
Phloem in gymnosperms lacks.
(a) Albuminous cells and sieve cells
(b) Sieve tubes only
(c) Companion cells only
(d) Both sieve tubes and companion cells
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Phloem consists of many types of cells including sclerenchyma, parenchyma, sieve elements, and corresponding cells. The so-called "sieve part" can be more precisely referred to in angiosperms as a sieve tube member, and in gymnosperms and ferns as a sieve cell. Companion cells are the cells found in angiosperms with abundant plasma and nucleus.
Complete answer:
In Gymnosperms, the phloem lacks both the sieve tube and the corresponding cells. Instead they contain sieve cells for food material conduction.
The Sieve element is the phloem conductive element. Companion Cells for the sieve function are "life support" cells. Fibers developed from sclerenchyma cells and provide the plant with structural support. Parenchyma serves as material for packaging between other types of cells and helps to move materials to the SE / CC complex.
Gymnosperm sieve cells lack a sieve layer, and instead have sieve pores across the cell wall that allow flow between adjacent cells. The members of the sieve tube found in flowering plants are typically larger than sieve cells and have sieve plates that link the ends of adjacent cells. These sieve plates are areas with several pores, from which a continuous cytoplasm connects adjacent cells.
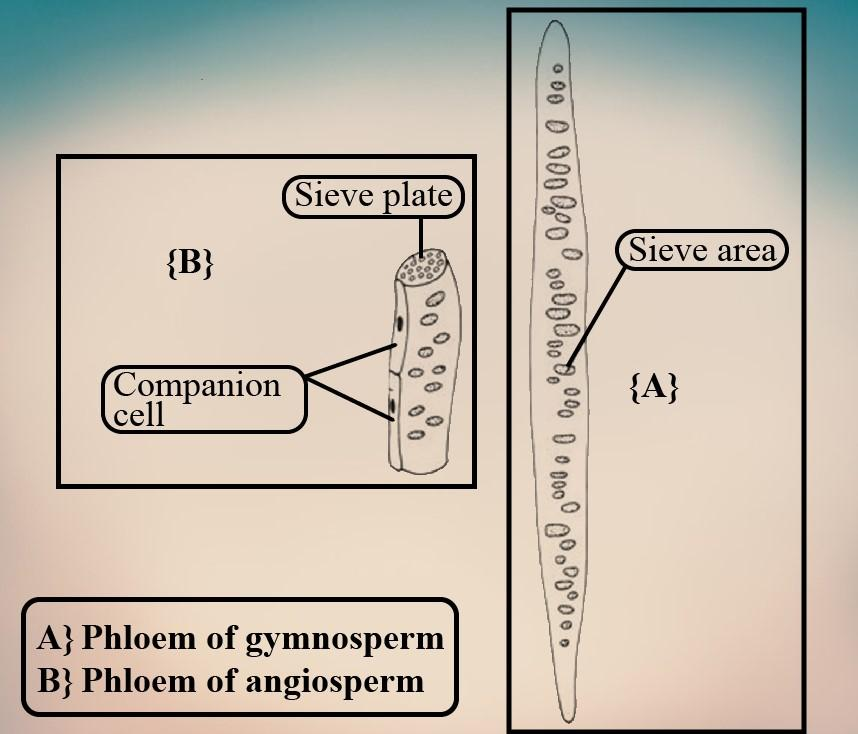
So, the correct answer is, 'Both sieve tubes and companion cells'.
Note: Phloem is the vascular tissue responsible for transmitting sugar from the source tissue (e.g. photosynthetic leaf cells) to the sink tissues (e.g. non-photosynthetic root cells or flowers). Even other molecules such as proteins and mRNAs are transported through phloem in the plant. Gymnosperms need no root pressure to get water from the soil, because most of them grow in cold and dry climates.
Complete answer:
In Gymnosperms, the phloem lacks both the sieve tube and the corresponding cells. Instead they contain sieve cells for food material conduction.
The Sieve element is the phloem conductive element. Companion Cells for the sieve function are "life support" cells. Fibers developed from sclerenchyma cells and provide the plant with structural support. Parenchyma serves as material for packaging between other types of cells and helps to move materials to the SE / CC complex.
Gymnosperm sieve cells lack a sieve layer, and instead have sieve pores across the cell wall that allow flow between adjacent cells. The members of the sieve tube found in flowering plants are typically larger than sieve cells and have sieve plates that link the ends of adjacent cells. These sieve plates are areas with several pores, from which a continuous cytoplasm connects adjacent cells.

So, the correct answer is, 'Both sieve tubes and companion cells'.
Note: Phloem is the vascular tissue responsible for transmitting sugar from the source tissue (e.g. photosynthetic leaf cells) to the sink tissues (e.g. non-photosynthetic root cells or flowers). Even other molecules such as proteins and mRNAs are transported through phloem in the plant. Gymnosperms need no root pressure to get water from the soil, because most of them grow in cold and dry climates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




