
How will you obtain:
A. Benzene from phenol
B. Ethylamine from methyl alcohol
C. Ethylene from ethyl alcohol
Answer
544.8k+ views
Hint: We will use a reducing agent for reduction of alcohol group from phenol. For addition, extra carbon potassium cyanide is used. Alumina converts alcohol to alkene.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A. Conversion of phenol to benzene:
We will reduce phenol using some reducing agent such as zinc dust to convert alcoholic groups present in the phenol. Phenol is heated with zinc; the products formed are benzene and zinc oxide. The reaction occurs as:
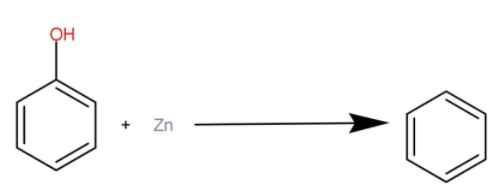
B. Conversion of methyl alcohol to ethylamine:
To add a carbon atom we always take the help of cyanide. We substitute the cyanide group from the existing group. To convert methyl alcohol into ethyl alcohol we will first substitute the hydroxide group from the cyanide group using phosphorus iodine and potassium cyanide to add an extra carbon atom. This cyanide can be reduced to amine using sodium in ethanol as a reducing agent. First of all methyl cyanide is formed and then ethanamine will form, the reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow[{2.{\text{ KCN}}}]{{1.{\text{ P}}/{{\text{I}}_2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CN}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Na}}/{\text{ethanol}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]
C. Conversion of ethyl alcohol to ethylene:
Heating alcohol in the presence of alumina will give us alkene. Ethyl alcohol is treated with alumina that is aluminium oxide and ethene or ethylene is formed. The reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}} + {\text{A}}{{\text{l}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]
Note: Phosphorus reacts vigorously with halogens like chlorine, bromine and iodine. Red phosphorus reacts with halogens to form tri halo compounds with phosphorus. The reaction in the presence of potassium cyanide forms nitrile where as if we react to compounds with silver cyanide then the formation of isocyanide occurs. As both carbon and nitrogen gas are lone pairs of electrons so the attack is feasible from both sides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A. Conversion of phenol to benzene:
We will reduce phenol using some reducing agent such as zinc dust to convert alcoholic groups present in the phenol. Phenol is heated with zinc; the products formed are benzene and zinc oxide. The reaction occurs as:

B. Conversion of methyl alcohol to ethylamine:
To add a carbon atom we always take the help of cyanide. We substitute the cyanide group from the existing group. To convert methyl alcohol into ethyl alcohol we will first substitute the hydroxide group from the cyanide group using phosphorus iodine and potassium cyanide to add an extra carbon atom. This cyanide can be reduced to amine using sodium in ethanol as a reducing agent. First of all methyl cyanide is formed and then ethanamine will form, the reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow[{2.{\text{ KCN}}}]{{1.{\text{ P}}/{{\text{I}}_2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CN}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Na}}/{\text{ethanol}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]
C. Conversion of ethyl alcohol to ethylene:
Heating alcohol in the presence of alumina will give us alkene. Ethyl alcohol is treated with alumina that is aluminium oxide and ethene or ethylene is formed. The reaction occurs as:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}} + {\text{A}}{{\text{l}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]
Note: Phosphorus reacts vigorously with halogens like chlorine, bromine and iodine. Red phosphorus reacts with halogens to form tri halo compounds with phosphorus. The reaction in the presence of potassium cyanide forms nitrile where as if we react to compounds with silver cyanide then the formation of isocyanide occurs. As both carbon and nitrogen gas are lone pairs of electrons so the attack is feasible from both sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




