
Non-metallic oxides are:
(A) Acidic in nature
(B) Amphoteric in nature
(C) Basic in nature
(D) None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Non-metal oxides such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide are responsible for acid rain. Using this application of non-metal oxides, try and determine their nature.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Let us first analyse what non-metallic oxides really are before moving on towards the specifics of this question.
All non-metals form covalent oxides with oxygen, which react with water to form acids or with bases to form salts. Most non-metal oxides are acidic and form oxyacids, which in turn yield hydronium ions (\[{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}\]) in aqueous solution. There are two general statements that describe the behaviour of acidic oxides. First, oxides such as sulphur trioxide (\[S{{O}_{3}}\]) and dinitrogen pentoxide (\[{{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}\]), in which the non-metal exhibits one of its common oxidation numbers, are known as acid anhydrides. These oxides react with water to form oxyacids, with no change in the oxidation number of the non-metal; for example,
\[{{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}~+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O\to 2HN{{O}_{3}}\]
The non-metal oxides can be neutralized with a base to form salt and water.
\[Non-Metal\text{ }Oxide\text{ }+\text{ }Base~\to ~Salt\text{ }+\text{ }Water\]
For example,
$\begin{matrix}
S{{O}_{3(g)}}~+\text{ }Ba{{\left( OH \right)}_{2(aq)}}~\to ~BaS{{O}_{4(aq)}}~+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}} \\
{{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10(s)}}~+\text{ }12\text{ }NaO{{H}_{(aq)}}~\to ~4\text{ }N{{a}_{3}}P{{O}_{4(aq)}}~+\text{ }6\text{ }{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}} \\
\end{matrix}$
Generally, the more metallic character an element has, the more basic its oxide will be. Likewise, the more non-metallic character an element has, the more acidic its oxide will be. The non-metallic character of an element can be determined by its position on the periodic table:
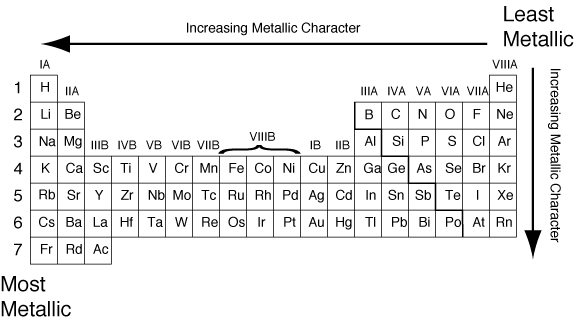

Therefore, per our analysis, the answer to this question is a) Acidic in nature
Note: Most non-metal oxides are acidic, but not all. For example, carbon monoxide (CO) is not acidic.
The addition of water to a non-metal oxide results in a compound that consists of a non-metal atom surrounded by oxo (=O) and hydroxy (-OH) groups. For example,
\[S{{O}_{3\left( l \right)}}\text{ }+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{\left( l \right)}}\text{ }\to \text{ }{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4\left( l \right)}}\]
Step-by-Step Solution:
Let us first analyse what non-metallic oxides really are before moving on towards the specifics of this question.
All non-metals form covalent oxides with oxygen, which react with water to form acids or with bases to form salts. Most non-metal oxides are acidic and form oxyacids, which in turn yield hydronium ions (\[{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}\]) in aqueous solution. There are two general statements that describe the behaviour of acidic oxides. First, oxides such as sulphur trioxide (\[S{{O}_{3}}\]) and dinitrogen pentoxide (\[{{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}\]), in which the non-metal exhibits one of its common oxidation numbers, are known as acid anhydrides. These oxides react with water to form oxyacids, with no change in the oxidation number of the non-metal; for example,
\[{{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}~+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O\to 2HN{{O}_{3}}\]
The non-metal oxides can be neutralized with a base to form salt and water.
\[Non-Metal\text{ }Oxide\text{ }+\text{ }Base~\to ~Salt\text{ }+\text{ }Water\]
For example,
$\begin{matrix}
S{{O}_{3(g)}}~+\text{ }Ba{{\left( OH \right)}_{2(aq)}}~\to ~BaS{{O}_{4(aq)}}~+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}} \\
{{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10(s)}}~+\text{ }12\text{ }NaO{{H}_{(aq)}}~\to ~4\text{ }N{{a}_{3}}P{{O}_{4(aq)}}~+\text{ }6\text{ }{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}} \\
\end{matrix}$
Generally, the more metallic character an element has, the more basic its oxide will be. Likewise, the more non-metallic character an element has, the more acidic its oxide will be. The non-metallic character of an element can be determined by its position on the periodic table:


Therefore, per our analysis, the answer to this question is a) Acidic in nature
Note: Most non-metal oxides are acidic, but not all. For example, carbon monoxide (CO) is not acidic.
The addition of water to a non-metal oxide results in a compound that consists of a non-metal atom surrounded by oxo (=O) and hydroxy (-OH) groups. For example,
\[S{{O}_{3\left( l \right)}}\text{ }+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{\left( l \right)}}\text{ }\to \text{ }{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4\left( l \right)}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




