
Oxidation of succinate ion produces ethylene and carbon dioxide gases, On passing \[0.2\] Faraday electricity through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate, the total volume of gases (at both cathode and anode) at STP ($1$ atm and $273K$ ) is $5L$ .
A . True
B . False
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint : This numerical can be solved with the help of Faraday’s law of electrolysis.According to the first law of electrolysis the mass of any substance deposited or liberated at an electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity or charge passed through that solution. And the second law states that the mass of substance deposited or liberated at the electrodes is directly proportional to their equivalent weight when the same amount of current is passed through different electrolytes connected in series.
Complete step by step solution:
Oxidation reaction of succinate ions is given below, it produces ethylene and carbon dioxide gases.
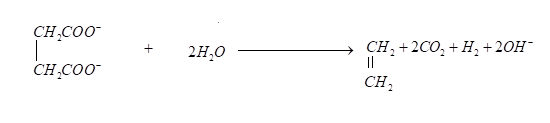 Now we can see that it is given in the problem that \[0.2\] Faraday electricity through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate then according to Faraday’s law mass equivalent for each gas will be \[0.2\]
Now we can see that it is given in the problem that \[0.2\] Faraday electricity through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate then according to Faraday’s law mass equivalent for each gas will be \[0.2\]
Equivalents of the product of the above reaction $({C_2}{H_4} + C{O_2} + {H_2}) = 0.2 + 0.2 + 0.2 = 0.6$ .
Actual number of moles of gases (n) $ = 0.2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + 0.2 \times 1 + 0.2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 0.4$ .
We know that at standard temperature and pressure $1$ mol of gas is equivalent to $22.4L$. Therefore $0.4$ mole of gas will be equal to $ \Rightarrow 0.4 \times 22.4 = 8.964L$
Hence total volume of gases produced is $8.964L$ but in the question it is given that the total volume of gases produced at STP is $5L$
So option B is correct, that is it is false.
Note : We have approached this problem with the help of Faraday’s law of electrolysis . It is given in the problem that \[0.2\] Faraday electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate hence with the help of the second law we get the equivalent weight of each gas. After that we have calculated the actual number of moles and which leads to the volume of the gas at STP.
Complete step by step solution:
Oxidation reaction of succinate ions is given below, it produces ethylene and carbon dioxide gases.
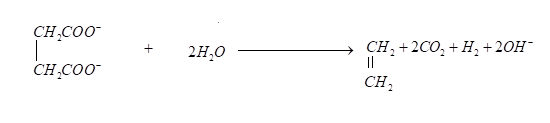 Now we can see that it is given in the problem that \[0.2\] Faraday electricity through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate then according to Faraday’s law mass equivalent for each gas will be \[0.2\]
Now we can see that it is given in the problem that \[0.2\] Faraday electricity through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate then according to Faraday’s law mass equivalent for each gas will be \[0.2\] Equivalents of the product of the above reaction $({C_2}{H_4} + C{O_2} + {H_2}) = 0.2 + 0.2 + 0.2 = 0.6$ .
Actual number of moles of gases (n) $ = 0.2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + 0.2 \times 1 + 0.2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 0.4$ .
We know that at standard temperature and pressure $1$ mol of gas is equivalent to $22.4L$. Therefore $0.4$ mole of gas will be equal to $ \Rightarrow 0.4 \times 22.4 = 8.964L$
Hence total volume of gases produced is $8.964L$ but in the question it is given that the total volume of gases produced at STP is $5L$
So option B is correct, that is it is false.
Note : We have approached this problem with the help of Faraday’s law of electrolysis . It is given in the problem that \[0.2\] Faraday electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of potassium succinate hence with the help of the second law we get the equivalent weight of each gas. After that we have calculated the actual number of moles and which leads to the volume of the gas at STP.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




