
Organs that perform the same function but are not similar in structural details and origin are called
(a)Analogous organs
(b)Homologous organs
(c)Vestigial organs
(d)None of these
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Evolution is a change in the morphological and physiological characters of species as the characters pass on from one generation to another. Some anatomically different organs get modified for the same functions and vice versa.
Complete answer:
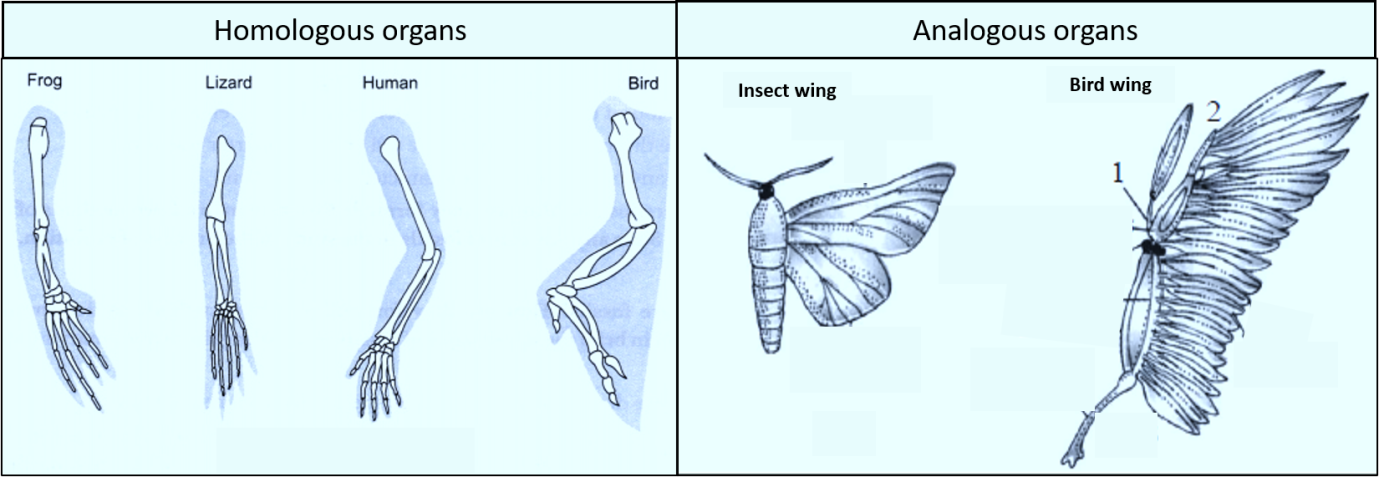
The organs of animals are mainly classified into two categories and they are homologous organs and analogous organs. Analogous organs are the inverse of homologous organs and are organs that perform the same functions but have different ancestors and structures. For example, the wings of butterflies and birds have a different structure and embryonic origin but perform the same function of flying. The bird's wings are covered by flesh, skin, and feathers whereas butterflies' wings are an extension of the integument. It is convergent evolution as despite having different ancestors they are performing the same functions. The evolution term was coined by Charles Darwin. Molecular biology and comparative embryology are other shreds of evidence of evolution. The wings of a bird and bat are both homologous and analogous as they have the same function and somewhat similar appearance.
So, the correct option is 'Analogous organs'.
Note: Homologous organs are those organs that are inherited from the same ancestors and have the same structure, but due to evolution they now perform different functions. For example, Limbs of Human, Bat, and Mouse are strikingly similar but, humans write from hand-limbs, mice run, and bat flies. This similarity arises because they all share a common ancestor but differ in function due to evolution and to survive in their habitat. This is commonly known as divergent evolution.
Complete answer:
The organs of animals are mainly classified into two categories and they are homologous organs and analogous organs. Analogous organs are the inverse of homologous organs and are organs that perform the same functions but have different ancestors and structures. For example, the wings of butterflies and birds have a different structure and embryonic origin but perform the same function of flying. The bird's wings are covered by flesh, skin, and feathers whereas butterflies' wings are an extension of the integument. It is convergent evolution as despite having different ancestors they are performing the same functions. The evolution term was coined by Charles Darwin. Molecular biology and comparative embryology are other shreds of evidence of evolution. The wings of a bird and bat are both homologous and analogous as they have the same function and somewhat similar appearance.
So, the correct option is 'Analogous organs'.
Note: Homologous organs are those organs that are inherited from the same ancestors and have the same structure, but due to evolution they now perform different functions. For example, Limbs of Human, Bat, and Mouse are strikingly similar but, humans write from hand-limbs, mice run, and bat flies. This similarity arises because they all share a common ancestor but differ in function due to evolution and to survive in their habitat. This is commonly known as divergent evolution.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




