
Phenol can be converted into anisole by:
(A) $C{{H}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}$ / ether
(B) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ / $NaOH$
(C) $C{{H}_{3}}I$
(D) All of these
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: An attempt to this question can be made by determining the action of the reagents mentioned in the options. Draw the expanded structure of the starting compound and the final product i.e. phenol and anisole. Now determine the reagent that can possibly give the desired product. Based on this you can answer the question.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw the expanded structure of the starting compound and the final product i.e. phenol and anisole as suggested in the hint.
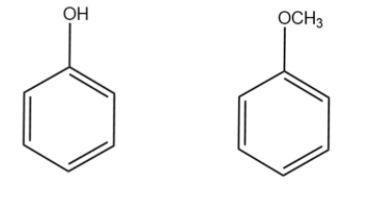
$\,\,\,Phenol\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Anisole$
We will determine the reaction of phenol with the reagents mentioned in the options.
(A) $C{{H}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}$ / ether
Diazomethane in the presence of ether converts alcohols into ethers. This is because the \[-C{{H}_{2}}\] group attaches to the alcohol group releasing molecular nitrogen. Thus, phenol when reacted with $C{{H}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}$ / ether produces the ether anisole.
(B) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ / $NaOH$
Dimethyl sulfate is a reagent whose behavior is similar to sulfuric acid. The only difference is instead of hydrogen ions the compound releases $C{{H}_{3}}^{+}$ ions in the solution. These ions, when reacted with phenol, form an ether. The ether is called anisole.
(C) $C{{H}_{3}}I$
Methyl iodide, like dimethyl sulfate, releases $C{{H}_{3}}^{+}$ ions in the solution. Thus $C{{H}_{3}}I$ also converts phenol into anisole.
From the above statements we can conclude that all the three reagents convert phenol into anisole.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D) i.e. all of these.
Note: It is important to know that along with dimethyl sulfate we use sodium hydroxide to enhance the rate of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw the expanded structure of the starting compound and the final product i.e. phenol and anisole as suggested in the hint.

$\,\,\,Phenol\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Anisole$
We will determine the reaction of phenol with the reagents mentioned in the options.
(A) $C{{H}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}$ / ether
Diazomethane in the presence of ether converts alcohols into ethers. This is because the \[-C{{H}_{2}}\] group attaches to the alcohol group releasing molecular nitrogen. Thus, phenol when reacted with $C{{H}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}$ / ether produces the ether anisole.
(B) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ / $NaOH$
Dimethyl sulfate is a reagent whose behavior is similar to sulfuric acid. The only difference is instead of hydrogen ions the compound releases $C{{H}_{3}}^{+}$ ions in the solution. These ions, when reacted with phenol, form an ether. The ether is called anisole.
(C) $C{{H}_{3}}I$
Methyl iodide, like dimethyl sulfate, releases $C{{H}_{3}}^{+}$ ions in the solution. Thus $C{{H}_{3}}I$ also converts phenol into anisole.
From the above statements we can conclude that all the three reagents convert phenol into anisole.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D) i.e. all of these.
Note: It is important to know that along with dimethyl sulfate we use sodium hydroxide to enhance the rate of the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




