
Nitrosyl ligand binds to d-metal atoms in linear and bent fashion and behaves , respectively as
A.$N{O^ + }$ and $N{O^ + }$
B.$N{O^ + }$ and $N{O^ - }$
C.$N{O^ - }$ and $N{O^ - }$
D.$N{O^ - }$ and $N{O^ + }$
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint:Nitrosyl complexes or metal nitrosyl complexes are complexes which contain nitric oxide, $NO$ bonded to the transitional metal. Of the many kinds of the nitrosyl complexes, they differ both in co ligand and structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Most complexes which have $NO$ ligand may be seen or viewed as a nitrosyl cation $N{O^ + }$ . It feeds two electrons to the metal and in return accepts electrons from the metal via back-bonding.
The \[M - N - O\] present in nitrosyl complexes are usually linear, or have no more than \[15^\circ \] from linear. But in some complexes, however, it is noticed, especially when back-bonding is a little less important, the \[M - N - O\] angle can strongly deviate from \[180^\circ \] .
We will see that, in \[N{O^ + }\] structure, there exists a triple bond between $N$ and ${O^ - }$ atoms and two electrons which act as a lone pair of electrons or coordinate, so the angle between \[M - N - O\] is \[180^\circ \]
While in \[N{O^ - }\] structure double bond exist between $N$ and ${O^ - }$ atoms while the \[4{\text{ }}{e^\_}\] acts as two lone pairs of electrons , so only one lone pair of electron coordinate with metal atom.
Suppose for a metal $M$ the bonding with $N{O^ + }$ goes as -
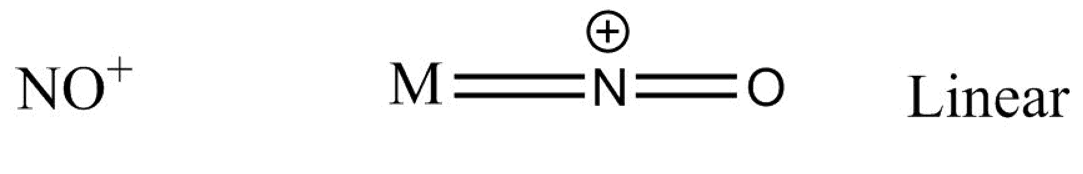
Which gives us a linear structure.
And bonding with $N{O^ - }$ goes as –
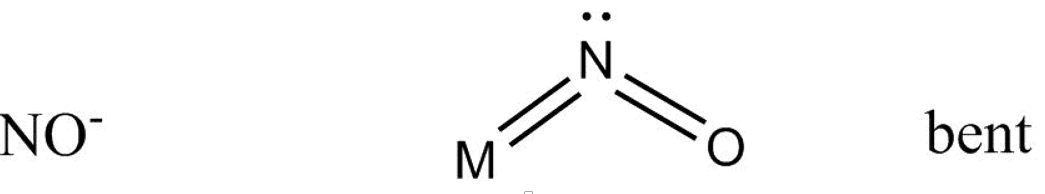
Which gives us a bent structure.
Therefore we can conclude that for the mentioned question,
Option (B). $N{O^ + }$ and $N{O^ - }$ is the correct answer.
Additional information –
The linear and bent \[NO\] ligands can be distinguished using infrared spectroscopy. Linear \[M - N - O\] groups absorb in the range \[1650-1900{\text{ }}c{m^{ - 1}}\], where as, the bent nitrosyls tend to absorb in the range of \[1525-1690{\text{ }}c{m^{ - 1}}\]. They differ in their vibrational frequencies and it reflects the differing \[N - O\] bond orders for linear (triple bond) and bent \[NO\] (double bond).
Note:
The bent $NO$ ligand is sometimes described as the anion, \[N{O^ - }\]. Examples for such compounds are the organic nitroso compounds, such as nitrosobenzene. For example a complex with a bent \[NO\] ligand is trans\[ - {\left[ {Co{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}\left( {NO} \right)Cl} \right]^ + }\]
Complete step by step answer:
Most complexes which have $NO$ ligand may be seen or viewed as a nitrosyl cation $N{O^ + }$ . It feeds two electrons to the metal and in return accepts electrons from the metal via back-bonding.
The \[M - N - O\] present in nitrosyl complexes are usually linear, or have no more than \[15^\circ \] from linear. But in some complexes, however, it is noticed, especially when back-bonding is a little less important, the \[M - N - O\] angle can strongly deviate from \[180^\circ \] .
We will see that, in \[N{O^ + }\] structure, there exists a triple bond between $N$ and ${O^ - }$ atoms and two electrons which act as a lone pair of electrons or coordinate, so the angle between \[M - N - O\] is \[180^\circ \]
While in \[N{O^ - }\] structure double bond exist between $N$ and ${O^ - }$ atoms while the \[4{\text{ }}{e^\_}\] acts as two lone pairs of electrons , so only one lone pair of electron coordinate with metal atom.
Suppose for a metal $M$ the bonding with $N{O^ + }$ goes as -

Which gives us a linear structure.
And bonding with $N{O^ - }$ goes as –

Which gives us a bent structure.
Therefore we can conclude that for the mentioned question,
Option (B). $N{O^ + }$ and $N{O^ - }$ is the correct answer.
Additional information –
The linear and bent \[NO\] ligands can be distinguished using infrared spectroscopy. Linear \[M - N - O\] groups absorb in the range \[1650-1900{\text{ }}c{m^{ - 1}}\], where as, the bent nitrosyls tend to absorb in the range of \[1525-1690{\text{ }}c{m^{ - 1}}\]. They differ in their vibrational frequencies and it reflects the differing \[N - O\] bond orders for linear (triple bond) and bent \[NO\] (double bond).
Note:
The bent $NO$ ligand is sometimes described as the anion, \[N{O^ - }\]. Examples for such compounds are the organic nitroso compounds, such as nitrosobenzene. For example a complex with a bent \[NO\] ligand is trans\[ - {\left[ {Co{{\left( {en} \right)}_2}\left( {NO} \right)Cl} \right]^ + }\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




