
On what factors does the internal resistance of a cell depend?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Using the simple circuit diagram consisting of a cell, the current flow and a load, the expression for the internal resistance of the cell can be obtained and hence the dependable factors can be determined.
Formula used: \[E=I(R+r)\]
Complete step by step answer:
A circuit diagram representing the internal resistance of a cell is as follows.
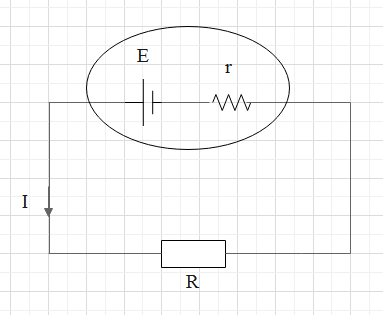
The internal resistance of a cell depends on the following factors.
1. The internal resistance of a cell is directly proportional to the distance between the electrodes. This implies that, as the distance between the electrodes increases, the internal resistance also increases and vice versa.
2. The internal resistance of a cell is inversely proportional to the effective area of the electrodes. This implies that, as the effective area of the electrodes increases, the internal resistance decreases and vice versa.
3. The internal resistance of a cell increases with the concentration of the solution. Because, with the increase in the concentration of the solution, the number of ions per unit volume increases and, in turn, their bombardment also increases.
4. The increase in temperature of the solution increases the kinetic energy of the ions present, thus, the internal resistance of a cell also increases.
The electromotive force of a cell is always greater than the potential difference across the same cell.
Thus, the internal resistance of a cell depends on the factors like distance between the electrodes, the temperature, the effective area of the electrodes and the concentration of the solution.
Additional Information: The formula for calculating the internal resistance of a cell can be derived from the electromotive force equation, given by,
\[\begin{align}
& E=I(R+r) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{E}{I}=R+r \\
\end{align}\]
Rearranging the terms in the above equation to obtain the expression in terms of the internal resistance is,
\[r=\dfrac{E}{I}-R\]
Where E is the electromotive force of the circuit, I is the current through the circuit, R is the resistance of the load in the circuit and r is the internal resistance of the cell.
Note: The things to be on your finger-tips for further information on solving these types of problems are: The internal resistance of the cell is different from the resistance of the load present in a circuit. The internal resistance of the cell is due to the electromotive force of that cell, whereas, the resistance of the load is its ability to resist the flow of current through it.
Formula used: \[E=I(R+r)\]
Complete step by step answer:
A circuit diagram representing the internal resistance of a cell is as follows.

The internal resistance of a cell depends on the following factors.
1. The internal resistance of a cell is directly proportional to the distance between the electrodes. This implies that, as the distance between the electrodes increases, the internal resistance also increases and vice versa.
2. The internal resistance of a cell is inversely proportional to the effective area of the electrodes. This implies that, as the effective area of the electrodes increases, the internal resistance decreases and vice versa.
3. The internal resistance of a cell increases with the concentration of the solution. Because, with the increase in the concentration of the solution, the number of ions per unit volume increases and, in turn, their bombardment also increases.
4. The increase in temperature of the solution increases the kinetic energy of the ions present, thus, the internal resistance of a cell also increases.
The electromotive force of a cell is always greater than the potential difference across the same cell.
Thus, the internal resistance of a cell depends on the factors like distance between the electrodes, the temperature, the effective area of the electrodes and the concentration of the solution.
Additional Information: The formula for calculating the internal resistance of a cell can be derived from the electromotive force equation, given by,
\[\begin{align}
& E=I(R+r) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{E}{I}=R+r \\
\end{align}\]
Rearranging the terms in the above equation to obtain the expression in terms of the internal resistance is,
\[r=\dfrac{E}{I}-R\]
Where E is the electromotive force of the circuit, I is the current through the circuit, R is the resistance of the load in the circuit and r is the internal resistance of the cell.
Note: The things to be on your finger-tips for further information on solving these types of problems are: The internal resistance of the cell is different from the resistance of the load present in a circuit. The internal resistance of the cell is due to the electromotive force of that cell, whereas, the resistance of the load is its ability to resist the flow of current through it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




