
Phenyl isocyanide is formed when chloroform is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide and:
a.) Benzaldehyde
b.) Aniline
c.) Phenol
d.) Nitrobenzene
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we should recall the Carbylamine reaction. It involves a primary amine, chloroform and alcoholic KOH.
Complete step by step answer:
As we can already guess that this is the Carbylamine reaction. Carbylamine reaction or Hoffmann isocyanide is the synthesis reaction of an isocyanide involving a primary amine, chloroform, and base. This reaction involves a dichlorocarbene intermediate which is very essential for this conversion. But the carbylamine reaction cannot be used to synthesize isocyanides from secondary and tertiary amines since the intermediate does not form.
Let us now get a general idea of the reaction mechanism which will make it easier for us to understand what actually takes place during the Hofmann isocyanide synthesis.
The first step of this reaction is the dehydrohalogenation which means removal of hydrogen and halide from the given substrate of chloroform to produce dichlorocarbene intermediate. This dichlorocarbene intermediate is very reactive in nature. The electrophilic dichlorocarbene then attacks the nucleophilic nitrogen of the primary amine used as reactant. The elimination of the hydrochloric acid ultimately causes the formation of an isonitrile.
The reaction is illustrated below:
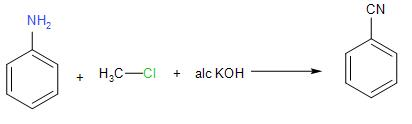
We can see that the only primary amine given to us as an option is aniline.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (B) Aniline.
Note:
We can now make an educated guess about the utility of this reaction. Since we can see that the carbylamine reaction produces results only for primary amines, this can be used as a chemical test to confirm the presence of the presence of primary amines. It is generally characterized by a very foul smell.
Complete step by step answer:
As we can already guess that this is the Carbylamine reaction. Carbylamine reaction or Hoffmann isocyanide is the synthesis reaction of an isocyanide involving a primary amine, chloroform, and base. This reaction involves a dichlorocarbene intermediate which is very essential for this conversion. But the carbylamine reaction cannot be used to synthesize isocyanides from secondary and tertiary amines since the intermediate does not form.
Let us now get a general idea of the reaction mechanism which will make it easier for us to understand what actually takes place during the Hofmann isocyanide synthesis.
The first step of this reaction is the dehydrohalogenation which means removal of hydrogen and halide from the given substrate of chloroform to produce dichlorocarbene intermediate. This dichlorocarbene intermediate is very reactive in nature. The electrophilic dichlorocarbene then attacks the nucleophilic nitrogen of the primary amine used as reactant. The elimination of the hydrochloric acid ultimately causes the formation of an isonitrile.
The reaction is illustrated below:
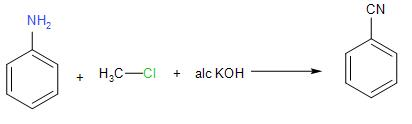
We can see that the only primary amine given to us as an option is aniline.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (B) Aniline.
Note:
We can now make an educated guess about the utility of this reaction. Since we can see that the carbylamine reaction produces results only for primary amines, this can be used as a chemical test to confirm the presence of the presence of primary amines. It is generally characterized by a very foul smell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




