
Opening in the skull is
A. Foramen of Monro
B. Foramen of magnum
C. Coronal nature
D. Lambdoidal suture
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: The skull is one of the main parts of the axial skeleton system. The skull is the protective flat bone that surrounds the brain and other vital organs. The base of the skull has an opening in the occipital section. It is required as a passage for the brainstem and the spinal cord.
Complete answer:
The skull is a hard flat bone that surrounds the brain and other related vital organs. It provides protection against external pressures or injuries. The base of the skull in the occipital region has a remarkable opening required for the passage of the brainstem and spinal cord. The occipital section refers to the lowermost posterior side of the brain. Here, the brain stem ends in the medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata connects to the cervical region of the spinal cord. This is possible only due to the presence of the cranial cavity called the foramen of the magnum. It is also called the foramen magnum. It not only provides a passage for the connection of the spinal cord but also various vertebral arteries pass through it. Anterior and posterior spinal arteries, tectorial membranes, and alar ligaments of the brain also pass through the foramen magnum. Another important function of the foramen magnum is the passage of the accessory nerve into the skull. Maintenance of posture and locomotion is also regulated by the positional aspects of the foramen magnum.
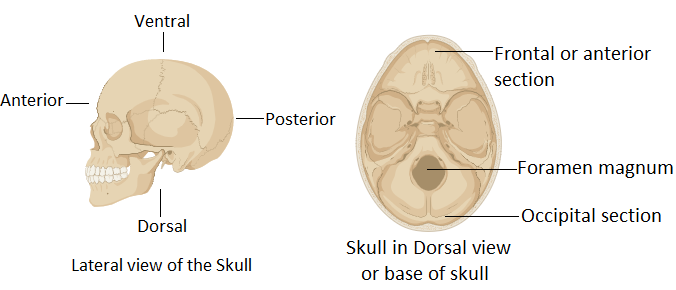
The foramen of Monroe is a part of the ventricular system. It is a connection between the third ventricle and the lateral ventricle of the brain. Coronal nature is one of the coronal sections of the brain. The lambdoidal suture is the connection between parietal bones and occipital bone.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The foramen magnum is a common feature of all of those animals that uses their two rear limbs for terrestrial locomotion. However, it has been studied that in humans the foramen magnum lies farther underneath the head as compared to the great apes. Thus, in humans to hold the head upright, the neck muscles do not need to be robust.
Complete answer:
The skull is a hard flat bone that surrounds the brain and other related vital organs. It provides protection against external pressures or injuries. The base of the skull in the occipital region has a remarkable opening required for the passage of the brainstem and spinal cord. The occipital section refers to the lowermost posterior side of the brain. Here, the brain stem ends in the medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata connects to the cervical region of the spinal cord. This is possible only due to the presence of the cranial cavity called the foramen of the magnum. It is also called the foramen magnum. It not only provides a passage for the connection of the spinal cord but also various vertebral arteries pass through it. Anterior and posterior spinal arteries, tectorial membranes, and alar ligaments of the brain also pass through the foramen magnum. Another important function of the foramen magnum is the passage of the accessory nerve into the skull. Maintenance of posture and locomotion is also regulated by the positional aspects of the foramen magnum.

The foramen of Monroe is a part of the ventricular system. It is a connection between the third ventricle and the lateral ventricle of the brain. Coronal nature is one of the coronal sections of the brain. The lambdoidal suture is the connection between parietal bones and occipital bone.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The foramen magnum is a common feature of all of those animals that uses their two rear limbs for terrestrial locomotion. However, it has been studied that in humans the foramen magnum lies farther underneath the head as compared to the great apes. Thus, in humans to hold the head upright, the neck muscles do not need to be robust.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




