
How many nodal planes are present in $\delta $ bonding molecular orbital?
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Nodal planes can be defined as the region around the nucleus in an atomic orbital where the chances of electrons being present is negligible. In Delta bonding of a molecular orbital, all four lobes of D orbital of an atom overlap the lobes of another atom. We can use this concept to understand the answer to this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Atomic orbitals are the ones where an electron is attached to a single nucleus whereas a molecular orbital is when an electron can be found in the presence of two or more nuclei.
A molecule is an assembly of atoms and by extension, a molecular orbital is a bond between two or more atomic orbitals. Molecular orbitals serve the purpose of holding multiple atoms together while an atomic orbital holds the electrons and the neutrons together.
There are three types of bonding between molecular orbitals – sigma$\left( \sigma \right)$, pi$\left( \pi \right)$ and delta$\left( \delta \right)$.
Sigma bond is a single covalent bond which is formed by head to head overlap of two atomic orbitals. The nuclei in both the atomic orbitals is joined along the bonding axis.
Pi bond is formed by side to side overlap of two atomic orbitals.
$\delta $ bonds are covalent bonds in which all four lobes of an atomic orbital exactly overlap the lobes of another atomic orbital.
It allows the formation of a quadruple bond.
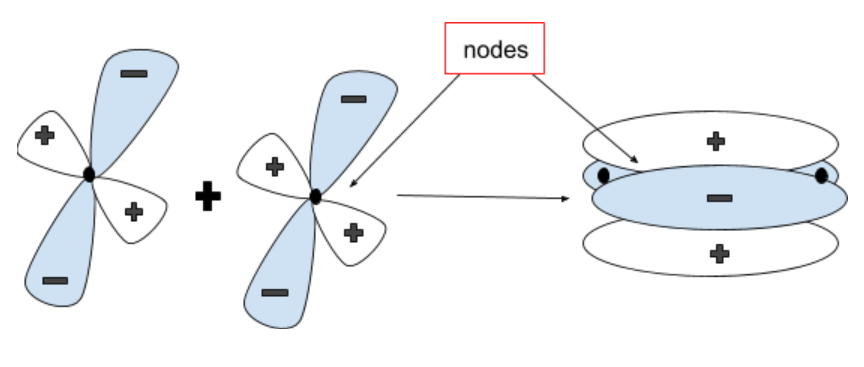
Hence, a $\delta $ bonding molecular orbital has two Nodal planes.
Note – Sigma, pi and delta bonds depict how many Nodal planes are there in the bond. A Sigma bond does not have any nodal plane since it is joined along a bonding axis. Pi bonds have one and delta bonds have two nodal planes. One can tell what bond is being formed by judging how the orbitals overlap each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Atomic orbitals are the ones where an electron is attached to a single nucleus whereas a molecular orbital is when an electron can be found in the presence of two or more nuclei.
A molecule is an assembly of atoms and by extension, a molecular orbital is a bond between two or more atomic orbitals. Molecular orbitals serve the purpose of holding multiple atoms together while an atomic orbital holds the electrons and the neutrons together.
There are three types of bonding between molecular orbitals – sigma$\left( \sigma \right)$, pi$\left( \pi \right)$ and delta$\left( \delta \right)$.
Sigma bond is a single covalent bond which is formed by head to head overlap of two atomic orbitals. The nuclei in both the atomic orbitals is joined along the bonding axis.
Pi bond is formed by side to side overlap of two atomic orbitals.
$\delta $ bonds are covalent bonds in which all four lobes of an atomic orbital exactly overlap the lobes of another atomic orbital.
It allows the formation of a quadruple bond.

Hence, a $\delta $ bonding molecular orbital has two Nodal planes.
Note – Sigma, pi and delta bonds depict how many Nodal planes are there in the bond. A Sigma bond does not have any nodal plane since it is joined along a bonding axis. Pi bonds have one and delta bonds have two nodal planes. One can tell what bond is being formed by judging how the orbitals overlap each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




