
What is the phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross?
(a) 1:3
(b) 3:1
(c) 1:2:2:1
(d) 9:3:3:1
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: This experiment was first performed by Gregor John Mendel in the mid-nineteenth century on pea plants by cultivating and observing the pattern of inheritance in different stages of generation. The phenotypic ratio is related to the relative number of offspring showing a particular trait or combination of traits.
Complete answer:
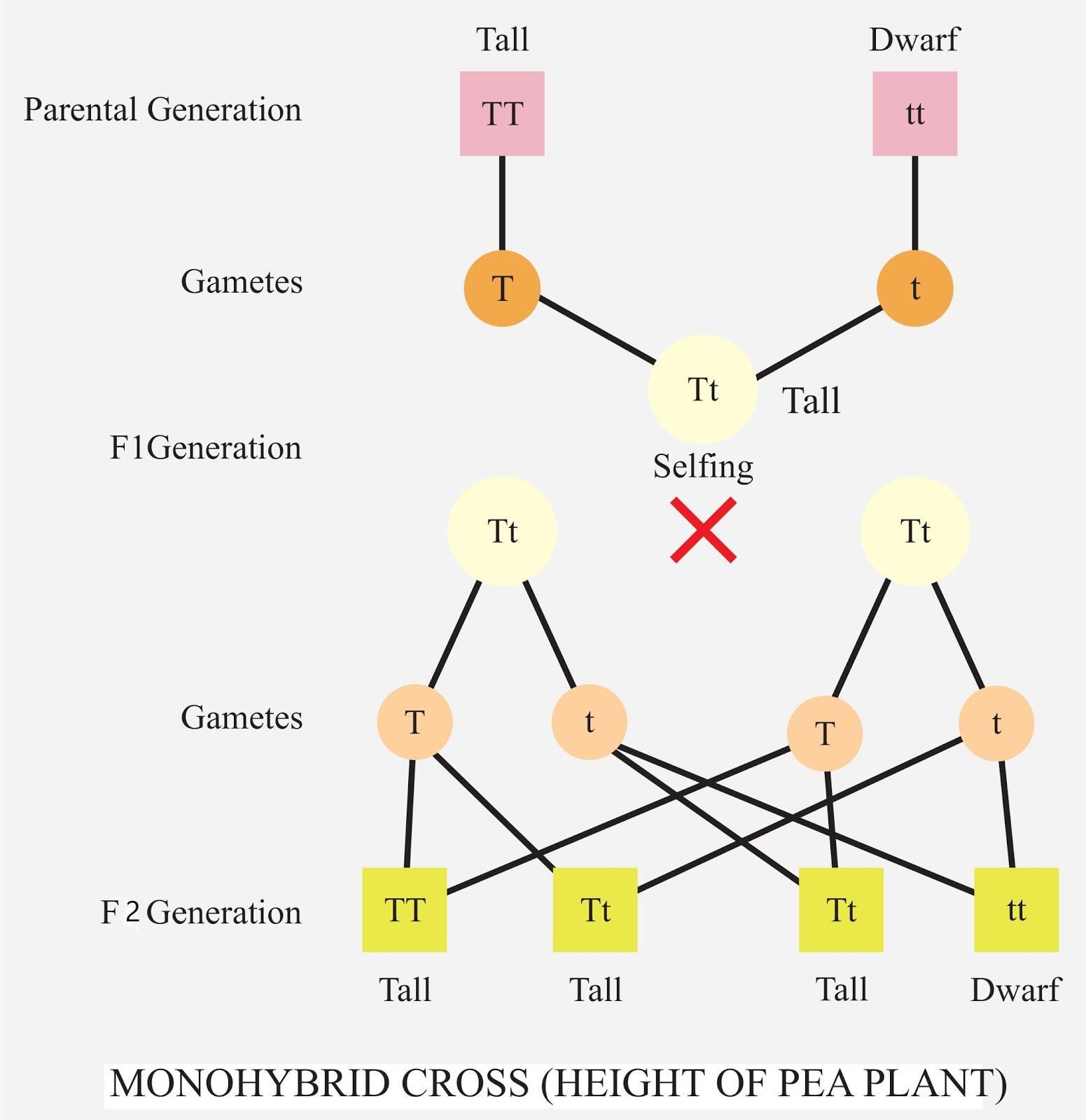
3:1 is the phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross. Gregor John Mendel who is considered the father of genetics has given the phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross. He crossed two homozygous plants and observed that the offspring is heterozygous. He named this cross a monohybrid cross.
-In his experiment, he considered two contrasting traits of pea plants i.e., one tall (TT) and one dwarf (tt) plant.
-After crossing the tall and the dwarf plant he observed that all the new plants were tall. He called them first-generation ${ F }_{ 1 }$ offsprings or ${ F }_{ 1 }$ progeny.
-He explained his observations that in first-generation the offspring shows the characteristics of only one parent and the characteristics of the other parent are completely absent. This means one of the parent's characters is dominant and the other' s is recessive.
-Then in continuation of his experiment, he self-crossed the plants of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ progeny. He observed that out of four progeny only one is dwarf and the rest three are tall.
-The ratio of tall and dwarf plants was 3:1 and this was the phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross in the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation.
-He repeated this experiment with other traits of plants and observed the same result. Then he named them second-generation ${ F }_{ 2 }$ offsprings or ${ F }_{ 2 }$ progeny.
-He also observed that some traits which were absent in the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation reappeared in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation. He termed the expressed traits as dominant traits and the suppressed traits as recessive traits.
-He also observed that some factors were inherited by the offspring from the parents over successive generations. These factors were later called 'genes' which were responsible for the inheritance of traits from one generation to another.
So, the correct answer is ‘3:1’.
Note:
-In the world of biology Gregor John Mendel is known as the father of genetics.
-The phenotypic ratio is the number of times a specific trait appears in the offsprings.
-A monohybrid cross is a cross made between two homozygous parent plants resulting in heterozygous ${ F }_{ 1 }$ progeny. This cross gives the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ phenotypic ratio as 3:1 and the genotypic ratio as 1:2:1.
Complete answer:
3:1 is the phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross. Gregor John Mendel who is considered the father of genetics has given the phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross. He crossed two homozygous plants and observed that the offspring is heterozygous. He named this cross a monohybrid cross.
-In his experiment, he considered two contrasting traits of pea plants i.e., one tall (TT) and one dwarf (tt) plant.
-After crossing the tall and the dwarf plant he observed that all the new plants were tall. He called them first-generation ${ F }_{ 1 }$ offsprings or ${ F }_{ 1 }$ progeny.
-He explained his observations that in first-generation the offspring shows the characteristics of only one parent and the characteristics of the other parent are completely absent. This means one of the parent's characters is dominant and the other' s is recessive.
-Then in continuation of his experiment, he self-crossed the plants of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ progeny. He observed that out of four progeny only one is dwarf and the rest three are tall.
-The ratio of tall and dwarf plants was 3:1 and this was the phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross in the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation.
-He repeated this experiment with other traits of plants and observed the same result. Then he named them second-generation ${ F }_{ 2 }$ offsprings or ${ F }_{ 2 }$ progeny.
-He also observed that some traits which were absent in the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation reappeared in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation. He termed the expressed traits as dominant traits and the suppressed traits as recessive traits.
-He also observed that some factors were inherited by the offspring from the parents over successive generations. These factors were later called 'genes' which were responsible for the inheritance of traits from one generation to another.
So, the correct answer is ‘3:1’.
Note:
-In the world of biology Gregor John Mendel is known as the father of genetics.
-The phenotypic ratio is the number of times a specific trait appears in the offsprings.
-A monohybrid cross is a cross made between two homozygous parent plants resulting in heterozygous ${ F }_{ 1 }$ progeny. This cross gives the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ phenotypic ratio as 3:1 and the genotypic ratio as 1:2:1.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




