzene is more difficult than that of benzene. The reason behind is the electron withdrawing character of the nitro group. It attracts the electron density on the benzene ring towards it. Then the benzene ring becomes electron deficient. This makes the benzene ring less vulnerable to electrophilic attack.
Nitration of benzene containing electron donating groups give ortho- and para- products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




