
Nitrobenzene on reaction with conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}/{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ at $80-{{100}^{\circ }}C$ forms which one of the following products?
(A) 1,2- Dinitrobenzene
(B) 1,3- Dinitrobenzene
(C) 1,4- Dinitrobenzene
(D) 1,2,4- Trinitrobenzene
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The reaction involves the electrophilic substitution reaction and also the substituent attached to the benzene ring plays an important role in deciding the position of the electrophile to replace the hydrogen in the benzene ring.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the concentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acid reacts with the nitrobenzene leading to addition of another nitro group by replacement of hydrogen in the benzene ring. This is known as the nitration process. It takes place as follows:
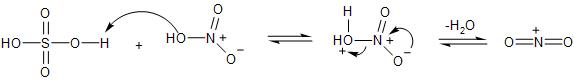
- Firstly the $HN{{O}_{3}}\,and\,{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$, react to form the electrophile, as the nitric acid gains proton from sulphuric acid, followed by losing a water molecule and forming the nitronium ion.
- In the nitrobenzene compound, the nitro- group is an electron-withdrawing group which deactivates the ortho- and the para- position for the electrophilic substitution by decreasing the electron density at these position as can be seen in its resonating structures.
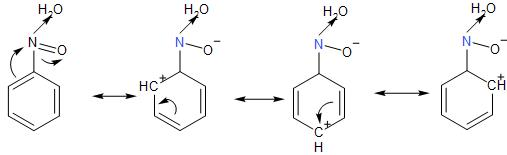
This leads to the meta-position being most electron-dense, the favourable position for the electrophile to attach.
- So, when the nitronium ion electrophile attacks the benzene ring of the nitrobenzene compound, to forming the intermediate carbocation, which loses its proton to the Lewis base of $HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$. Thus, forming a meta-substituted dinitrobenzene compound.
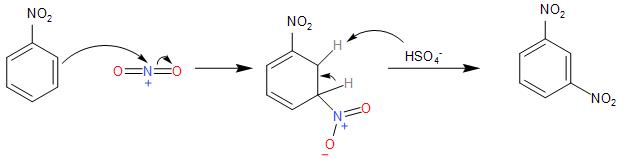
Therefore, the nitration of Nitrobenzene compound forms option (B) 1,3- Dinitrobenzene as the end product.
Note: During the reaction, the sulphuric acid acts as the catalyst and is regained back in the end. Also, the nitration process followed is similar for the formation of the nitrobenzene compound, having the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the concentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acid reacts with the nitrobenzene leading to addition of another nitro group by replacement of hydrogen in the benzene ring. This is known as the nitration process. It takes place as follows:
- Firstly the $HN{{O}_{3}}\,and\,{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$, react to form the electrophile, as the nitric acid gains proton from sulphuric acid, followed by losing a water molecule and forming the nitronium ion.

- In the nitrobenzene compound, the nitro- group is an electron-withdrawing group which deactivates the ortho- and the para- position for the electrophilic substitution by decreasing the electron density at these position as can be seen in its resonating structures.

This leads to the meta-position being most electron-dense, the favourable position for the electrophile to attach.
- So, when the nitronium ion electrophile attacks the benzene ring of the nitrobenzene compound, to forming the intermediate carbocation, which loses its proton to the Lewis base of $HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$. Thus, forming a meta-substituted dinitrobenzene compound.

Therefore, the nitration of Nitrobenzene compound forms option (B) 1,3- Dinitrobenzene as the end product.
Note: During the reaction, the sulphuric acid acts as the catalyst and is regained back in the end. Also, the nitration process followed is similar for the formation of the nitrobenzene compound, having the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




