
When the object is placed beyond $2F$ in front of a convex lens, the image is formed--
$1$. between F and $2F$
$2$. at the focus
$3$. at the centre of curvature $2F$
$4$. at infinity
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: When an object is set beyond the centre of curvature, then a parallel light ray to the principal axis, moves through the focus F. Simultaneously, the other ray passes through the optical centre C and goes undeviating. In this way, a diminished, real and inverted image is formed on the other side of the lens between the focus F and centre of curvature $2F$.
Complete step by step answer:
If we take the object near the lens in the convex lens, the image size keeps on increasing. As we make the object closer to the lens, we get the image enlarged. So, we can tell that the images created can be of different types. We can have diminished inverted images, small sizes inverted images, enlarged inverted images, enlarged erect images. So, in a convex lens, there is a possibility of getting an actual and inverted image.
Image creation in a convex lens can be described with the help of three principal rays.
$1$. The parallel rays to the principal axis move through the focal point after refraction by the lens.
$2$. The ray moving through the optical centre passes directly through the lens and continues without deviation.
$3$. The ray travels through the focal point and becomes parallel to the principal axis.
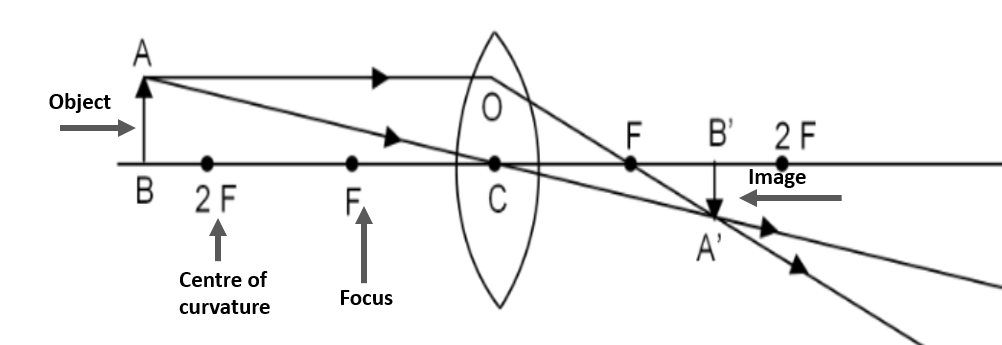
When an object is positioned beyond the centre of curvature $2F$, then a light ray AO which is parallel to the principal axis, moves through the focus F along the direction OF resulting refraction. Another ray of light AC crosses through the optical centre C and goes direct without any deviation. The two refracted rays meet each other at location A’, between the focus F and centre of curvature $2F$ on the different side of the lens. In this approach, a diminished, inverted, and real image A’B’ is formed.
So, the correct answer is “Option 1”.
Note: When an object is situated in between focus and pole, a virtual image is made. The size of the image is more significant than that of an object. When an object is set at the focus, an actual image is made at infinity. The image size is much greater than the object's size. When an object is situated at infinity, the actual image is made at the focus. The image size is much more petite than the object size.
Complete step by step answer:
If we take the object near the lens in the convex lens, the image size keeps on increasing. As we make the object closer to the lens, we get the image enlarged. So, we can tell that the images created can be of different types. We can have diminished inverted images, small sizes inverted images, enlarged inverted images, enlarged erect images. So, in a convex lens, there is a possibility of getting an actual and inverted image.
Image creation in a convex lens can be described with the help of three principal rays.
$1$. The parallel rays to the principal axis move through the focal point after refraction by the lens.
$2$. The ray moving through the optical centre passes directly through the lens and continues without deviation.
$3$. The ray travels through the focal point and becomes parallel to the principal axis.

When an object is positioned beyond the centre of curvature $2F$, then a light ray AO which is parallel to the principal axis, moves through the focus F along the direction OF resulting refraction. Another ray of light AC crosses through the optical centre C and goes direct without any deviation. The two refracted rays meet each other at location A’, between the focus F and centre of curvature $2F$ on the different side of the lens. In this approach, a diminished, inverted, and real image A’B’ is formed.
So, the correct answer is “Option 1”.
Note: When an object is situated in between focus and pole, a virtual image is made. The size of the image is more significant than that of an object. When an object is set at the focus, an actual image is made at infinity. The image size is much greater than the object's size. When an object is situated at infinity, the actual image is made at the focus. The image size is much more petite than the object size.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




