
P-dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:The melting point of p-, o- and m-isomers of dichlorobenzene is decided on the basis of lattice energy. The compounds having a close packed structure are most stable. High lattice energy leads to a higher melting point. Lattice energy is directly proportional to the melting point.
Complete step-by-step solution
The temperature at which the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium is known as the melting point. As the phase is changing and the solid phase has a higher force of attraction than the liquid phase, heat is required to break the force of attraction.
The structure of p-, o-, and m-isomers of dichlorobenzene are as follows:
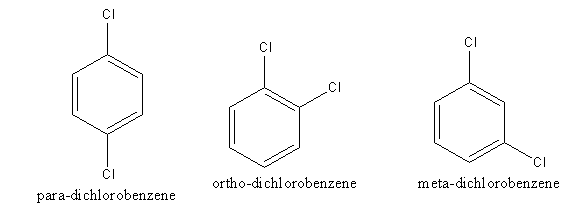
The structure of p-dichlorobenzene is symmetrical rather than Ortho and Meta isomer. So, p- dichlorobenzene forms a closed packed crystal. Due to close packing, the intermolecular forces are very strong. The force which binds molecules is known as intermolecular force. Strong intermolecular force leads to a stable crystal. The stability of the p- dichlorobenzene leads to high lattice energy.
So, the braking of p- dichlorobenzene crystal requires high energy. High energy requirements lead to a high melting point. Whereas o- and m-isomers are unsymmetrical structures. Their crystal is not as stable as p-dichlorobenzene. Thus less energy is required for the breaking of o- and m-isomers.
Note:The force that binds atoms in molecules is known as intramolecular force. Molecules are bound through intermolecular force. The energy released by the formation of the lattice is known as lattice energy. More lattice energy means high stability. On increasing strength of intermolecular force the lattice energy and melting point both increase.
Complete step-by-step solution
The temperature at which the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium is known as the melting point. As the phase is changing and the solid phase has a higher force of attraction than the liquid phase, heat is required to break the force of attraction.
The structure of p-, o-, and m-isomers of dichlorobenzene are as follows:

The structure of p-dichlorobenzene is symmetrical rather than Ortho and Meta isomer. So, p- dichlorobenzene forms a closed packed crystal. Due to close packing, the intermolecular forces are very strong. The force which binds molecules is known as intermolecular force. Strong intermolecular force leads to a stable crystal. The stability of the p- dichlorobenzene leads to high lattice energy.
So, the braking of p- dichlorobenzene crystal requires high energy. High energy requirements lead to a high melting point. Whereas o- and m-isomers are unsymmetrical structures. Their crystal is not as stable as p-dichlorobenzene. Thus less energy is required for the breaking of o- and m-isomers.
Note:The force that binds atoms in molecules is known as intramolecular force. Molecules are bound through intermolecular force. The energy released by the formation of the lattice is known as lattice energy. More lattice energy means high stability. On increasing strength of intermolecular force the lattice energy and melting point both increase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




