
Phenol is:
A.A base weaker than ammonia
B.An acid stronger than carbonic acid
C.An acid weaker than carbonic acid
D.A neutral compound
Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint:To solve the above question we will compare basicity or acidity of phenol with ammonia and carbonic acid. We will use the basic chemical properties of phenol. Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula ${C_6}{H_5}OH$.
Complete answer:
Phenol is an organic hydroxy compound that consists of a benzene ring and a single hydroxy group as a substituent. The chemical structure of phenol is given below.
Now we will check all the options one by one. So let’s consider the first option (A) A base weaker than ammonia. We know that base is a substance that accepts hydrogen ions and releases hydroxide ions. Let’s understand it with the help of a reaction.
$N{H_3} + {H_2}O\underset {} \leftrightarrows NH_4^ + + O{H^ - }$
$NH_4^ + $ The ammonium ion is formed along with the hydroxide ion. Oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen. Ammonia is more basic than ammonia. So this potion is wrong.
Now for options (B) and (C), we will compare the acidic nature of phenol with carbonic acid. Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with a molecular formula ${H_2}C{O_3}$. So let’s try to understand it properly.
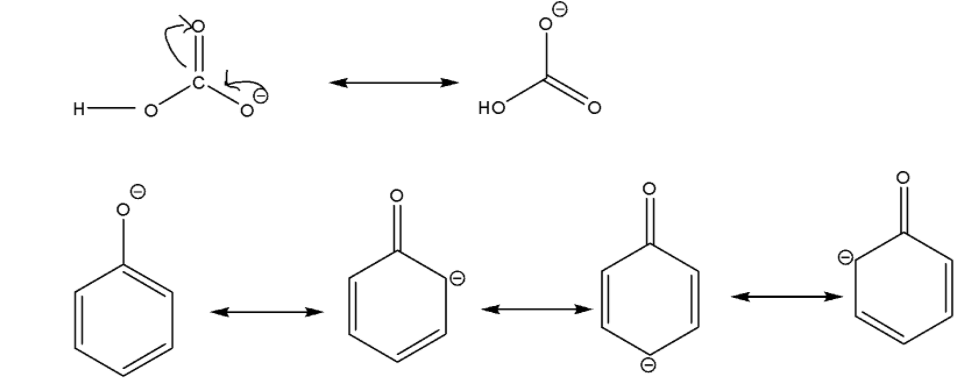
We can easily observe that carbonic acid forms bicarbonate ion and phenol forms phenoxide ion after losing ${H^ + }$ ion. Bicarbonate ions have two and phenoxide ions have four resonance structures. It will be easy for carbonic acid to lose ${H^ + }$ ion.
Now considering the last option (D) A neutral compound. We already observed that phenol is acidic.
We can conclude that phenol is an acid weaker than carbonic acid.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Resonance structures are the two examples of molecules in which the chemical interaction is the same but the electrons are distributed around the structure differently.
More the number of resonance structures formed, the more the stability of the chemical compound.
Complete answer:
Phenol is an organic hydroxy compound that consists of a benzene ring and a single hydroxy group as a substituent. The chemical structure of phenol is given below.

Now we will check all the options one by one. So let’s consider the first option (A) A base weaker than ammonia. We know that base is a substance that accepts hydrogen ions and releases hydroxide ions. Let’s understand it with the help of a reaction.
$N{H_3} + {H_2}O\underset {} \leftrightarrows NH_4^ + + O{H^ - }$
$NH_4^ + $ The ammonium ion is formed along with the hydroxide ion. Oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen. Ammonia is more basic than ammonia. So this potion is wrong.
Now for options (B) and (C), we will compare the acidic nature of phenol with carbonic acid. Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with a molecular formula ${H_2}C{O_3}$. So let’s try to understand it properly.

We can easily observe that carbonic acid forms bicarbonate ion and phenol forms phenoxide ion after losing ${H^ + }$ ion. Bicarbonate ions have two and phenoxide ions have four resonance structures. It will be easy for carbonic acid to lose ${H^ + }$ ion.
Now considering the last option (D) A neutral compound. We already observed that phenol is acidic.
We can conclude that phenol is an acid weaker than carbonic acid.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Resonance structures are the two examples of molecules in which the chemical interaction is the same but the electrons are distributed around the structure differently.
More the number of resonance structures formed, the more the stability of the chemical compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




