
Why is photorespiration also called $C_{2}$ cycle?
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Photorespiration is a reverse process as compared to photosynthesis. It involves the uptake of $O_{2}$ and the release of $CO_{2}$ in light and results from the biosynthesis of glycolate in the chloroplast, after which, the glycolate acid is metabolized in the same leaf cell. Peroxisomes are the cellular site for photorespiration.
Complete step by step answer:
Photorespiration is also called the $C_{2}$ cycle because the first main product formed is phosphoglycolate which is a 2 carbon molecule. Phosphoglycolate is later converted to glycolate. Plants, which do not have the adaptation to combat photorespiration, such plants are known as $C_{3}$ plants. The $C_{4}$ plants can efficiently combat photorespiration and can fix (assimilate or take in) the carbon dioxide more efficiently than $C_{3}$ plants.
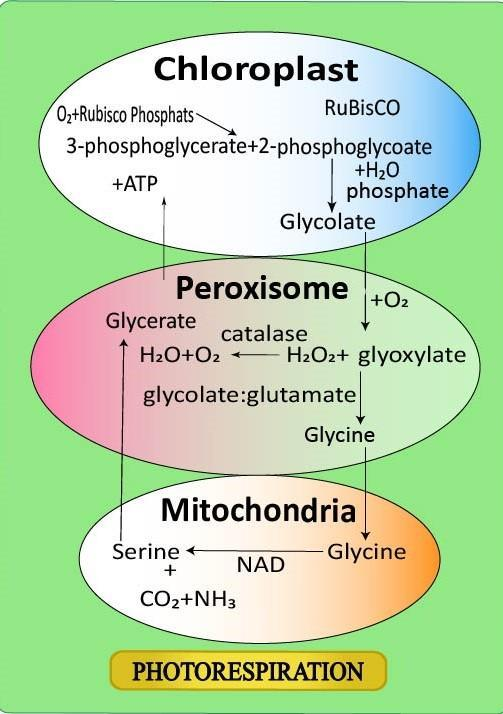
This process of photorespiration converts the sugar phosphates back to carbon dioxide. It is initiated by the oxygenation of RuBP (Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate) (an organic substance that is involved in photosynthesis). The combination of gas with RuBP yields only one molecule of PGA and one molecule of a two-carbon acid, phosphoglycolate, which is subsequently converted in part to carbon dioxide.
The relative concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide as well as the leaf temperature, within the chloroplasts, determine whether oxygenation or carboxylation is favored. Phosphoglycolate formed by the fixation of oxygen is recycled to the Calvin cycle.
Note:
- In early 1920, Otto Warburg observed that oxygen inhibits photosynthesis. This phenomenon, originally known as the “Warburg effect,” was later recognized as the light-dependent release of carbon dioxide by photosynthetic organisms, or photorespiration.
- Photorespiration is a wasteful process because no energy-rich compound is produced and loss of carbon takes place during such a process. This process has a significant impact on $C_{3}$ plants but in $C_{4}$ plants such a process is insignificant.
Complete step by step answer:
Photorespiration is also called the $C_{2}$ cycle because the first main product formed is phosphoglycolate which is a 2 carbon molecule. Phosphoglycolate is later converted to glycolate. Plants, which do not have the adaptation to combat photorespiration, such plants are known as $C_{3}$ plants. The $C_{4}$ plants can efficiently combat photorespiration and can fix (assimilate or take in) the carbon dioxide more efficiently than $C_{3}$ plants.

This process of photorespiration converts the sugar phosphates back to carbon dioxide. It is initiated by the oxygenation of RuBP (Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate) (an organic substance that is involved in photosynthesis). The combination of gas with RuBP yields only one molecule of PGA and one molecule of a two-carbon acid, phosphoglycolate, which is subsequently converted in part to carbon dioxide.
The relative concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide as well as the leaf temperature, within the chloroplasts, determine whether oxygenation or carboxylation is favored. Phosphoglycolate formed by the fixation of oxygen is recycled to the Calvin cycle.
Note:
- In early 1920, Otto Warburg observed that oxygen inhibits photosynthesis. This phenomenon, originally known as the “Warburg effect,” was later recognized as the light-dependent release of carbon dioxide by photosynthetic organisms, or photorespiration.
- Photorespiration is a wasteful process because no energy-rich compound is produced and loss of carbon takes place during such a process. This process has a significant impact on $C_{3}$ plants but in $C_{4}$ plants such a process is insignificant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




