
Who performed the gold foil experiment?
A. Thomson
B. Goldstein
C. Chadwick
D. Rutherford
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: He is a British physicist from New Zealand who studied the atomic structure and gave the atomic model under his name which was proposed in 1911. The model is also known by planetary models of the atom or nuclear atom.
Complete step by step answer:
After the failure of the plum pudding model by J.J Thomson, another scientist named Ernest Rutherford guided an experiment by bombarding the $\alpha $-particles to the thin sheet of gold foil from a radioactive source in order to study the deflection created by the $\alpha $-particles.
He fixed a fluorescent screen surrounding the gold foil.
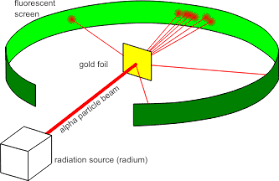
The following observations were made after the experiment.
(i) A large amount of $\alpha $-particles passed through the gold foil without getting deflected. This shows that a major amount of space present in the atom is vacant.
(ii) Some of the $\alpha $-particles get deflected by small angles. This shows that the positive charged particles present in the atom are localized in small space.
(iii) Very few $\alpha $-particles get deflected back by $180^\circ $angle. This shows that the positive charged particles are present in small amounts in comparison with the total atomic volume.
Depending upon the observations, Rutherford discovered the atomic structure and gave Rutherford an atomic model.
According to the model:
(i) The region where the positively charged particles are concentrated in the atom is called the nucleus.
(ii) The model shows that the negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus in a circular manner. This circular path is called an orbit.
(iii) The negatively charged electrons and positively charged particles concentrated in a small space in the atom are bonded together by electrostatic force of attraction.
Thus, Rutherford performed the gold foil experiment.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
Rutherford atomic model does not clarify the atom’s stability. Calculations prove that according to Rutherford atomic model, the electrons present in the nucleus of the atom collapse within it in less than ${10^{ - 8}}$ seconds.
Complete step by step answer:
After the failure of the plum pudding model by J.J Thomson, another scientist named Ernest Rutherford guided an experiment by bombarding the $\alpha $-particles to the thin sheet of gold foil from a radioactive source in order to study the deflection created by the $\alpha $-particles.
He fixed a fluorescent screen surrounding the gold foil.

The following observations were made after the experiment.
(i) A large amount of $\alpha $-particles passed through the gold foil without getting deflected. This shows that a major amount of space present in the atom is vacant.
(ii) Some of the $\alpha $-particles get deflected by small angles. This shows that the positive charged particles present in the atom are localized in small space.
(iii) Very few $\alpha $-particles get deflected back by $180^\circ $angle. This shows that the positive charged particles are present in small amounts in comparison with the total atomic volume.
Depending upon the observations, Rutherford discovered the atomic structure and gave Rutherford an atomic model.
According to the model:
(i) The region where the positively charged particles are concentrated in the atom is called the nucleus.
(ii) The model shows that the negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus in a circular manner. This circular path is called an orbit.
(iii) The negatively charged electrons and positively charged particles concentrated in a small space in the atom are bonded together by electrostatic force of attraction.
Thus, Rutherford performed the gold foil experiment.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
Rutherford atomic model does not clarify the atom’s stability. Calculations prove that according to Rutherford atomic model, the electrons present in the nucleus of the atom collapse within it in less than ${10^{ - 8}}$ seconds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




