
No. of 5 membered ring in \[{{\left[ \text{Ca}\left( \text{EDTA} \right) \right]}^{-2}}\] is:
A.5
B.6
C.7
D.8
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: EDTA is a chelating ligand with multiple donor atoms. In total there are 6 donating sites including two nitrogen and four oxygen atoms. Both nitrogen and oxygen atoms form strong bonds with the calcium ion which make the \[{{\left[ \text{Ca}\left( \text{EDTA} \right) \right]}^{-2}}\] structure stable.
Complete step by step answer:
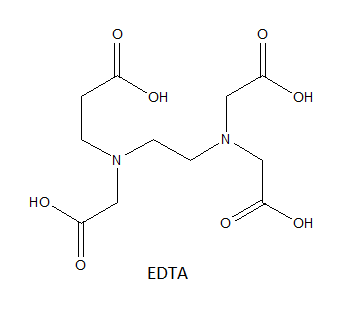
EDTA or Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is aminopolycarboxylic acid and is a colourless water-soluble solid. It is useful because of its role as a hexadentate ligand and a chelating agent in its ability to sequester metal ions such as $\text{C}{{\text{a}}^{+2}}$, \[\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{+3}}\] etc. the structure of EDTA is given below where it can be seen that there are two nitrogen atoms and each is bonded to two ethanoic acid group. The acidic oxygen atoms of these acids form strong bonds with the calcium atom and release bond formation energy making the structure stable. A total of 5 rings are formed with calcium through the different bonding sites of EDTA. The figure shows the five rings and the total structure of the complex:
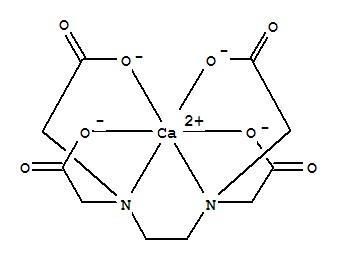
Hence option A is correct.
Note:
Denticity of a ligand is defined as the number of donor sites it has. For example: the denticity of $\text{C}{{\text{N}}^{-}}$ is one and hence called monodentate.
Chelate complex is the formation of a ring like structure from two or more donating sites of the same with multiple denticity and chelate formation releases for energy than normal complex formation due to the formation of the cyclic or ring like structure.
Complete step by step answer:
EDTA or Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is aminopolycarboxylic acid and is a colourless water-soluble solid. It is useful because of its role as a hexadentate ligand and a chelating agent in its ability to sequester metal ions such as $\text{C}{{\text{a}}^{+2}}$, \[\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{+3}}\] etc. the structure of EDTA is given below where it can be seen that there are two nitrogen atoms and each is bonded to two ethanoic acid group. The acidic oxygen atoms of these acids form strong bonds with the calcium atom and release bond formation energy making the structure stable. A total of 5 rings are formed with calcium through the different bonding sites of EDTA. The figure shows the five rings and the total structure of the complex:


Hence option A is correct.
Note:
Denticity of a ligand is defined as the number of donor sites it has. For example: the denticity of $\text{C}{{\text{N}}^{-}}$ is one and hence called monodentate.
Chelate complex is the formation of a ring like structure from two or more donating sites of the same with multiple denticity and chelate formation releases for energy than normal complex formation due to the formation of the cyclic or ring like structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




