
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods:
(i) Zone refining
(ii) Electrolytic refining
(iii) Vapor phase refining
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Zone refining: It is used for refining \[Si,\,B,\,Ga,\,In,\] etc. impurities are more soluble in molten states of metal than in solid states.
>Electrorefining: It is carried out for refining of impure zinc. The anode is impure zinc and cathode is pure zinc.
>Vapor phase refining: Metal is converted into volatile compound and then decomposed to obtain pure metal.
Complete answer:
(i) Zone refining: Semiconductors like \[Si,Ge,Ga,\] etc. are purified by this method. Impurities are highly soluble in molten metal than in solid metal. This method is based on fractional crystallization. A circular heater surrounds a rod of impure metal. The heater is moved then the pure metal crystallizes out and impurities pass into the adjacent molten metal. The metal is repeated to shift the impurities to one end which is cut off.
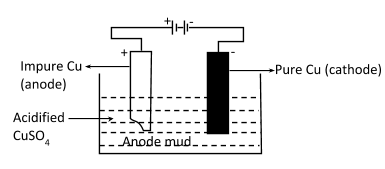
(ii) Electrolytic refining: In this method, impure copper metal is taken as anode and pure copper metal at cathode. Electrolyte is aqueous solution of some suitable salt of copper. On passing current, impure metal from anode gives metal ions into the solution and from the solution the metal ions produce metal at cathode. Sometimes the waste under the anode (anode mud) may contain precious metals, as in case of copper, the anode mud may contain gold, silver, zinc, etc.
\[
At{\text{ }}anode\,\mathop {Cu}\limits_{impure} \to \mathop {Cu}\limits^{ + 2} + \mathop {2e}\limits^ - \\
At{\text{ cathode}}\,\mathop {Cu}\limits^{ + 2} + \mathop {2e}\limits^ - \to \mathop {Cu}\limits_{pure} \\
\]
(iii) Vapor phase refining: It is the process of refining metal by converting it into its volatile compound and then decomposing it to obtain a pure metal. The metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent. The volatile compound should be easily decomposed so that the metal can be easily recovered like Nickel, zirconium and titanium.
Note:: Refining of a metal depends upon the nature of the metal and nature of impurities. The other methods used in refining of metals are liquation, distillation, oxidative refining, poling etc.
>Electrorefining: It is carried out for refining of impure zinc. The anode is impure zinc and cathode is pure zinc.
>Vapor phase refining: Metal is converted into volatile compound and then decomposed to obtain pure metal.
Complete answer:
(i) Zone refining: Semiconductors like \[Si,Ge,Ga,\] etc. are purified by this method. Impurities are highly soluble in molten metal than in solid metal. This method is based on fractional crystallization. A circular heater surrounds a rod of impure metal. The heater is moved then the pure metal crystallizes out and impurities pass into the adjacent molten metal. The metal is repeated to shift the impurities to one end which is cut off.
(ii) Electrolytic refining: In this method, impure copper metal is taken as anode and pure copper metal at cathode. Electrolyte is aqueous solution of some suitable salt of copper. On passing current, impure metal from anode gives metal ions into the solution and from the solution the metal ions produce metal at cathode. Sometimes the waste under the anode (anode mud) may contain precious metals, as in case of copper, the anode mud may contain gold, silver, zinc, etc.
\[
At{\text{ }}anode\,\mathop {Cu}\limits_{impure} \to \mathop {Cu}\limits^{ + 2} + \mathop {2e}\limits^ - \\
At{\text{ cathode}}\,\mathop {Cu}\limits^{ + 2} + \mathop {2e}\limits^ - \to \mathop {Cu}\limits_{pure} \\
\]

(iii) Vapor phase refining: It is the process of refining metal by converting it into its volatile compound and then decomposing it to obtain a pure metal. The metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent. The volatile compound should be easily decomposed so that the metal can be easily recovered like Nickel, zirconium and titanium.
Note:: Refining of a metal depends upon the nature of the metal and nature of impurities. The other methods used in refining of metals are liquation, distillation, oxidative refining, poling etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




