
Phosgene is the common name given to
A.Carbonyl chloride
B.Phosphine
C.Phosphorous hydroxychloride
D.Phosphorus trichloride
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint:
-Phosgene is a poisonous gas.
-It is a colorless gas , chemically reactive, highly toxic gas that has unpleasant odour.
-The structure of phosgene is planar.
Complete step by step answer:
Phosgene is a common name given to carbonyl chloride.
The structure of carbonyl chloride is-
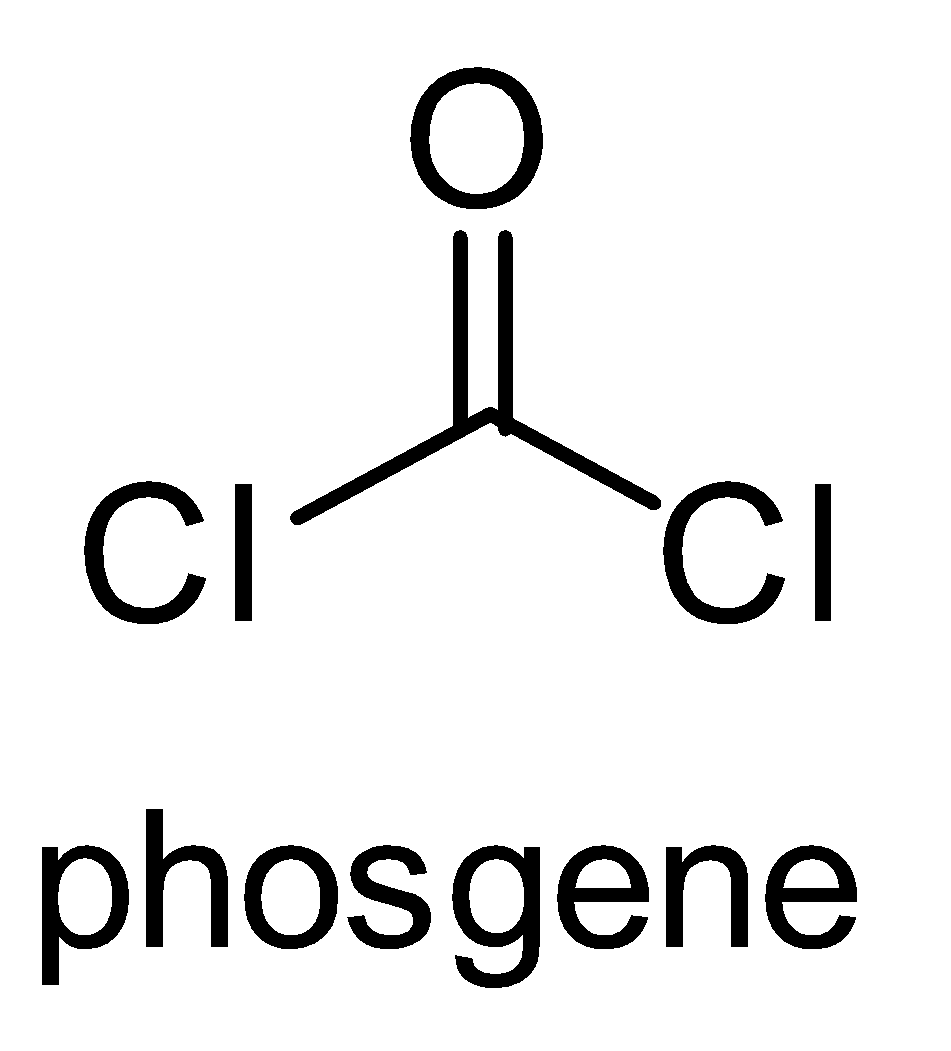
It is used to manufacture organic chemicals, resins, dyes, plastics and pesticides. It is used to manufacture polycarbonate plastics are urethanes. When cooled under pressure it can be converted into liquid form.
It was used as a chemical weapon during World War $1$ .
Industrially phosgene is prepared by passing purified carbon monoxide and chlorine gas through activated carbon. Activated carbon serves as a catalyst. The reaction can be represented as follows-
$CO + C{l_2} \to COC{l_2}$
This reaction is exothermic.
Phosgene can also be prepared from chloroform in presence of oxygen and UV light. This reaction is a radical reaction. Oxygen oxidises the chloroform molecule.
So the correct option is A.
Note:Phosphine is a colorless, flammable, very toxic gas having the molecular formula $P{H_3}$ .It is a weaker base than ammonia. Pure phosphine is odorless.
-Phosphorus trichloride is $PC{l_3}$. It is a volatile gas. It reacts violently with water to form phosphorous acid and hydrochloric acid.
$PC{l_3} + {H_2}O \to {H_3}P{O_3} + HCl$
The structure is represented as –
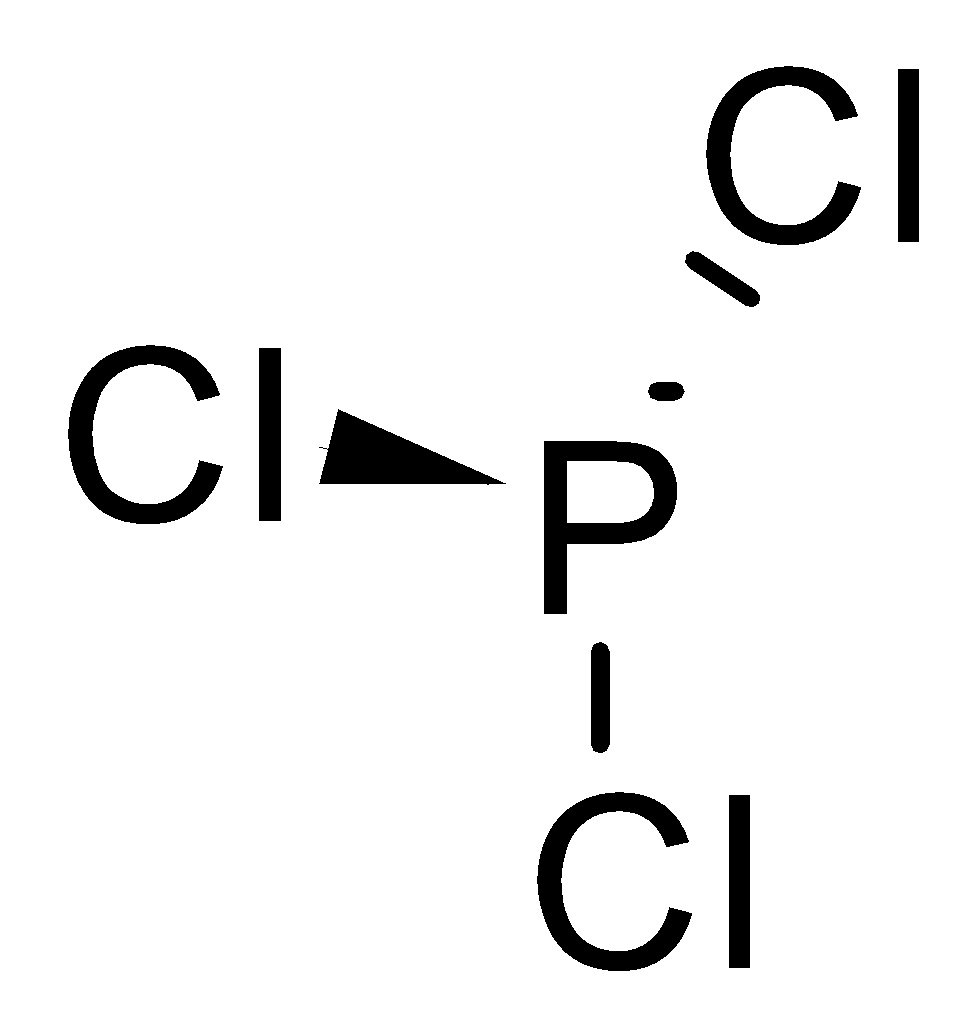
-There are also compounds such as diphosgene and triphosgene related to phosgene.
- Phosgene is also called carbonyl chloride.
-The chemical formula of phosphine is $P{H_3}$ .
-Phosgene is a poisonous gas.
-It is a colorless gas , chemically reactive, highly toxic gas that has unpleasant odour.
-The structure of phosgene is planar.
Complete step by step answer:
Phosgene is a common name given to carbonyl chloride.
The structure of carbonyl chloride is-

It is used to manufacture organic chemicals, resins, dyes, plastics and pesticides. It is used to manufacture polycarbonate plastics are urethanes. When cooled under pressure it can be converted into liquid form.
It was used as a chemical weapon during World War $1$ .
Industrially phosgene is prepared by passing purified carbon monoxide and chlorine gas through activated carbon. Activated carbon serves as a catalyst. The reaction can be represented as follows-
$CO + C{l_2} \to COC{l_2}$
This reaction is exothermic.
Phosgene can also be prepared from chloroform in presence of oxygen and UV light. This reaction is a radical reaction. Oxygen oxidises the chloroform molecule.
So the correct option is A.
Note:Phosphine is a colorless, flammable, very toxic gas having the molecular formula $P{H_3}$ .It is a weaker base than ammonia. Pure phosphine is odorless.
-Phosphorus trichloride is $PC{l_3}$. It is a volatile gas. It reacts violently with water to form phosphorous acid and hydrochloric acid.
$PC{l_3} + {H_2}O \to {H_3}P{O_3} + HCl$
The structure is represented as –

-There are also compounds such as diphosgene and triphosgene related to phosgene.
- Phosgene is also called carbonyl chloride.
-The chemical formula of phosphine is $P{H_3}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




