
Phenolphthalein of pH range 8 – 10 is used in which of the following types of titration as a suitable indicator?
a.) \[N{H_4}OH\] and HCl
b.) \[N{H_4}OH\]and HCOOH
c.) \[N{H_4}OH\] and ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$
d.) NaOH and ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Before attempting this question one should have prior knowledge about the titration and about the Phenolphthalein which belongs to phthalein family and its formula is${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$, use the given information to approach towards the solution of the question.
 Complete step by step solution:
Phenolphthalein is basically an organic compound of the phthalein family and its formula is${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$. The use of Phenolphthalein acts as an acid-base indicator. Usually Phenolphthalein is colorless below pH 8.5 but it attains/acquires pink color to deep red colour if the pH is above 9.0. Thus, according to the question the pH range indicates that it may show pink color or deep red or may be it appears colorless.
Complete step by step solution:
Phenolphthalein is basically an organic compound of the phthalein family and its formula is${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$. The use of Phenolphthalein acts as an acid-base indicator. Usually Phenolphthalein is colorless below pH 8.5 but it attains/acquires pink color to deep red colour if the pH is above 9.0. Thus, according to the question the pH range indicates that it may show pink color or deep red or may be it appears colorless.
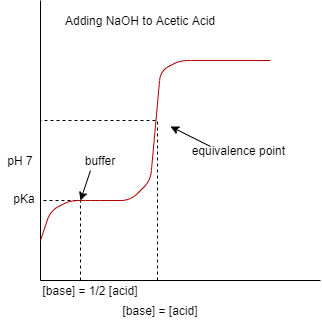
So, in titration if one reagent is weak acid or maybe weak base while the other one is strong acid or base, then the curve of titration becomes irregular and so the pH shifts less with small addition of titrant near the equivalence point. Let us understand this by an example, let us take a weak acid i.e. acetic acid and strong base i.e. sodium hydroxide, then the titration curve for titration between them, then the equivalence point occurs between pH 8 – 10, and we know that if the pH is more than 7 the pH is considered to be basic, thus we can say that the solution is basic at the equivalence point and for indicating this, the indicator such as Phenolphthalein would be appropriate
Thus, from this conclusion we can say that to indicate the base in the titration, Phenolphthalein will be best and we have taken strong base as sodium hydroxide which is NaOH
Hence option D is the correct option.
Note: Titration can be defined as determination of concentration of any substance in a solution by adding a measured amount of some different substance very slowly, until a reaction is shown to be complete. This method can widely be used in the food industry. It helps to determine the quantity of a reactant in a particular sample, as for example it can be used to determine the amount of salt, sugar, vitamin C or vitamin E, etc.

So, in titration if one reagent is weak acid or maybe weak base while the other one is strong acid or base, then the curve of titration becomes irregular and so the pH shifts less with small addition of titrant near the equivalence point. Let us understand this by an example, let us take a weak acid i.e. acetic acid and strong base i.e. sodium hydroxide, then the titration curve for titration between them, then the equivalence point occurs between pH 8 – 10, and we know that if the pH is more than 7 the pH is considered to be basic, thus we can say that the solution is basic at the equivalence point and for indicating this, the indicator such as Phenolphthalein would be appropriate
Thus, from this conclusion we can say that to indicate the base in the titration, Phenolphthalein will be best and we have taken strong base as sodium hydroxide which is NaOH
Hence option D is the correct option.
Note: Titration can be defined as determination of concentration of any substance in a solution by adding a measured amount of some different substance very slowly, until a reaction is shown to be complete. This method can widely be used in the food industry. It helps to determine the quantity of a reactant in a particular sample, as for example it can be used to determine the amount of salt, sugar, vitamin C or vitamin E, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




