
When phenol is treated with ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$ and \[{\text{NaOH}}\] the product formed is:
A. benzaldehyde
B. salicyladehyde
C. salicylic acid
D. benzoic acid
Answer
529k+ views
Hint: The given reaction is called Riemer-Tiemann reaction. It is an example of electrophilic substitution reaction. It is used in ortho-formylation of phenols.
Complete step by step solution:
Phenols is the organic compound which contain a phenyl group \[\left( { - {{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}} \right)\]and a hydroxyl group\[\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)\]. It has the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}\].
When phenol \[{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}\] is treated with ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$(chloroform) and \[{\text{NaOH}}\](sodium hydroxide), there forms an aldehyde group \[\left( { - {\text{CHO}}} \right)\]. It leads to the formation of 2-hydroxy benzaldehyde, also called salicylaldehyde. The reaction involving the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde is given below:
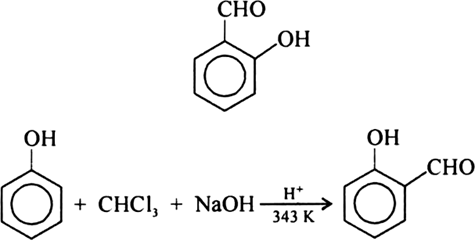
Aldehyde group is at the ortho position of the benzene ring. Ortho is used for such functional groups which are placed 1, 2 positions attached to a benzene ring.
The diagram showing the whole mechanism of Riemer-Tiemann reaction is given below:
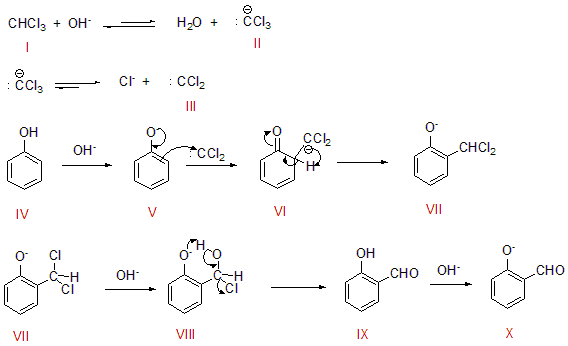
Steps involved in the reaction mechanism are:
- It is the chloroform. It converts to chloroform carbanion(II) and then to dichlorocarbene(III) when treated with \[{\text{NaOH}}\].
- Phenol loses its proton using \[{\text{NaOH}}\]and it produces a phenoxide ion which is negatively charged. This negative charge helps in delocalization of the benzene ring which makes it more nucleophilic. Now it is prone to electrophilic attack.
- Now, the dichlorocarbene attacks at the ortho position. It produces an intermediate dichloromethyl substituted phenol(VIII).
- This undergoes hydrolysis and then forms the salicylaldehyde(X)
Additional information:
Riemer-Tiemann reaction was introduced by Karl Riemer and Ferdinand Tiemann. The simplest example of this reaction is conversion of phenols to salicylaldehyde. Aromatic electrophilic substitution occurs easily in phenols because of the p electrons in the oxygen can be donated very easily to the ring.
Note: Dichlorocarbene is electron deficient because of two chlorine atoms attached to it. Chlorine atoms are highly electron withdrawing. While phenoxide is highly electron sufficient. So the bond will be very strong.
Complete step by step solution:
Phenols is the organic compound which contain a phenyl group \[\left( { - {{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}} \right)\]and a hydroxyl group\[\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)\]. It has the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}\].
When phenol \[{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}\] is treated with ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$(chloroform) and \[{\text{NaOH}}\](sodium hydroxide), there forms an aldehyde group \[\left( { - {\text{CHO}}} \right)\]. It leads to the formation of 2-hydroxy benzaldehyde, also called salicylaldehyde. The reaction involving the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde is given below:

Aldehyde group is at the ortho position of the benzene ring. Ortho is used for such functional groups which are placed 1, 2 positions attached to a benzene ring.
The diagram showing the whole mechanism of Riemer-Tiemann reaction is given below:

Steps involved in the reaction mechanism are:
- It is the chloroform. It converts to chloroform carbanion(II) and then to dichlorocarbene(III) when treated with \[{\text{NaOH}}\].
- Phenol loses its proton using \[{\text{NaOH}}\]and it produces a phenoxide ion which is negatively charged. This negative charge helps in delocalization of the benzene ring which makes it more nucleophilic. Now it is prone to electrophilic attack.
- Now, the dichlorocarbene attacks at the ortho position. It produces an intermediate dichloromethyl substituted phenol(VIII).
- This undergoes hydrolysis and then forms the salicylaldehyde(X)
Additional information:
Riemer-Tiemann reaction was introduced by Karl Riemer and Ferdinand Tiemann. The simplest example of this reaction is conversion of phenols to salicylaldehyde. Aromatic electrophilic substitution occurs easily in phenols because of the p electrons in the oxygen can be donated very easily to the ring.
Note: Dichlorocarbene is electron deficient because of two chlorine atoms attached to it. Chlorine atoms are highly electron withdrawing. While phenoxide is highly electron sufficient. So the bond will be very strong.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




