
When an object is placed between the focus and pole of a concave mirror, the image formed is:
A. Real, inverted and small
B. Real, inverted and same size
C. Real, inverted and large
D. Virtual, erect and enlarged
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Using the knowledge of rules of ray diagrams and laws of reflection, we can find out the mirror image of the object placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror by drawing a ray diagram. The mirror image will tell us the nature of the image and its size.
Complete step by step answer:
Mirrors with curved reflecting surfaces are called spherical mirrors, they are of two types- concave mirror and convex mirror. Concave mirrors are also known as converging mirrors as they converge/focus the light at one point. These mirrors have a reflecting surface recessed inwards and the outer side is polished.

Rules to obtain the image by a ray diagram:
- Ray parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focus after reflection.
- Ray passing through focus will become parallel to the principal axis after reflection.
- Ray passing through the center of curvature will follow the same path back after reflection.
- The Ray incident at the pole is reflected making the same angle with the principal axis.
These rules are formed based on the laws of reflection that are as follows:
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal (at the point of incidence) all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of reflection (r) is always equal to the angle of incidence (i).
Now considering the rules mentioned above we will draw the ray diagram of the object placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror:
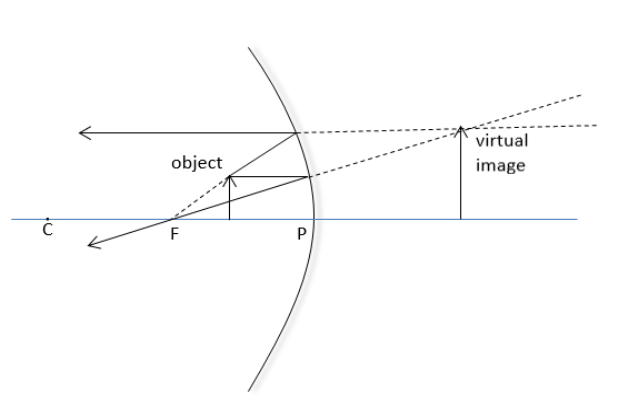
Thus, we observe that the image formed is virtual, erect and enlarged.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
A Convex mirror is another type of spherical mirror, in these mirrors reflecting surface bulges out towards the light source. They are also called diverging mirrors as they diverge the light away.
Note:
A Concave mirror forms a real and inverted image at all the points except the ones between pole and focus so don’t get confused and be careful while drawing diagrams. The size of the image formed by the concave mirror goes on increasing as we move the object closer to the mirror. That’s why they are used as shaving mirrors and also in telescopes.
Complete step by step answer:
Mirrors with curved reflecting surfaces are called spherical mirrors, they are of two types- concave mirror and convex mirror. Concave mirrors are also known as converging mirrors as they converge/focus the light at one point. These mirrors have a reflecting surface recessed inwards and the outer side is polished.

Rules to obtain the image by a ray diagram:
- Ray parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focus after reflection.
- Ray passing through focus will become parallel to the principal axis after reflection.
- Ray passing through the center of curvature will follow the same path back after reflection.
- The Ray incident at the pole is reflected making the same angle with the principal axis.
These rules are formed based on the laws of reflection that are as follows:
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal (at the point of incidence) all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of reflection (r) is always equal to the angle of incidence (i).
Now considering the rules mentioned above we will draw the ray diagram of the object placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror:

Thus, we observe that the image formed is virtual, erect and enlarged.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
A Convex mirror is another type of spherical mirror, in these mirrors reflecting surface bulges out towards the light source. They are also called diverging mirrors as they diverge the light away.
Note:
A Concave mirror forms a real and inverted image at all the points except the ones between pole and focus so don’t get confused and be careful while drawing diagrams. The size of the image formed by the concave mirror goes on increasing as we move the object closer to the mirror. That’s why they are used as shaving mirrors and also in telescopes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




