
What is photorespiration? Explain the mechanism and its significance.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Photorespiration is a process which involves loss of fixed carbon as $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, in plants in the presence of light it is initiated in chloroplasts. This process does not produce ATP or NADPH and is a wasteful process.
Complete answer:
Photorespiration is usually a wasteful process and is not performed in the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $ plants that are plants that possess kranz anatomy .
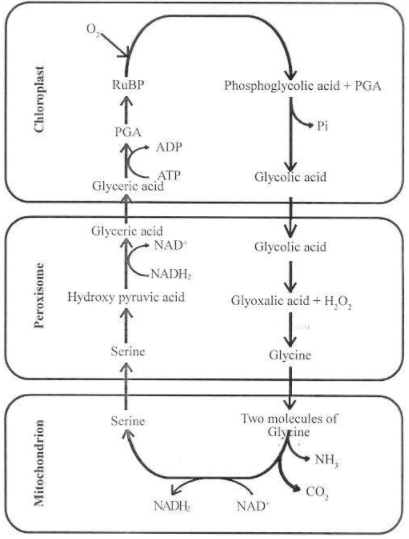
Mechanism of photorespiration:
Photorespiration occurs usually when there is high concentration of oxygen.
Under such circumstances, Rubisco, the enzyme that catalyses the carboxylation of RuBP during the first step of the Calvin cycle, functions as an oxygenase.
Some $\mathop O\nolimits_2 $ does bind to Rubisco and hence $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, fixation is decreased.
The RuBP binds with $\mathop O\nolimits_2 $, to form one molecule of PGA (3C compound) and phosphoglycerate (2C compound) in the pathway of photorespiration.
There is neither the synthesis of sugar, nor of ATP. Rather, it results in the release of $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, with the utilisation of ATP. It leads to a 25 percent loss of the fixed $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, $\mathop O\nolimits_2 $, is first utilized in chloroplast and then in peroxisomes.
This process is also called the $\mathop C\nolimits_2 $ cycle. This requires organelles such as chloroplast peroxisome and mitochondria .
Significance of photorespiration :-
In $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $. plants, photorespiration does not occur. This is because these plants have a mechanism that increases the concentration of $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, at the enzyme site. During the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $ pathway, when the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $, acid from the mesophyll cells is broken down in the bundle sheath cells, it releases con- this results in increasing the intracellular concentration of $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $. This in turn, ensures that the Rubisco functions as a carboxylase minimising the oxygenase activity. Thus, the productivity and yields are better in CA plants as compared to $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $, plants. In addition, the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $ plants show tolerance to higher temperature also.
Note: Photorespiration is not related to aerobic respiration as aerobic respiration occurs throughout the day and night in all types of cells, but photorespiration occurs in presence of light in green cells only. ATP is produced in aerobic respiration unlike photorespiration where ATP is consumed. Photorespiration utilizes a part of light energy and saves the plant from photo-oxidative damage.
Complete answer:
Photorespiration is usually a wasteful process and is not performed in the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $ plants that are plants that possess kranz anatomy .
Mechanism of photorespiration:
Photorespiration occurs usually when there is high concentration of oxygen.
Under such circumstances, Rubisco, the enzyme that catalyses the carboxylation of RuBP during the first step of the Calvin cycle, functions as an oxygenase.
Some $\mathop O\nolimits_2 $ does bind to Rubisco and hence $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, fixation is decreased.
The RuBP binds with $\mathop O\nolimits_2 $, to form one molecule of PGA (3C compound) and phosphoglycerate (2C compound) in the pathway of photorespiration.
There is neither the synthesis of sugar, nor of ATP. Rather, it results in the release of $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, with the utilisation of ATP. It leads to a 25 percent loss of the fixed $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, $\mathop O\nolimits_2 $, is first utilized in chloroplast and then in peroxisomes.
This process is also called the $\mathop C\nolimits_2 $ cycle. This requires organelles such as chloroplast peroxisome and mitochondria .

Significance of photorespiration :-
In $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $. plants, photorespiration does not occur. This is because these plants have a mechanism that increases the concentration of $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $, at the enzyme site. During the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $ pathway, when the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $, acid from the mesophyll cells is broken down in the bundle sheath cells, it releases con- this results in increasing the intracellular concentration of $\mathop {CO}\nolimits_2 $. This in turn, ensures that the Rubisco functions as a carboxylase minimising the oxygenase activity. Thus, the productivity and yields are better in CA plants as compared to $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $, plants. In addition, the $\mathop C\nolimits_4 $ plants show tolerance to higher temperature also.
Note: Photorespiration is not related to aerobic respiration as aerobic respiration occurs throughout the day and night in all types of cells, but photorespiration occurs in presence of light in green cells only. ATP is produced in aerobic respiration unlike photorespiration where ATP is consumed. Photorespiration utilizes a part of light energy and saves the plant from photo-oxidative damage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




