
What is the nucleosome? Draw a diagram of the double-stranded polynucleotide chain of DNA and explain its structure.
Answer
528.1k+ views
Hint: This is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging and is the fundamental subunit of chromatin material. Their existence and structure as histone octamer was proposed by Roger Kornberg.
Complete step by step answer:
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes and its structure consists of a segment of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins similar to a thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin and every nucleosome consists of touch but two turns of DNA wrapped around a group of eight proteins called histones or the histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies of each histone proteins i.e., H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. and the chromatin is further compacted by being folded into a series forming a chromosome which is eventually a more complex structure.
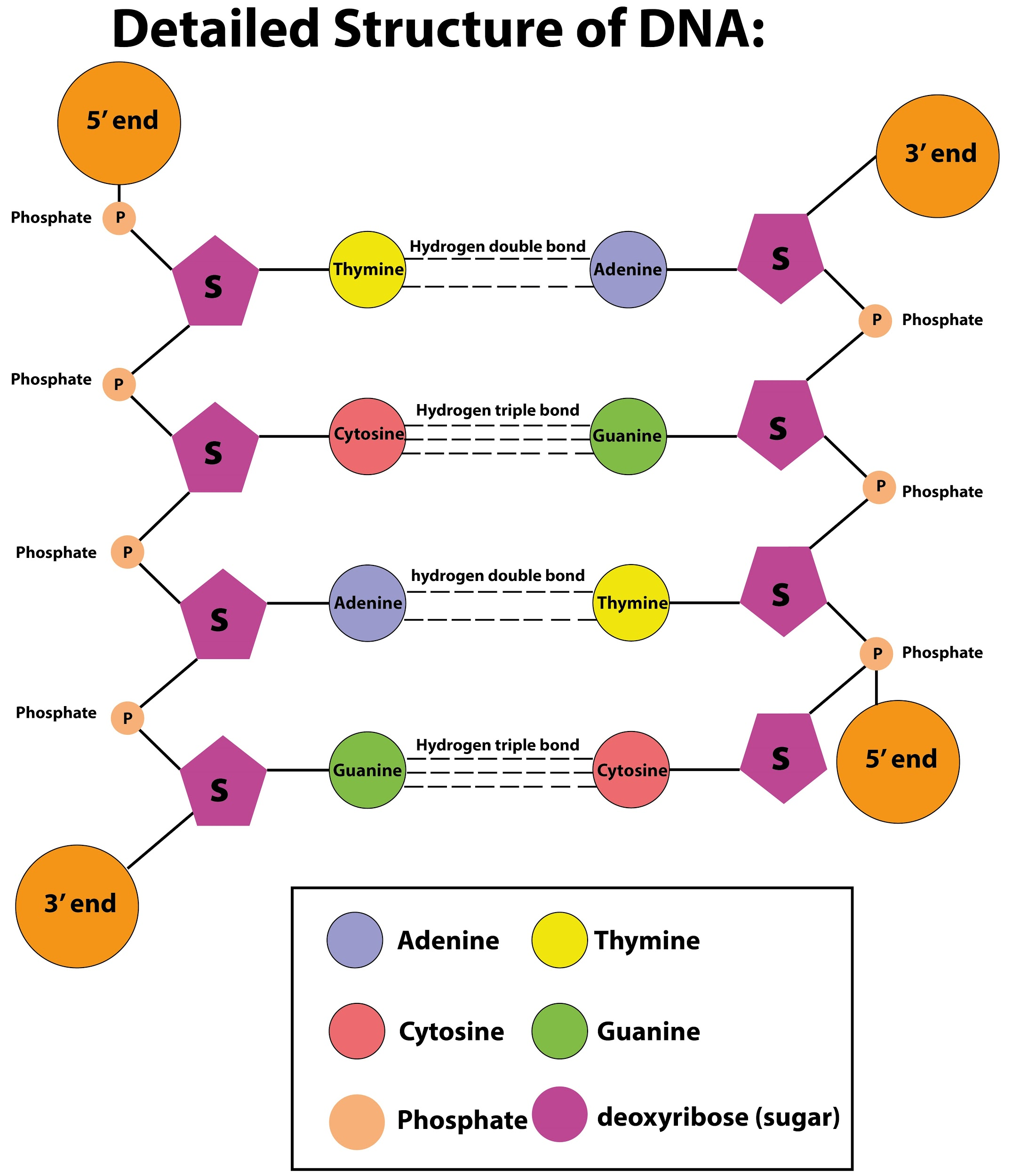
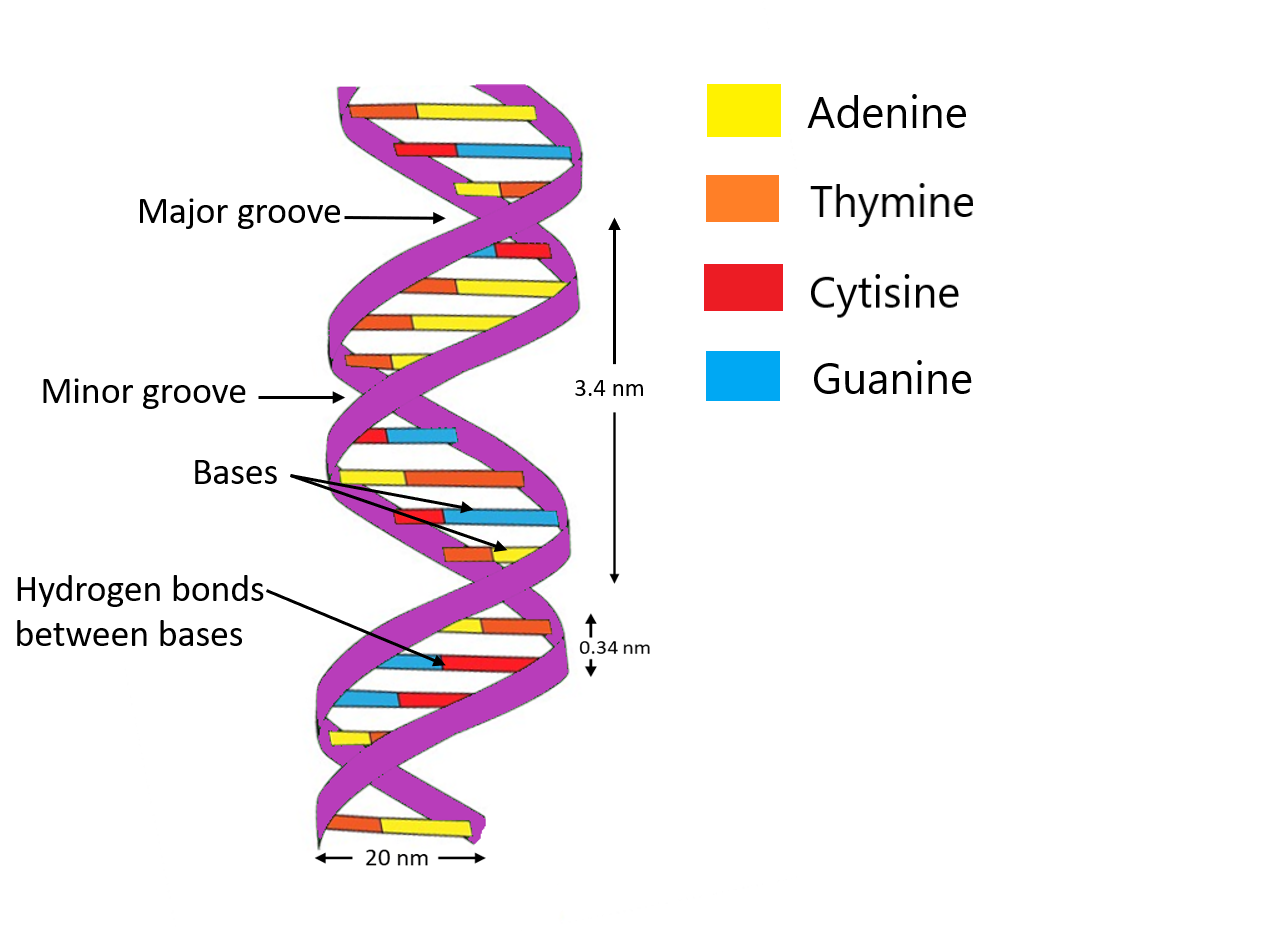
DNA is made up of nucleotide molecules. Each molecule of nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group, and a nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases of nucleotides are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The order of these bases determines the DNA's instructions or genetic code. The nucleotides are attached to form two long strands that spiral to create a structure called a double helix. If we imagine the double helix structure as a ladder, the phosphate and sugar molecules would be the sides of the ladder, while the bases would be the rungs of the ladder. The bases on one strand pair with the bases on another strand that means adenine on one strand pairs with the thymine of another strand, and similarly the guanine of one strand pairs with the cytosine of the other strand. The bond between adenine and thymine is a hydrogen double bond whereas the bond between guanine and cytosine is the hydrogen triple bond. The DNA molecules are so long that they can't fit into cells without the right packaging. To fit inside cells, DNA is coiled tightly to form structures called chromosomes.
Note:
- In the electron microscope the nucleosomes were first observed as particles by Don and Ada Olins in 1974.
- The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch in vitro, and by Han and Grunstein in vivo in 1987 and 1988, respectively.
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are found inside the nucleus of the cell and each chromosome contains a single DNA molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes and its structure consists of a segment of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins similar to a thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin and every nucleosome consists of touch but two turns of DNA wrapped around a group of eight proteins called histones or the histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies of each histone proteins i.e., H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. and the chromatin is further compacted by being folded into a series forming a chromosome which is eventually a more complex structure.
DNA is made up of nucleotide molecules. Each molecule of nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group, and a nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases of nucleotides are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The order of these bases determines the DNA's instructions or genetic code. The nucleotides are attached to form two long strands that spiral to create a structure called a double helix. If we imagine the double helix structure as a ladder, the phosphate and sugar molecules would be the sides of the ladder, while the bases would be the rungs of the ladder. The bases on one strand pair with the bases on another strand that means adenine on one strand pairs with the thymine of another strand, and similarly the guanine of one strand pairs with the cytosine of the other strand. The bond between adenine and thymine is a hydrogen double bond whereas the bond between guanine and cytosine is the hydrogen triple bond. The DNA molecules are so long that they can't fit into cells without the right packaging. To fit inside cells, DNA is coiled tightly to form structures called chromosomes.


Note:
- In the electron microscope the nucleosomes were first observed as particles by Don and Ada Olins in 1974.
- The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch in vitro, and by Han and Grunstein in vivo in 1987 and 1988, respectively.
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are found inside the nucleus of the cell and each chromosome contains a single DNA molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




